- Midodrine
-
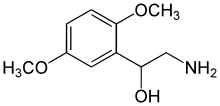
Midodrine 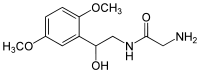
Systematic (IUPAC) name (RS)- N-[2-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxyethyl]glycinamide Clinical data Trade names Proamatine AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a602023 Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status ? Identifiers CAS number 133163-28-7 
ATC code C01CA17 PubChem CID 4195 DrugBank APRD01116 ChemSpider 4050 
UNII 6YE7PBM15H 
KEGG D08220 
ChEBI CHEBI:6933 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1076 
Synonyms 2-amino-N-[2-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxy-ethyl]-acetamide Chemical data Formula C12H18N2O4 Mol. mass 254.282 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Midodrine (brand names Amatine, ProAmatine, Gutron) is a vasopressor/antihypotensive agent. Midodrine was approved in the United States by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1996 for the treatment of orthostatic hypotension. In August 2010, the FDA proposed withdrawing this approval because the manufacturer, Shire plc, has failed to complete required studies after the medicine reached the market.[1][2]
In September of 2010, the FDA reversed in decision to remove Midodrine from the market and has allowed it to remain available to patients while Shire plc collects further data regarding the efficacy and safety of the drug[3]. Shire plc announced on September 27, 2011 that it was continuing the process to work with the FDA towards a final approval of the drug[4].
Contents
Chemical properties
Midodrine is an odorless, white, crystalline powder, soluble in water and sparingly soluble in methanol.
Mechanism of action
Midodrine is a prodrug which forms an active metabolite, desglymidodrine, which is an α1-receptor agonist and exerts its actions via activation of the alpha-adrenergic receptors of the arteriolar and venous vasculature, producing an increase in vascular tone and elevation of blood pressure. Desglymidodrine does not stimulate cardiac beta-adrenergic receptors. Desglymidodrine diffuses poorly across the blood-brain barrier, and is therefore not associated with effects on the central nervous system.
Metabolism
After oral administration, midodrine is rapidly absorbed. The plasma levels of the prodrug peak after about half an hour, and decline with a half-life of approximately 25 minutes, while the metabolite reaches peak blood concentrations about 1 to 2 hours after a dose of midodrine and has a half-life of about 3 to 4 hours. The absolute bioavailability of midodrine (measured as desglymidodrine) is 93%.
Indications
Midodrine hydrochloride tablets are indicated for the treatment of symptomatic orthostatic hypotension. In a critical care settings, it is widely used as an adjunctive therapy to weaning patients off of intravenous vasopressive medications. It has been suggested also as a treatment for chronic fatigue syndrome[5] as well as for hepato-pulmonary syndrome. It is also used with octreotide for hepatorenal syndrome; the proposed mechanism is constriction of splanchinc vessels and dilation of renal vasculature.
Contraindications
Midodrine is contraindicated in patients with severe organic heart disease, acute renal disease, urinary retention, pheochromocytoma or thyrotoxicosis. Midodrine should not be used in patients with persistent and excessive supine hypertension.
Side effects
Headache; feeling of pressure/fullness in the head, vasodilation/flushing face, confusion/thinking abnormality, dry mouth; nervousness/anxiety and rash.[citation needed]
See also
- Lisdexamphetamine
References
- ^ U.S. proposes withdrawal of Shire hypotension drug, Aug 16, 2010
- ^ O'Riordan, Michael. "FDA recommends withdrawal of midodrine". Food and Drug Administration. FDA proposes withdrawal of low blood pressure drug [press release]. August 16, 2010.. TheHeart.org. http://www.theheart.org/article/1110411.do. Retrieved 1 April 2011.
- ^ Midodrine (ProAmatine, generic) Proposed Market Withdrawal – Update September 10, 2010
- ^ Shire Announces Update on ProAmatime September 27, 2011
- ^ Naschitz J, Dreyfuss D, Yeshurun D, Rosner I (April 2004). "Midodrine treatment for chronic fatigue syndrome". Postgrad Med J 80 (942): 230–2. doi:10.1136/pgmj.2003.011429. PMC 1742969. PMID 15082846. http://pmj.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=15082846.
External links
- Midodrine at drugs.com
Adrenergics Receptor ligands Agonists: 5-FNE • 6-FNE • Amidephrine • Anisodamine • Anisodine • Cirazoline • Dipivefrine • Dopamine • Ephedrine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Etilefrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Indanidine • Levonordefrin • Metaraminol • Methoxamine • Methyldopa • Midodrine • Naphazoline • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Octopamine • Oxymetazoline • Phenylephrine • Phenylpropanolamine • Pseudoephedrine • Synephrine • Tetrahydrozoline
Antagonists: Abanoquil • Adimolol • Ajmalicine • Alfuzosin • Amosulalol • Arotinolol • Atiprosin • Benoxathian • Buflomedil • Bunazosin • Carvedilol • CI-926 • Corynanthine • Dapiprazole • DL-017 • Domesticine • Doxazosin • Eugenodilol • Fenspiride • GYKI-12,743 • GYKI-16,084 • Indoramin • Ketanserin • L-765,314 • Labetalol • Mephendioxan • Metazosin • Monatepil • Moxisylyte (Thymoxamine) • Naftopidil • Nantenine • Neldazosin • Nicergoline • Niguldipine • Pelanserin • Phendioxan • Phenoxybenzamine • Phentolamine • Piperoxan • Prazosin • Quinazosin • Ritanserin • RS-97,078 • SGB-1,534 • Silodosin • SL-89.0591 • Spiperone • Talipexole • Tamsulosin • Terazosin • Tibalosin • Tiodazosin • Tipentosin • Tolazoline • Trimazosin • Upidosin • Urapidil • Zolertine
* Note that many TCAs, TeCAs, antipsychotics, ergolines, and some piperazines like buspirone, trazodone, nefazodone, etoperidone, and mepiprazole all antagonize α1-adrenergic receptors as well, which contributes to their side effects such as orthostatic hypotension.Agonists: (R)-3-Nitrobiphenyline • 4-NEMD • 6-FNE • Amitraz • Apraclonidine • Brimonidine • Cannabivarin • Clonidine • Detomidine • Dexmedetomidine • Dihydroergotamine • Dipivefrine • Dopamine • Ephedrine • Ergotamine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Esproquin • Etilefrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Guanabenz • Guanfacine • Guanoxabenz • Levonordefrin • Lofexidine • Medetomidine • Methyldopa • Mivazerol • Naphazoline • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Phenylpropanolamine • Piperoxan • Pseudoephedrine • Rilmenidine • Romifidine • Talipexole • Tetrahydrozoline • Tizanidine • Tolonidine • Urapidil • Xylazine • Xylometazoline
Antagonists: 1-PP • Adimolol • Aptazapine • Atipamezole • BRL-44408 • Buflomedil • Cirazoline • Efaroxan • Esmirtazapine • Fenmetozole • Fluparoxan • GYKI-12,743 • GYKI-16,084 • Idazoxan • Mianserin • Mirtazapine • MK-912 • NAN-190 • Olanzapine • Phentolamine • Phenoxybenzamine • Piperoxan • Piribedil • Rauwolscine • Rotigotine • SB-269,970 • Setiptiline • Spiroxatrine • Sunepitron • Tolazoline • Yohimbine
* Note that many atypical antipsychotics and azapirones like buspirone and gepirone (via metabolite 1-PP) antagonize α2-adrenergic receptors as well.βAgonists: 2-FNE • 5-FNE • Amibegron • Arbutamine • Arformoterol • Arotinolol • BAAM • Bambuterol • Befunolol • Bitolterol • Broxaterol • Buphenine • Carbuterol • Cimaterol • Clenbuterol • Denopamine • Deterenol • Dipivefrine • Dobutamine • Dopamine • Dopexamine • Ephedrine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Etafedrine • Etilefrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Fenoterol • Formoterol • Hexoprenaline • Higenamine • Indacaterol • Isoetarine • Isoprenaline (Isoproterenol) • Isoxsuprine • Labetalol • Levonordefrin • Levosalbutamol • Mabuterol • Methoxyphenamine • Methyldopa • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Orciprenaline • Oxyfedrine • Phenylpropanolamine • Pirbuterol • Prenalterol • Ractopamine • Procaterol • Pseudoephedrine • Reproterol • Rimiterol • Ritodrine • Salbutamol (Albuterol) • Salmeterol • Solabegron • Terbutaline • Tretoquinol • Tulobuterol • Xamoterol • Zilpaterol • Zinterol
Antagonists: Acebutolol • Adaprolol • Adimolol • Afurolol • Alprenolol • Alprenoxime • Amosulalol • Ancarolol • Arnolol • Arotinolol • Atenolol • Befunolol • Betaxolol • Bevantolol • Bisoprolol • Bopindolol • Bormetolol • Bornaprolol • Brefonalol • Bucindolol • Bucumolol • Bufetolol • Buftiralol • Bufuralol • Bunitrolol • Bunolol • Bupranolol • Burocrolol • Butaxamine • Butidrine • Butofilolol • Capsinolol • Carazolol • Carpindolol • Carteolol • Carvedilol • Celiprolol • Cetamolol • Cicloprolol • Cinamolol • Cloranolol • Cyanopindolol • Dalbraminol • Dexpropranolol • Diacetolol • Dichloroisoprenaline • Dihydroalprenolol • Dilevalol • Diprafenone • Draquinolol • Dropranolol • Ecastolol • Epanolol • Ericolol • Ersentilide • Esatenolol • Esmolol • Esprolol • Eugenodilol • Exaprolol • Falintolol • Flestolol • Flusoxolol • Hydroxycarteolol • Hydroxytertatolol • ICI-118,551 • Idropranolol • Indenolol • Indopanolol • Iodocyanopindolol • Iprocrolol • Isoxaprolol • Isamoltane • Labetalol • Landiolol • Levobetaxolol • Levobunolol • Levocicloprolol • Levomoprolol • Medroxalol • Mepindolol • Metalol • Metipranolol • Metoprolol • Moprolol • Nadolol • Nadoxolol • Nafetolol • Nebivolol • Neraminol • Nifenalol • Nipradilol • Oberadilol • Oxprenolol • Pacrinolol • Pafenolol • Pamatolol • Pargolol • Parodilol • Penbutolol • Penirolol • PhQA-33 • Pindolol • Pirepolol • Practolol • Primidolol • Procinolol • Pronethalol • Propafenone • Propranolol • Ridazolol • Ronactolol • Soquinolol • Sotalol • Spirendolol • SR 59230A • Sulfinalol • TA-2005 • Talinolol • Tazolol • Teoprolol • Tertatolol • Terthianolol • Tienoxolol • Tilisolol • Timolol • Tiprenolol • Tolamolol • Toliprolol • Tribendilol • Trigevolol • Xibenolol • XipranololReuptake inhibitors Selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors: Amedalin • Atomoxetine (Tomoxetine) • Ciclazindol • Daledalin • Esreboxetine • Lortalamine • Mazindol • Nisoxetine • Reboxetine • Talopram • Talsupram • Tandamine • Viloxazine; Norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors: Amineptine • Bupropion (Amfebutamone) • Fencamine • Fencamfamine • Lefetamine • Levophacetoperane • LR-5182 • Manifaxine • Methylphenidate • Nomifensine • O-2172 • Radafaxine; Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors: Bicifadine • Desvenlafaxine • Duloxetine • Eclanamine • Levomilnacipran • Milnacipran • Sibutramine • Venlafaxine; Serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors: Brasofensine • Diclofensine • DOV-102,677 • DOV-21,947 • DOV-216,303 • JNJ-7925476 • JZ-IV-10 • Methylnaphthidate • Naphyrone • NS-2359 • PRC200-SS • SEP-225,289 • SEP-227,162 • Tesofensine; Tricyclic antidepressants: Amitriptyline • Butriptyline • Cianopramine • Clomipramine • Desipramine • Dosulepin • Doxepin • Imipramine • Lofepramine • melitracen • Nortriptyline • Protriptyline • Trimipramine; Tetracyclic antidepressants: Amoxapine • Maprotiline • Mianserin • Oxaprotiline • Setiptiline; Others: Cocaine • CP-39,332 • EXP-561 • Fezolamine • Ginkgo biloba • Indeloxazine • Nefazodone • Nefopam • Pridefrine • Tapentadol • Tedatioxetine • Teniloxazine • Tramadol • ZiprasidoneEnzyme inhibitors 3,4-DihydroxystyreneDBHCGS-19281A • SKF-64139 • SKF-7698Nonselective: Benmoxin • Caroxazone • Echinopsidine • Furazolidone • Hydralazine • Indantadol • Iproclozide • Iproniazid • Isocarboxazid • Isoniazid • Linezolid • Mebanazine • Metfendrazine • Nialamide • Octamoxin • Paraxazone • Phenelzine • Pheniprazine • Phenoxypropazine • Pivalylbenzhydrazine • Procarbazine • Safrazine • Tranylcypromine; MAO-A selective: Amiflamine • Bazinaprine • Befloxatone • Befol • Brofaromine • Cimoxatone • Clorgiline • Esuprone • Harmala alkaloids (Harmine, Harmaline, Tetrahydroharmine, Harman, Norharman, etc) • Methylene Blue • Metralindole • Minaprine • Moclobemide • Pirlindole • Sercloremine • Tetrindole • Toloxatone • Tyrima; MAO-B selective: D-Deprenyl • Selegiline (L-Deprenyl) • Ladostigil • Lazabemide • Milacemide • Mofegiline • Pargyline • Rasagiline • Safinamide
* Note that MAO-B inhibitors also influence norepinephrine/epinephrine levels since they inhibit the breakdown of their precursor dopamine.COMTOthers Ferrous Iron (Fe2+) • S-Adenosyl-L-Methionine • Vitamin B3 (Niacin, Nicotinamide → NADPH) • Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine, Pyridoxamine, Pyridoxal → Pyridoxal Phosphate) • Vitamin B9 (Folic acid → Tetrahydrofolic acid) • Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid) • Zinc (Zn2+)OthersActivity enhancers: BPAP • PPAP; Release blockers: Bethanidine • Bretylium • Guanadrel • Guanazodine • Guanclofine • Guanethidine • Guanoxan; Toxins: Oxidopamine (6-Hydroxydopamine)List of adrenergic drugsCardiac stimulants excluding cardiac glycosides (C01C) Adrenergic and
dopaminergic agentsαβmixedBothUnknown/ungroupedPhosphodiesterase inhibitors (PDE3I) Other cardiac stimulants Categories:- Alpha-adrenergic agonists
- Cardiac stimulants
- Phenethylamines
- Prodrugs
- Phenol ethers
- Acetamides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.