- Reboxetine
-
Reboxetine 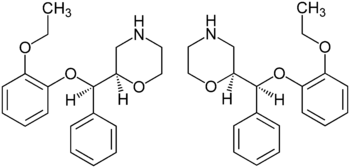
Systematic (IUPAC) name (R*,R*)-2-[(2-ethoxyphenoxy)-phenyl-methyl]morpholine Clinical data Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status ℞ Prescription only Routes Oral Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability 94.5%[1] Protein binding 98% Metabolism Hepatic, CYP3A4-mediated Half-life 13 hours[2] Excretion Renal Identifiers CAS number 98769-81-4 
ATC code N06AX18 PubChem CID 127151 DrugBank DB00234 ChemSpider 112870 
UNII 947S0YZ36I 
KEGG D08472 
ChEMBL CHEMBL14370 
Chemical data Formula C19H23NO3 Mol. mass 313.391 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Reboxetine is a drug marketed as an antidepressant for use in the treatment of clinical depression, panic disorder and ADD/ADHD, developed by Pharmacia (now Pfizer). Its mesylate (i.e. methanesulfonate) salt is sold under tradenames including Edronax, Norebox, Prolift, Solvex, Davedax or Vestra. It is approved for use in many European countries, but has not been approved for use in the United States because of a lack of proven efficacy.
According to a meta-analysis of 12 new-generation antidepressants, reboxetine was no more effective than placebo, was "significantly less" effective, and was less acceptable, than the other drugs in treating the acute-phase treatment of adults with unipolar major depression.[3][4][5]
According to a systematic review and meta-analysis by IQWiG, including unpublished data, published data on reboxetine overestimated the benefit of reboxetine versus placebo by up to 115% and reboxetine versus SSRIs by up to 23%, and also underestimated harm, concluding that reboxetine was an ineffective and potentially harmful antidepressant. The study also showed that nearly three quarters of the data on patients who took part in trials of reboxetine were not published by Pfizer until now.[6]
Reboxetine has two chiral centers. Thus, four stereoisomers may exist, the (R,R)-, (S,S)-, (R,S)-, and (S,R)-isomers. The active ingredient of reboxetine is a racemic mixture of two enantiomers, the (R,R)-(–)- and (S,S)-(+)-isomer.[7]
Contents
Mode of action
Unlike most antidepressants on the market, reboxetine is a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NRI); it does not inhibit the reuptake of serotonin.[8]
Side effects
Common side effects of reboxetine include: dry mouth, constipation, headache, drowsiness, dizziness, excessive sweating and insomnia. Hypertension has been infrequently seen.
In 4 to 8% of all patients treated the medication has to be discontinued due to following reasons (percentages represent mean values):
- insomnia 1.3%
- excessive sweating 1.1%
- vertigo/hypotension and paraesthesia 0.8%
- dizziness, impotence, and other urological problems 0.5% each
Some other rare side effects include anxiety, loss of appetite, loss of libido, urinary retention in men, pain on ejaculation, increased orgasm intensity, and premature/quickened ejaculation.
Reboxetine is normally well tolerated. So far no attributable fatalities have been noted.
Metabolism
Both the (R,R)-(–) and (S,S)-(+)-enantiomers of reboxetine are predominantly metabolized by the CYP3A4 isoenzyme.[9] The primary metabolite of reboxetine is O-desethylreboxetine, and there are also three minor metabolites—Phenol A, Phenol B, and UK1, Phenol B being the most minor.[9]
Interactions with other medications
Because of its reliance on CYP3A4, reboxetine O-desethylation is markedly inhibited by papaverine and ketoconazole.[9]
According to Weiss et al., reboxetine is an intermediate-level inhibitor of P-glycoprotein, which gives it the potential to interact with ciclosporin, tacrolimus, paroxetine, sertraline, quinidine, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine.[10]
The potency and duration of the effects of benzodiazepines can be increased because reboxetine interferes with their excretion.
History
By mid-2007, reboxetine was licensed worldwide in over 50 countries, including Italy, Germany and the United Kingdom. In May 2007, however, the Food and Drug Administration declined Pharmacia's license application for the American market. Therefore it is yet to be available in the United States.
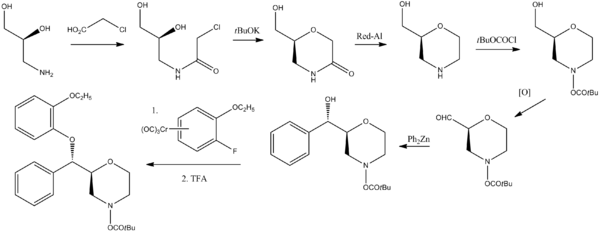
Chemistry
Notes and references
- ^ Fleishaker JC (2000). "Clinical pharmacokinetics of reboxetine, a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor for the treatment of patients with depression". Clinical Pharmacokinetics 39 (6): 413–27. doi:10.2165/00003088-200039060-00003. PMID 11192474.
- ^ Edwards DM, Pellizzoni C, Breuel HP, Berardi A, Castelli MG, Frigerio E, Poggesi I, Rocchetti M, Dubini A, Strolin Benedetti M (1995). "Pharmacokinetics of reboxetine in healthy volunteers. Single oral doses, linearity and plasma protein binding". Biopharmaceutics & Drug Disposition 16 (6): 443–60. doi:10.1002/bdd.2510160603. PMID 7579027.
- ^ Analysis shows sertraline and escitalopram are the best of 12 new-generation antidepressants Lancet Public release date: 28-Jan-2009
- ^ Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 new-generation antidepressants: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis, Andrea Cipriani, Toshiaki A Furukawa, Georgia Salanti, John R Geddes, et al. The Lancet, Published Online, January 29, 2009, DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60046-5
- ^ Zoloft, Lexapro the Best of Newer Antidepressants, HealthDay News, Washington Post, January 29, 2009
- ^ Reboxetine for acute treatment of major depression: systematic review and meta-analysis of published and unpublished placebo and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor controlled trials British Medical Journal Public release date: 12-Oct-2010
- ^ Melloni P, Della Torre A, Lazzari E, Mazzini G and Meroni M (1985). "Configuration studies on 2-[alpha -(2-ethoxyphenoxy)benzyl]-morpholine FCE 20124". Tetrahedron 41 (1): 1393–1399. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)96541-X.
- ^ Kent JM. (2000). "SNaRIs, NaSSAs, and NaRIs: new agents for the treatment of depression". The Lancet 355 (9207): 911–918. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(99)11381-3. PMID 10752718.
- ^ a b c Wienkers LC, Allievi C, Hauer MJ, Wynalda MA. (1999). "Cytochrome P-450-Mediated Metabolism of the Individual Enantiomers of the Antidepressant Agent Reboxetine in Human Liver Microsomes". Drug Metabolism & Disposition 27 (11): 1334–1340. PMID 10534319.
- ^ Weiss J, Dormann SM, Martin-Facklam M, Kerpen CJ, Ketabi-Kiyanvash N, Haefeli WE (2003). "Inhibition of P-glycoprotein by newer antidepressants". Journal of Pharmacology & Experimental Therapeutics 305 (1): 197–204. doi:10.1124/jpet.102.046532. PMID 12649369.
- ^ Brenner, Eric; Baldwin, Ronald M.; Tamagnan, Gilles (2005). "Asymmetric Synthesis of (+)-(S,S)-Reboxetine via a New (S)-2-(Hydroxymethyl)morpholine Preparation". Organic Letters 7 (5): 937–9. doi:10.1021/ol050059g. PMID 15727479.
External links
Stimulants (N06B) Adamantanes Adaphenoxate • Adapromine • Amantadine • Bromantane • Chlodantane • Gludantane • Memantine • Midantane
Adenosine antagonists 8-Chlorotheophylline • 8-Cyclopentyltheophylline • 8-Phenyltheophylline • Aminophylline • Caffeine • CGS-15943 • Dimethazan • Paraxanthine • SCH-58261 • Theobromine • TheophyllineAlkylamines Arylcyclohexylamines Benocyclidine • Dieticyclidine • Esketamine • Eticyclidine • Gacyclidine • Ketamine • Phencyclamine • Phencyclidine • Rolicyclidine • Tenocyclidine • Tiletamine
Benzazepines 6-Br-APB • SKF-77434 • SKF-81297 • SKF-82958
Cholinergics A-84543 • A-366,833 • ABT-202 • ABT-418 • AR-R17779 • Altinicline • Anabasine • Arecoline • Cotinine • Cytisine • Dianicline • Epibatidine • Epiboxidine • GTS-21 • Ispronicline • Nicotine • PHA-543,613 • PNU-120,596 • PNU-282,987 • Pozanicline • Rivanicline • Sazetidine A • SIB-1553A • SSR-180,711 • TC-1698 • TC-1827 • TC-2216 • TC-5619 • Tebanicline • UB-165 • Varenicline • WAY-317,538
Convulsants Anatoxin-a • Bicuculline • DMCM • Flurothyl • Gabazine • Pentetrazol • Picrotoxin • Strychnine • Thujone
Eugeroics Adrafinil • Armodafinil • CRL-40941 • Modafinil
Oxazolines 4-Methylaminorex • Aminorex • Clominorex • Cyclazodone • Fenozolone • Fluminorex • Pemoline • Thozalinone
Phenethylamines 1-(4-Methylphenyl)-2-aminobutane • 1-Phenyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)pentan-3-one • 1-Methylamino-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)propane • 2-Fluoroamphetamine • 2-Fluoromethamphetamine • 2-OH-PEA • 2-Phenyl-3-aminobutane • 2-Phenyl-3-methylaminobutane • 2,3-MDA • 3-Fluoroamphetamine • 3-Fluoroethamphetamine • 3-Fluoromethcathinone • 3-Methoxyamphetamine • 3-Methylamphetamine • 3,4-DMMC • 4-BMC • 4-Ethylamphetamine • 4-FA • 4-FMA • 4-MA • 4-MMA • 4-MTA • 6-FNE • Alfetamine • α-Ethylphenethylamine • Amfecloral • Amfepentorex • Amfepramone • Amidephrine • Amphetamine (Dextroamphetamine, Levoamphetamine) • Amphetaminil • Arbutamine • β-Methylphenethylamine • β-Phenylmethamphetamine • Benfluorex • Benzedrone • Benzphetamine • BDB (J) • BOH (Hydroxy-J) • BPAP • Buphedrone • Bupropion (Amfebutamone) • Butylone • Cathine • Cathinone • Chlorphentermine • Cinnamedrine • Clenbuterol • Clobenzorex • Cloforex • Clortermine • D-Deprenyl • Denopamine • Dimethoxyamphetamine • Dimethylamphetamine • Dimethylcathinone (Dimethylpropion, Metamfepramone) • Dobutamine • DOPA (Dextrodopa, Levodopa) • Dopamine • Dopexamine • Droxidopa • EBDB (Ethyl-J) • Ephedrine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Epinine (Deoxyepinephrine) • Etafedrine • Ethcathinone (Ethylpropion) • Ethylamphetamine (Etilamfetamine) • Ethylnorepinephrine (Butanefrine) • Ethylone • Etilefrine • Famprofazone • Fenbutrazate • Fencamine • Fenethylline • Fenfluramine (Dexfenfluramine) • Fenmetramide • Fenproporex • Flephedrone • Fludorex • Furfenorex • Gepefrine • HMMA • Hordenine • Ibopamine • IMP • Indanylamphetamine • Isoetarine • Isoethcathinone • Isoprenaline (Isoproterenol) • L-Deprenyl (Selegiline) • Lefetamine • Lisdexamfetamine • Lophophine (Homomyristicylamine) • Manifaxine • MBDB (Methyl-J; "Eden") • MDA (Tenamfetamine) • MDBU • MDEA ("Eve") • MDMA ("Ecstasy", "Adam") • MDMPEA (Homarylamine) • MDOH • MDPR • MDPEA (Homopiperonylamine) • Mefenorex • Mephedrone • Mephentermine • Metanephrine • Metaraminol • Methamphetamine (Desoxyephedrine, Methedrine; Dextromethamphetamine, Levomethamphetamine) • Methoxamine • Methoxyphenamine • MMA • Methcathinone (Methylpropion) • Methedrone • Methoxyphenamine • Methylone • MMDA • MMDMA • MMMA • Morazone • N-Benzyl-1-phenethylamine • N,N-Dimethylphenethylamine • Naphthylamphetamine • Nisoxetine • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Norfenefrine • Norfenfluramine • Normetanephrine • Octopamine • Orciprenaline • Ortetamine • Oxilofrine • Paredrine (Norpholedrine, Oxamphetamine, Mycadrine) • PBA • PCA • PHA • Pargyline • Pentorex (Phenpentermine) • Pentylone • Phendimetrazine • Phenmetrazine • Phenpromethamine • Phentermine • Phenylalanine • Phenylephrine (Neosynephrine) • Phenylpropanolamine • Pholedrine • PIA • PMA • PMEA • PMMA • PPAP • Prenylamine • Propylamphetamine • Pseudoephedrine • Radafaxine • Ropinirole • Salbutamol (Albuterol; Levosalbutamol) • Sibutramine • Synephrine (Oxedrine) • Theodrenaline • Tiflorex (Flutiorex) • Tranylcypromine • Tyramine • Tyrosine • Xamoterol • Xylopropamine • Zylofuramine
Piperazines Piperidines 1-Benzyl-4-(2-(diphenylmethoxy)ethyl)piperidine • 1-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-1-(piperidin-2-yl)butane • 2-Benzylpiperidine • 2-Methyl-3-phenylpiperidine • 3,4-Dichloromethylphenidate • 4-Benzylpiperidine • 4-Methylmethylphenidate • Desoxypipradrol • Difemetorex • Diphenylpyraline • Ethylphenidate • Methylnaphthidate • Methylphenidate (Dexmethylphenidate) • N-Methyl-3β-propyl-4β-(4-chlorophenyl)piperidine • Nocaine • Phacetoperane • Pipradrol • SCH-5472
Pyrrolidines 2-Diphenylmethylpyrrolidine • α-PPP • α-PBP • α-PVP • Diphenylprolinol • MDPPP • MDPBP • MDPV • MPBP • MPHP • MPPP • MOPPP • Naphyrone • PEP • Prolintane • Pyrovalerone
Tropanes 3-CPMT • 3'-Chloro-3α-(diphenylmethoxy)tropane • 3-Pseudotropyl-4-fluorobenzoate • 4'-Fluorococaine • AHN-1055 • Altropane (IACFT) • Brasofensine • CFT (WIN 35,428) • β-CIT (RTI-55) • Cocaethylene • Cocaine • Dichloropane (RTI-111) • Difluoropine • FE-β-CPPIT • FP-β-CPPIT • Ioflupane (123I) • Norcocaine • PIT • PTT • RTI-31 • RTI-32 • RTI-51 • RTI-105 • RTI-112 • RTI-113 • RTI-117 • RTI-120 • RTI-121 (IPCIT) • RTI-126 • RTI-150 • RTI-154 • RTI-171 • RTI-177 • RTI-183 • RTI-193 • RTI-194 • RTI-199 • RTI-202 • RTI-204 • RTI-229 • RTI-241 • RTI-336 • RTI-354 • RTI-371 • RTI-386 • Salicylmethylecgonine • Tesofensine • Troparil (β-CPT, WIN 35,065-2) • Tropoxane • WF-23 • WF-33 • WF-60
Others 1-(Thiophen-2-yl)-2-aminopropane • 2-Amino-1,2-dihydronaphthalene • 2-Aminoindane • 2-Aminotetralin • 2-MDP • 2-Phenylcyclohexylamine • 2-Phenyl-3,6-dimethylmorpholine • 3-Benzhydrylmorpholine • 3,3-Diphenylcyclobutanamine • 5-(2-Aminopropyl)indole • 5-Iodo-2-aminoindane • AL-1095 • Amfonelic acid • Amineptine • Amiphenazole • Atipamezole • Atomoxetine (Tomoxetine) • Bemegride • Benzydamine • BTQ • BTS 74,398 • Carphedon • Ciclazindol • Cilobamine • Clofenciclan • Cropropamide • Crotetamide • Cypenamine • D-161 • Diclofensine • Dimethocaine • Efaroxan • Etamivan • EXP-561 • Fencamfamine • Fenpentadiol • Feprosidnine • G-130 • Gamfexine • Gilutensin • GSK1360707F • GYKI-52895 • Hexacyclonate • Idazoxan • Indanorex • Indatraline • JNJ-7925476 • JZ-IV-10 • Lazabemide • Leptacline • Levopropylhexedrine • Lomevactone • LR-5182 • Mazindol • Meclofenoxate • Medifoxamine • Mefexamide • Mesocarb • Methastyridone • Methiopropamine • N-Methyl-3-phenylnorbornan-2-amine • Nefopam • Nikethamide • Nomifensine • O-2172 • Oxaprotiline • Phthalimidopropiophenone • PNU-99,194 • Propylhexedrine • PRC200-SS • Rasagiline • Rauwolscine • Rubidium chloride • Setazindol • Tametraline • Tandamine • Trazium • UH-232 • Yohimbine
See also Sympathomimetic aminesAntidepressants (N06A) Specific reuptake inhibitors (RIs), enhancers (REs), and releasing agents (RAs) Alaproclate • Citalopram • Escitalopram • Femoxetine • Fluoxetine# • Fluvoxamine • Indalpine • Ifoxetine • Litoxetine • Lubazodone • Panuramine • Paroxetine • Pirandamine • Seproxetine • Sertraline# • Vilazodone • Zimelidine‡Bicifadine • Clovoxamine • Desvenlafaxine • Duloxetine • Levomilnacipran • Eclanamine • Milnacipran • Sibutramine • VenlafaxineSerotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitors (SNDRIs)Brasofensine • BTS-74,398 • Cocaine • Diclofensine • DOV-21,947 • DOV-102,677 • DOV-216,303 • EXP-561 • Fezolamine • JNJ-7925476 • NS-2359 • PRC200-SS • Pridefine • SEP-225,289 • SEP-227,162 • TesofensineAmedalin • Atomoxetine/Tomoxetine • Binedaline • Ciclazindol • Daledalin • Esreboxetine • Lortalamine • Mazindol • Nisoxetine • Reboxetine • Talopram • Talsupram • Tandamine • ViloxazineDopamine reuptake inhibitors (DRIs)Amineptine • Bupropion/Amfebutamone# • Cilobamine • Manifaxine • Methylphenidate • Nomifensine • Radafaxine • TametralineNorepinephrine-dopamine releasing agents (NDRAs)Serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine releasing agents (SNDRAs)4-Methyl-αMT • αET/Etryptamine • αMT/MetryptamineOthersIndeloxazine • Teniloxazine • Tramadol • ViqualineReceptor antagonists and/or reuptake inhibitors Serotonin antagonists and reuptake inhibitors (SARIs)Serotonin modulators and stimulators (SMSs)VortioxetineTricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants (TCAs/TeCAs) TricyclicsAmezepine • Amineptine • Amitriptyline# • Amitriptylinoxide • Azepindole • Butriptyline • Cianopramine • Clomipramine • Cotriptyline • Cyanodothiepin • Demexiptiline • Depramine/Balipramine • Desipramine • Dibenzepin • Dimetacrine • Dosulepin/Dothiepin • Doxepin • Enprazepine • Fluotracen • Hepzidine • Homopipramol • Imipramine • Imipraminoxide • Intriptyline • Iprindole • Ketipramine • Litracen • Lofepramine • Losindole • Mariptiline • Melitracen • Metapramine • Mezepine • Naranol • Nitroxazepine • Nortriptyline • Noxiptiline • Octriptyline • Opipramol • Pipofezine • Propizepine • Protriptyline • Quinupramine • Tampramine • Tianeptine • Tienopramine • Trimipramine;7-OH-Amoxapine • Amoxapine • Aptazapine • Azipramine • Ciclazindol • Ciclopramine • Esmirtazapine • Loxapine • Maprotiline • Mazindol • Mianserin • Mirtazapine • Oxaprotiline • Setiptiline/TeciptilineMonoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) NonselectiveIrreversible: Benmoxin • Echinopsidine • Iproclozide • Iproniazid • Isocarboxazid • Mebanazine • Metfendrazine • Nialamide • Octamoxin • Phenelzine • Pheniprazine • Phenoxypropazine • Pivalylbenzhydrazine • Safrazine • Tranylcypromine; Reversible: Caroxazone • Paraxazone;MAOA-SelectiveIrreversible: Clorgiline; Reversible: Amiflamine • Bazinaprine • Befloxatone • Befol • Brofaromine • Cimoxatone • Esuperone • Harmala Alkaloids (Harmine, Harmaline, Tetrahydroharmine, Harman, Norharman, etc) • Methylene Blue • Metralindole • Minaprine • Moclobemide • Pirlindole • Sercloremine • Tetrindole • Toloxatone • Tyrima;MAOB-SelectiveIrreversible: Ladostigil • Mofegiline • Pargyline • Rasagiline • Selegiline; Reversible: Lazabemide • MilacemideAzapirones and other 5-HT1A receptor agonists Alnespirone • Aripiprazole • Befiradol • Buspirone • Eptapirone • Flesinoxan • Flibanserin • Gepirone • Ipsapirone • Oxaflozane • Tandospirone • Vilazodone • ZalospironePsychostimulants, agents used for ADHD, and nootropics (N06B) Centrally acting sympathomimetics Xanthine derivatives Glutamate receptor CX-516 • CX-546 • CX-614 • CX-691 • CX-717 • IDRA-21 • LY-404,187 • LY-503,430 • PEPA • S-18986 • Sunifiram • UnifiramEugeroics / Benzhydryl compounds Histamine H3 receptor antagonists GABAA α5 inverse agonists Dopamine D1 receptor agonists α7 nicotinic agonists / PAMs AR-R17779 • PNU-282,987 • SSR-180,711Prolyl endopeptidase inhibitors S-17092Alpha-adrenergic agonists Other psychostimulants and nootropics Acetylcarnitine • Adafenoxate • Bifemelane • Carbenoxolone • Citicoline • Cyprodenate • Ensaculin • Idebenone • Ispronicline • Deanol • Dimebon • Fipexide • Leteprinim • Linopirdine • Meclofenoxate • Nizofenone • P7C3 • Pirisudanol • Pyritinol • Rubidium • Sulbutiamine • Taltirelin • Tricyanoaminopropene • VinpocetineAdrenergics Receptor ligands Agonists: 5-FNE • 6-FNE • Amidephrine • Anisodamine • Anisodine • Cirazoline • Dipivefrine • Dopamine • Ephedrine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Etilefrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Indanidine • Levonordefrin • Metaraminol • Methoxamine • Methyldopa • Midodrine • Naphazoline • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Octopamine • Oxymetazoline • Phenylephrine • Phenylpropanolamine • Pseudoephedrine • Synephrine • Tetrahydrozoline
Antagonists: Abanoquil • Adimolol • Ajmalicine • Alfuzosin • Amosulalol • Arotinolol • Atiprosin • Benoxathian • Buflomedil • Bunazosin • Carvedilol • CI-926 • Corynanthine • Dapiprazole • DL-017 • Domesticine • Doxazosin • Eugenodilol • Fenspiride • GYKI-12,743 • GYKI-16,084 • Indoramin • Ketanserin • L-765,314 • Labetalol • Mephendioxan • Metazosin • Monatepil • Moxisylyte (Thymoxamine) • Naftopidil • Nantenine • Neldazosin • Nicergoline • Niguldipine • Pelanserin • Phendioxan • Phenoxybenzamine • Phentolamine • Piperoxan • Prazosin • Quinazosin • Ritanserin • RS-97,078 • SGB-1,534 • Silodosin • SL-89.0591 • Spiperone • Talipexole • Tamsulosin • Terazosin • Tibalosin • Tiodazosin • Tipentosin • Tolazoline • Trimazosin • Upidosin • Urapidil • Zolertine
* Note that many TCAs, TeCAs, antipsychotics, ergolines, and some piperazines like buspirone, trazodone, nefazodone, etoperidone, and mepiprazole all antagonize α1-adrenergic receptors as well, which contributes to their side effects such as orthostatic hypotension.Agonists: (R)-3-Nitrobiphenyline • 4-NEMD • 6-FNE • Amitraz • Apraclonidine • Brimonidine • Cannabivarin • Clonidine • Detomidine • Dexmedetomidine • Dihydroergotamine • Dipivefrine • Dopamine • Ephedrine • Ergotamine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Esproquin • Etilefrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Guanabenz • Guanfacine • Guanoxabenz • Levonordefrin • Lofexidine • Medetomidine • Methyldopa • Mivazerol • Naphazoline • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Phenylpropanolamine • Piperoxan • Pseudoephedrine • Rilmenidine • Romifidine • Talipexole • Tetrahydrozoline • Tizanidine • Tolonidine • Urapidil • Xylazine • Xylometazoline
Antagonists: 1-PP • Adimolol • Aptazapine • Atipamezole • BRL-44408 • Buflomedil • Cirazoline • Efaroxan • Esmirtazapine • Fenmetozole • Fluparoxan • GYKI-12,743 • GYKI-16,084 • Idazoxan • Mianserin • Mirtazapine • MK-912 • NAN-190 • Olanzapine • Phentolamine • Phenoxybenzamine • Piperoxan • Piribedil • Rauwolscine • Rotigotine • SB-269,970 • Setiptiline • Spiroxatrine • Sunepitron • Tolazoline • Yohimbine
* Note that many atypical antipsychotics and azapirones like buspirone and gepirone (via metabolite 1-PP) antagonize α2-adrenergic receptors as well.βAgonists: 2-FNE • 5-FNE • Amibegron • Arbutamine • Arformoterol • Arotinolol • BAAM • Bambuterol • Befunolol • Bitolterol • Broxaterol • Buphenine • Carbuterol • Cimaterol • Clenbuterol • Denopamine • Deterenol • Dipivefrine • Dobutamine • Dopamine • Dopexamine • Ephedrine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Etafedrine • Etilefrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Fenoterol • Formoterol • Hexoprenaline • Higenamine • Indacaterol • Isoetarine • Isoprenaline (Isoproterenol) • Isoxsuprine • Labetalol • Levonordefrin • Levosalbutamol • Mabuterol • Methoxyphenamine • Methyldopa • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Orciprenaline • Oxyfedrine • Phenylpropanolamine • Pirbuterol • Prenalterol • Ractopamine • Procaterol • Pseudoephedrine • Reproterol • Rimiterol • Ritodrine • Salbutamol (Albuterol) • Salmeterol • Solabegron • Terbutaline • Tretoquinol • Tulobuterol • Xamoterol • Zilpaterol • Zinterol
Antagonists: Acebutolol • Adaprolol • Adimolol • Afurolol • Alprenolol • Alprenoxime • Amosulalol • Ancarolol • Arnolol • Arotinolol • Atenolol • Befunolol • Betaxolol • Bevantolol • Bisoprolol • Bopindolol • Bormetolol • Bornaprolol • Brefonalol • Bucindolol • Bucumolol • Bufetolol • Buftiralol • Bufuralol • Bunitrolol • Bunolol • Bupranolol • Burocrolol • Butaxamine • Butidrine • Butofilolol • Capsinolol • Carazolol • Carpindolol • Carteolol • Carvedilol • Celiprolol • Cetamolol • Cicloprolol • Cinamolol • Cloranolol • Cyanopindolol • Dalbraminol • Dexpropranolol • Diacetolol • Dichloroisoprenaline • Dihydroalprenolol • Dilevalol • Diprafenone • Draquinolol • Dropranolol • Ecastolol • Epanolol • Ericolol • Ersentilide • Esatenolol • Esmolol • Esprolol • Eugenodilol • Exaprolol • Falintolol • Flestolol • Flusoxolol • Hydroxycarteolol • Hydroxytertatolol • ICI-118,551 • Idropranolol • Indenolol • Indopanolol • Iodocyanopindolol • Iprocrolol • Isoxaprolol • Isamoltane • Labetalol • Landiolol • Levobetaxolol • Levobunolol • Levocicloprolol • Levomoprolol • Medroxalol • Mepindolol • Metalol • Metipranolol • Metoprolol • Moprolol • Nadolol • Nadoxolol • Nafetolol • Nebivolol • Neraminol • Nifenalol • Nipradilol • Oberadilol • Oxprenolol • Pacrinolol • Pafenolol • Pamatolol • Pargolol • Parodilol • Penbutolol • Penirolol • PhQA-33 • Pindolol • Pirepolol • Practolol • Primidolol • Procinolol • Pronethalol • Propafenone • Propranolol • Ridazolol • Ronactolol • Soquinolol • Sotalol • Spirendolol • SR 59230A • Sulfinalol • TA-2005 • Talinolol • Tazolol • Teoprolol • Tertatolol • Terthianolol • Tienoxolol • Tilisolol • Timolol • Tiprenolol • Tolamolol • Toliprolol • Tribendilol • Trigevolol • Xibenolol • XipranololReuptake inhibitors Selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors: Amedalin • Atomoxetine (Tomoxetine) • Ciclazindol • Daledalin • Esreboxetine • Lortalamine • Mazindol • Nisoxetine • Reboxetine • Talopram • Talsupram • Tandamine • Viloxazine; Norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors: Amineptine • Bupropion (Amfebutamone) • Fencamine • Fencamfamine • Lefetamine • Levophacetoperane • LR-5182 • Manifaxine • Methylphenidate • Nomifensine • O-2172 • Radafaxine; Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors: Bicifadine • Desvenlafaxine • Duloxetine • Eclanamine • Levomilnacipran • Milnacipran • Sibutramine • Venlafaxine; Serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors: Brasofensine • Diclofensine • DOV-102,677 • DOV-21,947 • DOV-216,303 • JNJ-7925476 • JZ-IV-10 • Methylnaphthidate • Naphyrone • NS-2359 • PRC200-SS • SEP-225,289 • SEP-227,162 • Tesofensine; Tricyclic antidepressants: Amitriptyline • Butriptyline • Cianopramine • Clomipramine • Desipramine • Dosulepin • Doxepin • Imipramine • Lofepramine • melitracen • Nortriptyline • Protriptyline • Trimipramine; Tetracyclic antidepressants: Amoxapine • Maprotiline • Mianserin • Oxaprotiline • Setiptiline; Others: Cocaine • CP-39,332 • EXP-561 • Fezolamine • Ginkgo biloba • Indeloxazine • Nefazodone • Nefopam • Pridefrine • Tapentadol • Tedatioxetine • Teniloxazine • Tramadol • ZiprasidoneEnzyme inhibitors 3,4-DihydroxystyreneDBHCGS-19281A • SKF-64139 • SKF-7698Nonselective: Benmoxin • Caroxazone • Echinopsidine • Furazolidone • Hydralazine • Indantadol • Iproclozide • Iproniazid • Isocarboxazid • Isoniazid • Linezolid • Mebanazine • Metfendrazine • Nialamide • Octamoxin • Paraxazone • Phenelzine • Pheniprazine • Phenoxypropazine • Pivalylbenzhydrazine • Procarbazine • Safrazine • Tranylcypromine; MAO-A selective: Amiflamine • Bazinaprine • Befloxatone • Befol • Brofaromine • Cimoxatone • Clorgiline • Esuprone • Harmala alkaloids (Harmine, Harmaline, Tetrahydroharmine, Harman, Norharman, etc) • Methylene Blue • Metralindole • Minaprine • Moclobemide • Pirlindole • Sercloremine • Tetrindole • Toloxatone • Tyrima; MAO-B selective: D-Deprenyl • Selegiline (L-Deprenyl) • Ladostigil • Lazabemide • Milacemide • Mofegiline • Pargyline • Rasagiline • Safinamide
* Note that MAO-B inhibitors also influence norepinephrine/epinephrine levels since they inhibit the breakdown of their precursor dopamine.COMTOthers Ferrous Iron (Fe2+) • S-Adenosyl-L-Methionine • Vitamin B3 (Niacin, Nicotinamide → NADPH) • Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine, Pyridoxamine, Pyridoxal → Pyridoxal Phosphate) • Vitamin B9 (Folic acid → Tetrahydrofolic acid) • Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid) • Zinc (Zn2+)OthersActivity enhancers: BPAP • PPAP; Release blockers: Bethanidine • Bretylium • Guanadrel • Guanazodine • Guanclofine • Guanethidine • Guanoxan; Toxins: Oxidopamine (6-Hydroxydopamine)List of adrenergic drugsCategories:- Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors
- Morpholines
- Phenol ethers
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.