- Agomelatine
-
Agomelatine 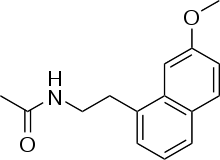
Systematic (IUPAC) name N-[2-(7-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)ethyl]acetamide Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com International Drug Names Licence data EMA:Link Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status ℞ Prescription only Routes Oral Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability <5% [1] Metabolism hepatic (90%CYP1A2;10%CYP2C9) Half-life < 2 h Identifiers CAS number 138112-76-2 
ATC code N06AX22 PubChem CID 82148 IUPHAR ligand 198 ChemSpider 74141 
UNII 137R1N49AD 
KEGG D02578 
ChEMBL CHEMBL10878 
Chemical data Formula C15H17NO2 Mol. mass 243.301 SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Agomelatine (trade names Valdoxan, Melitor, Thymanax) is an antidepressant developed by the pharmaceutical company Servier. It is marketed for the treatment of major depressive disorder and has been reported to have a reduced level of sexual side effects as well as discontinuation effects compared to some other antidepressants. Agomelatine may also have positive effects on sleep.
Contents
Mechanism of action
Agomelatine is a melatonergic agonist (MT1 and MT2 receptors) and 5-HT2C antagonist. Binding studies indicate that it has no effect on monoamine uptake and no affinity for α, β adrenergic, histaminergic, cholinergic, dopaminergic and benzodiazepine receptors.[2]
History
Agomelatine was discovered and developed by the European pharmaceutical company Servier Laboratories Ltd. Servier continued to develop the drug and conduct phase III trials in the European Union. In March 2005 Servier submitted agomelatine to the European Medicines Agency (EMEA) under the trade names Valdoxan and Thymanax.[3] On 27 July 2006 the Committee for Medical Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the EMEA recommended a refusal of the marketing authorisation of Valdoxan/Thymanax (agomelatine). The major concern was that efficacy had not been sufficiently shown. The CHMP had no special concerns about side effects.[3] In September 2007, Servier submitted a new marketing application for Valdoxan (agomelatine) to the EMEA.[4] On 20 November 2008, Valdoxan was given a positive opinion, with restrictions,[5] by the EMEA,[4] and was subsequently given marketing authorisation in the European Union on 20 February 2009.[6] Release dates in the individual countries of the EU were dependent on marketing arrangements.
In March 2006, Servier announced it had sold the rights to market agomelatine in the United States to Novartis.[7] It was undergoing several phase III clinical trials in the US, and until October 2011 Novartis listed the drug as scheduled for submission to the FDA no earlier than 2012.[8] However, the development for the US market was discontinued in October 2011, when the results from the last of those trials became available.[9]
It is currently sold in Australia under the Valdoxan trade name.
Indications
Agomelatine is indicated for the treatment of major depressive episodes in adults.[2] It is not recommended for use in children and adolescents below 18 years of age due to a lack of data on safety and efficacy.[2] Only limited clinical data is available on the use of agomelatine in elderly patients ≥ 65 years old with major depressive episodes. Therefore, caution should be exercised when prescribing it to these patients.[2]
Pharmacodynamics
Agomelatine resynchronises circadian rhythms in animal models of delayed sleep phase syndrome[10] and other circadian rhythm disruptions. It increases noradrenaline and dopamine release specifically in the frontal cortex and has no influence on the extracellular levels of serotonin. Agomelatine has shown an antidepressant-like effect in animal models of depression (learned helplessness test, despair test, chronic mild stress) as well as in models with circadian rhythm desynchronisation and in models related to stress and anxiety. In humans, agomelatine has positive phase shifting properties; it induces a phase advance of sleep, body temperature decline and melatonin onset.[2]
Six placebo controlled trials have been performed to investigate the short term efficacy of agomelatine in major depressive disorder. At the end of treatment, significant efficacy was demonstrated in three of the six short-term double-blind placebo-controlled studies.[2] Efficacy was also observed in more severely depressed patients in all positive placebo-controlled studies.[2] The maintenance of antidepressant efficacy was demonstrated in a relapse prevention study.[2]
Agomelatine does not alter daytime vigilance and memory in healthy volunteers. In depressed patients, treatment with the drug increased slow wave sleep without modification of REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep amount or REM latency. Agomelatine also induced an advance of the time of sleep onset and of minimum heart rate. From the first week of treatment, onset of sleep and the quality of sleep were significantly improved without daytime clumsiness as assessed by patients.[2]
Agomelatine has no abuse potential as measured in healthy volunteer studies.[2]
No relevant modification in agomelatine pharmacokinetic parameters in patients with severe renal impairment has been observed. However, only limited clinical data on its use in depressed patients with severe or moderate renal impairment with major depressive episodes is available. Therefore, caution should be exercised when prescribing agomelatine to these patients.[2] Agomelatine is contraindicated in patients with hepatic impairment.[2] No dosage tapering is needed on treatment discontinuation.[2]
Agomelatine’s onset of efficacy has been reported as early as the first week of treatment.[11]
The antidepressant efficacy of agomelatine 25 mg to 50 mg has been demonstrated in a 6-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study in 260 patients with MDD.[12]
Agomelatine appears to cause fewer sexual side effects and discontinuation effects than sertraline and paroxetine. Additionally, possibly because of its action on melatonin receptors, agomelatine appears to improve sleep quality, with no reported daytime drowsiness.[13] Agomelatine has demonstrated anxiolytic properties in rodents.[14] Its efficacy in generalised anxiety disorder has been assessed by Stein et al (2008) who reported it significantly more effective than placebo treatment.[15]
Results of the meta-analysis of three positive, randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled studies in 357 patients treated with agomelatine and 360 patients treated with placebo show that agomelatine is effective in treating severe depression. Its antidepressant effect is greater for more severe depression. In patients with a greater baseline score (>30 on HAMD17 scale), the agomelatine-placebo difference was of 4.53 points.[16]
Controlled studies in humans have shown that agomelatine is as effective as the SSRI antidepressants paroxetine and sertraline in the treatment of major depression[17]. However, some of the first randomised controlled trials (unpublished) had failed to show that agomelatine is more effective than placebo [18]. Based on the results of the pivotal trials, Agomelatine's efficacy in comparison to placebo was considered to be of marginal clinical relevance by the European regulator. A minority of the CHMP members voted against the approval.[4]. A review of the research studies conducted to April 2011 concludes that "it should only be considered as an alternative drug for patients who do not respond to or cannot tolerate other antidepressant drugs" [19].
Structure
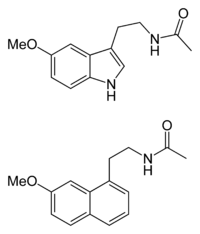
The chemical structure of agomelatine is very similar to that of melatonin. Where melatonin has an NH group, agomelatine has an HC=CH group. Thus melatonin contains an indole part, whereas agomelatine has a naphthalene bioisostere instead.[20]
See also
Discovery and development of melatonin receptor agonists
References
- ^ www.emea.europa.eu/
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m "Summary of Product Characteristics" (PDF). European Medicine Agency. 2003. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Information/human/000915/WC500046227.pdf. Retrieved 2010-09-22.
- ^ a b "Questions and Answers on Recommendation for Refusal of Marketing Authorisation". European Medicines Agency. 18 November 2006. http://www.emea.europa.eu/humandocs/PDFs/EPAR/valdoxan/H-656-657-RQ&A-en.pdf. Retrieved 6 July 2009.
- ^ a b c "CHMP Assessment Report for Valdoxan". European Medicines Agency. 20 November 2008. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/000915/WC500046226.pdf. Retrieved 6 July 2009.
- ^ Transaminases elavations and interactions with potent CYP 1A2 inhibitors (e.g. fluvoxamine, ciprofloxacin]
- ^ "VALDOXAN (AGOMELATINE), A NOVEL ANTIDEPRESSANT, RECEIVES EUROPEAN MARKETING AUTHORISATION". Servier UK. 25 February 2009. http://www.pharmiweb.com/PressReleases/pressrel.asp?ROW_ID=5770. Retrieved 6 July 2009.
- ^ Bentham, Clara (2006-03-29). "Servier and Novartis sign licensing agreement for agomelatine, a novel treatment for depression". Servier UK. http://www.servier.co.uk/news/news-details.asp?StoryID=76. Retrieved 2009-05-15.
- ^ "Clinical trials for agomelatine". ClinicalTrials.gov. National Institutes of Health. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=agomelatine. Retrieved 6 July 2009.
- ^ Novartis drops future blockbuster agomelatine. Scrip Intelligence, Oct 25 2011 (retrieved Oct 30, 2011).
- ^ Le Strat, Y; Philip Gorwood (27 August 2008). "Agomelatine, an innovative pharmacological response to unmet needs". J Psychopharmacol (SagePub) 22 (7): suppl 4–8. doi:10.1177/0269881108092593. PMID 18753276. http://jop.sagepub.com/content/22/7_suppl/4.abstract. Retrieved 2010-10-15.
- ^ Lemoine, P; Guilleminault, C; Alvarez, E (November 2007). "Improvement in subjective sleep in major depressive disorder with a novel antidepressant, agomelatine: randomized, double-blind comparison with venlafaxine.". J Clin Psychiatry 68 (11): 1723–32. doi:10.4088/JCP.v68n1112. PMID 18052566.
- ^ Olié, JP; Kasper, S (October 2007). "Efficacy of agomelatine, a MT1/MT2 receptor agonist with 5-HT2C antagonistic properties, in major depressive disorder.". Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 10 (5): 661–73. doi:10.1017/S1461145707007766. PMID 17477888.
- ^ "Valdoxan: A New Approach to The Treatment of Depression". Medical News Today (MediLexicon International Ltd). 2005-04-05. http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/22334.php. Retrieved 14 May 2009.
- ^ Millan MJ, Brocco M, Gobert A, Dekeyne A (February 2005). "Anxiolytic properties of agomelatine, an antidepressant with melatoninergic and serotonergic properties: role of 5-HT2C receptor blockade". Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 177 (4): 448–58. doi:10.1007/s00213-004-1962-z. PMID 15289999.
- ^ Stein, D.; Ahokas, A.; De Bodinat, C. (2008). "Efficacy of agomelatine in generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.". Journal of clinical psychopharmacology 28 (5): 561–566. doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e318184ff5b. PMID 18794654.
- ^ Montgomery, SA; Kasper, S (September 2007). "Severe depression and antidepressants: focus on a pooled analysis of placebo-controlled studies on agomelatine.". Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 22 (5): 283–91. doi:10.1097/YIC.0b013e3280c56b13. PMID 17690597.
- ^ Kasper S, Hajak G, Wulff K, Hoogendijk WJ, Montejo AL, Smeraldi E, Rybakowski JK, Quera-Salva MA, Wirz-Justice AM, Picarel-Blanchot F, Baylé FJ (February 2010). "Efficacy of the novel antidepressant agomelatine on the circadian rest-activity cycle and depressive and anxiety symptoms in patients with major depressive disorder: a randomized, double-blind comparison with sertraline". J Clin Psychiatry 71 (2): 109–20. doi:10.4088/JCP.09m05347blu. PMID 20193645.
- ^ Howland RH (2009). "Critical appraisal and update on the clinical utility of agomelatine, a melatonergic agonist, for the treatment of major depressive disease in adults". Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 5: 563–76. PMC 2785860. PMID 19966905. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2785860.
- ^ "A benefit-risk assessment of agomelatine in the treatment of major depression.". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21830835.
- ^ B. Tinant, J.-P. Declercq, J. H. Poupaert, S. Yous, D. Lesieur (1994). "N-[2-(7-Methoxy-1-naphthyl)ethyl]acetamide, a potent melatonin analog". Acta Cryst. C 50 (6): 907–910. doi:10.1107/S0108270193012922.
External links
- Official product site
- Manufacturer web site
- Agomelatine Psychonauts Google Group
- Novartis pipeline
- Antidepressant-like activity of S 20098 (agomelatine) in the forced swimming test in rodents: involvement of melatonin and serotonin receptors
- The Novel Melatonin Agonist Agomelatine (S20098) Is an Antagonist at 5-Hydroxytryptamine2C Receptors, Blockade of Which Enhances the Activity of Frontocortical Dopaminergic and Adrenergic Pathways
- Agomelatine treatment has promising results in transgenic murine model
- Clinical trial data in the United Kingdom via the NHS' National electronic Library of Medicines (NeLM)
- Clinical trial data in the United States via ClinicalTrials.gov
Antidepressants (N06A) Specific reuptake inhibitors (RIs), enhancers (REs), and releasing agents (RAs) Alaproclate • Citalopram • Escitalopram • Femoxetine • Fluoxetine# • Fluvoxamine • Indalpine • Ifoxetine • Litoxetine • Lubazodone • Panuramine • Paroxetine • Pirandamine • Seproxetine • Sertraline# • Vilazodone • Zimelidine‡Bicifadine • Clovoxamine • Desvenlafaxine • Duloxetine • Levomilnacipran • Eclanamine • Milnacipran • Sibutramine • VenlafaxineSerotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitors (SNDRIs)Brasofensine • BTS-74,398 • Cocaine • Diclofensine • DOV-21,947 • DOV-102,677 • DOV-216,303 • EXP-561 • Fezolamine • JNJ-7925476 • NS-2359 • PRC200-SS • Pridefine • SEP-225,289 • SEP-227,162 • TesofensineAmedalin • Atomoxetine/Tomoxetine • Binedaline • Ciclazindol • Daledalin • Esreboxetine • Lortalamine • Mazindol • Nisoxetine • Reboxetine • Talopram • Talsupram • Tandamine • ViloxazineDopamine reuptake inhibitors (DRIs)Amineptine • Bupropion/Amfebutamone# • Cilobamine • Manifaxine • Methylphenidate • Nomifensine • Radafaxine • TametralineNorepinephrine-dopamine releasing agents (NDRAs)Serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine releasing agents (SNDRAs)OthersReceptor antagonists and/or reuptake inhibitors Serotonin antagonists and reuptake inhibitors (SARIs)AgomelatineSerotonin modulators and stimulators (SMSs)VortioxetineTricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants (TCAs/TeCAs) TricyclicsAmezepine • Amineptine • Amitriptyline# • Amitriptylinoxide • Azepindole • Butriptyline • Cianopramine • Clomipramine • Cotriptyline • Cyanodothiepin • Demexiptiline • Depramine/Balipramine • Desipramine • Dibenzepin • Dimetacrine • Dosulepin/Dothiepin • Doxepin • Enprazepine • Fluotracen • Hepzidine • Homopipramol • Imipramine • Imipraminoxide • Intriptyline • Iprindole • Ketipramine • Litracen • Lofepramine • Losindole • Mariptiline • Melitracen • Metapramine • Mezepine • Naranol • Nitroxazepine • Nortriptyline • Noxiptiline • Octriptyline • Opipramol • Pipofezine • Propizepine • Protriptyline • Quinupramine • Tampramine • Tianeptine • Tienopramine • Trimipramine;7-OH-Amoxapine • Amoxapine • Aptazapine • Azipramine • Ciclazindol • Ciclopramine • Esmirtazapine • Loxapine • Maprotiline • Mazindol • Mianserin • Mirtazapine • Oxaprotiline • Setiptiline/TeciptilineMonoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) NonselectiveIrreversible: Benmoxin • Echinopsidine • Iproclozide • Iproniazid • Isocarboxazid • Mebanazine • Metfendrazine • Nialamide • Octamoxin • Phenelzine • Pheniprazine • Phenoxypropazine • Pivalylbenzhydrazine • Safrazine • Tranylcypromine; Reversible: Caroxazone • Paraxazone;MAOA-SelectiveIrreversible: Clorgiline; Reversible: Amiflamine • Bazinaprine • Befloxatone • Befol • Brofaromine • Cimoxatone • Esuperone • Harmala Alkaloids (Harmine, Harmaline, Tetrahydroharmine, Harman, Norharman, etc) • Methylene Blue • Metralindole • Minaprine • Moclobemide • Pirlindole • Sercloremine • Tetrindole • Toloxatone • Tyrima;MAOB-SelectiveIrreversible: Ladostigil • Mofegiline • Pargyline • Rasagiline • Selegiline; Reversible: Lazabemide • MilacemideAzapirones and other 5-HT1A receptor agonists Alnespirone • Aripiprazole • Befiradol • Buspirone • Eptapirone • Flesinoxan • Flibanserin • Gepirone • Ipsapirone • Oxaflozane • Tandospirone • Vilazodone • ZalospironeHypnotics/Sedatives (N05C) GABAA Agonists/PAMs Barbiturates: Allobarbital • Amobarbital • Aprobarbital • Barbital • Butabarbital • Butobarbital • Cyclobarbital • Ethallobarbital • Heptabarbital • Hexobarbital • Mephobarbital • Methohexital • Pentobarbital • Phenobarbital • Proxibarbal • Reposal • Secobarbital • Talbutal • Thiamylal • Thiopental • Vinbarbital • Vinylbital; Benzodiazepines: Brotizolam • Clonazepam • Cinolazepam • Climazolam • Doxefazepam • Estazolam • Flunitrazepam • Flurazepam • Flutoprazepam • Haloxazolam • Loprazolam • Lormetazepam • Midazolam • Nimetazepam • Nitrazepam • Quazepam • Temazepam • Triazolam; Carbamates: Carisoprodol • Ethinamate • Hexapropymate • Meprobamate • Methocarbamol • Procymate • Tybamate; Neuroactive Steroids: Acebrochol • Allopregnanolone • Alphadolone • Alphaxolone • Eltanolone • Ganaxolone • Hydroxydione • Minaxolone • Org 20599 • Org 21465 • Tetrahydrodeoxycorticosterone; Nonbenzodiazepines: CL-218,872 • Eszopiclone • Indiplon • JM-1232 • Lirequinil • Necopidem • Pazinaclone • ROD-188 • Saripidem • Suproclone • Suriclone • SX-3228 • U-89843A • U-90042 • Zaleplon • Zolpidem • Zopiclone; Phenols: Fospropofol • Propofol; Piperidinediones: Glutethimide • Methyprylon • Pyrithyldione • Piperidione; Quinazolinones: Afloqualone • Cloroqualone • Diproqualone • Etaqualone • Mebroqualone • Mecloqualone • Methaqualone • Methylmethaqualone • Nitromethaqualone; Others: 2-Methyl-2-butanol • Acetophenone • Acetylglycinamide chloral hydrate • Bromide (Lithium bromide, Potassium bromide, Sodium bromide) • Centalun • Chloral hydrate • Chloralose • Chloralodol • Clomethiazole • Dichloralphenazone • Ethanol (Alcohol) • Ethchlorvynol • Etomidate • Gaboxadol • Loreclezole • Methylpentynol • Metomidate • Paraldehyde • Petrichloral • Sulfonmethane • Trichloroethanol • Triclofos • Valerenic acid (Valerian)GABAB Agonists H1 Inverse agonists Antihistamines: Captodiame • Cyproheptadine • Dimenhydrinate • Diphenhydramine • Doxylamine • Hydroxyzine • Methapyrilene • Pheniramine • Promethazine • Propiomazine; Others: Tricyclic antidepressants (Amitriptyline, Doxepin, Trimipramine, etc.) • Tetracyclic antidepressants (Mianserin, Mirtazapine, etc.) • Typical antipsychotics (Chlorpromazine, Thioridazine, etc.) • Atypical antipsychotics (Olanzapine, Quetiapine, Risperidone, etc.)α1-Adrenergic Antagonists Mianserin • Niaprazine • Trazodone; Others: Tricyclic antidepressants (Amitriptyline, Doxepin, Trimipramine, etc.) • Typical antipsychotics (Chlorpromazine, Thioridazine, etc.) • Atypical antipsychotics (Olanzapine, Quetiapine, Risperidone, etc.)α2-Adrenergic Agonists 4-NEMD • Clonidine • Detomidine • Dexmedetomidine • Lofexidine • Medetomidine • Romifidine • Tizanidine • Xylazine5-HT2A Antagonists Eplivanserin • Niaprazine • Pruvanserin • Trazodone • Volinanserin; Others: Tricyclic antidepressants (Amitriptyline, Doxepin, Trimipramine, etc.) • Tetracyclic antidepressants (Mianserin, Mirtazapine, etc.) • Typical antipsychotics (Chlorpromazine, Thioridazine, etc.) • Atypical antipsychotics (Olanzapine, Quetiapine, Risperidone, etc.)Melatonin Agonists Orexin Antagonists Others Acecarbromal • Apronal • Bromisoval • Cannabidiol (Cannabis) • Carbromal • Embutramide • Evoxine • Fenadiazole • Gabapentin • Kavalactones (Kava) • Mephenoxalone • Opiates/Opioids (Hydrocodone, Morphine (Opium), etc.) • Passion flower • Scopolamine (Mandrake) • ValnoctamideMelatonergics Receptor
ligandsAfobazole • LuzindoleEnzyme
inhibitorsAANAT inhibitorsASMT inhibitorsOthers Ferrous Iron (Fe2+) • Magnesium (Mg2+) • S-Adenosyl-L-methionine • Tetrahydrobiopterin • Vitamin B3 (Niacin, nicotinamide → NADPH) • Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine, Pyridoxamine, Pyridoxal → Pyridoxal phosphate) • Vitamin B9 (Folic acid → Tetrahydrofolic acid) • Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid) • Zinc (Zn2+)Serotonergics 5-HT1 receptor ligands Agonists: Azapirones: Alnespirone • Binospirone • Buspirone • Enilospirone • Eptapirone • Gepirone • Ipsapirone • Perospirone • Revospirone • Tandospirone • Tiospirone • Umespirone • Zalospirone; Antidepressants: Etoperidone • Nefazodone • Trazodone • Vortioxetine; Antipsychotics: Aripiprazole • Asenapine • Clozapine • Quetiapine • Ziprasidone; Ergolines: Dihydroergotamine • Ergotamine • Lisuride • Methysergide • LSD; Tryptamines: 5-CT • 5-MeO-DMT • 5-MT • Bufotenin • DMT • Indorenate • Psilocin • Psilocybin; Others: 8-OH-DPAT • Adatanserin • Befiradol • BMY-14802 • Cannabidiol • Dimemebfe • Ebalzotan • Eltoprazine • F-11,461 • F-12,826 • F-13,714 • F-14,679 • F-15,063 • F-15,599 • Flesinoxan • Flibanserin • Lesopitron • LY-293,284 • LY-301,317 • MKC-242 • NBUMP • Osemozotan • Oxaflozane • Pardoprunox • Piclozotan • Rauwolscine • Repinotan • Roxindole • RU-24,969 • S 14,506 • S-14,671 • S-15,535 • Sarizotan • SSR-181,507 • Sunepitron • U-92,016-A • Urapidil • Vilazodone • Xaliproden • Yohimbine
Antagonists: Antipsychotics: Iloperidone • Risperidone • Sertindole; Beta blockers: Alprenolol • Cyanopindolol • Iodocyanopindolol • Oxprenolol • Pindobind • Pindolol • Propranolol • Tertatolol; Others: AV965 • BMY-7,378 • CSP-2503 • Dotarizine • Flopropione • GR-46611 • Isamoltane • Lecozotan • Mefway • Metitepine/Methiothepin • MPPF • NAN-190 • PRX-00023 • Robalzotan • S-15535 • SB-649,915 • SDZ 216-525 • Spiperone • Spiramide • Spiroxatrine • UH-301 • WAY-100,135 • WAY-100,635 • XylamidineAgonists: Lysergamides: Dihydroergotamine • Ergotamine • Methysergide; Piperazines: Eltoprazine • TFMPP; Triptans: Avitriptan • Eletriptan • Sumatriptan • Zolmitriptan; Tryptamines: 5-CT • 5-MT; Others: CGS-12066A • CP-93,129 • CP-94,253 • CP-135,807 • RU-24,969
Antagonists: Lysergamides: Metergoline; Others: AR-A000002 • Elzasonan • GR-127,935 • Isamoltane • Metitepine/Methiothepin • SB-216,641 • SB-224,289 • SB-236,057 • YohimbineAgonists: Lysergamides: Dihydroergotamine • Methysergide; Triptans: Almotriptan • Avitriptan • Eletriptan • Frovatriptan • Naratriptan • Rizatriptan • Sumatriptan • Zolmitriptan; Tryptamines: 5-CT • 5-Ethyl-DMT • 5-MT • 5-(Nonyloxy)tryptamine; Others: CP-135,807 • CP-286,601 • GR-46611 • L-694,247 • L-772,405 • PNU-109,291 • PNU-142,633
Antagonists: Lysergamides: Metergoline; Others: Alniditan • BRL-15,572 • Elzasonan • GR-127,935 • Ketanserin • LY-310,762 • LY-367,642 • LY-456,219 • LY-456,220 • Metitepine/Methiothepin • Ritanserin • Yohimbine • ZiprasidoneAgonists: Lysergamides: Methysergide; Triptans: Eletriptan; Tryptamines: BRL-54443 • Tryptamine
Antagonists: Metitepine/MethiothepinAgonists: Triptans: Eletriptan • Naratriptan • Sumatriptan; Tryptamines: 5-MT; Others: BRL-54443 • Lasmiditan • LY-334,370
Antagonists: Metitepine/Methiothepin5-HT2 receptor ligands Agonists: Lysergamides: ALD-52 • Ergometrine • Lisuride • LA-SS-Az • LSD • LSD-Pip • Lysergic acid 2-butyl amide • Lysergic acid 3-pentyl amide • Methysergide; Phenethylamines: 25I-NBF • 25I-NBMD • 25I-NBOH • 25I-NBOMe • 2C-B • 2C-B-FLY • 2CB-Ind • 2C-C-NBOMe • 2C-E • 2C-I • 2C-TFM-NBOMe • 2C-T-2 • 2C-T-7 • 2C-T-21 • 2CBCB-NBOMe • 2CBFly-NBOMe • Bromo-DragonFLY • DOB • DOC • DOI • DOM • MDA • MDMA • Mescaline • TCB-2 • TFMFly; Piperazines: BZP • Quipazine • TFMPP; Tryptamines: 5-CT • 5-MeO-α-ET • 5-MeO-α-MT • 5-MeO-DET • 5-MeO-DiPT • 5-MeO-DMT • 5-MeO-DPT • 5-MT • α-ET • α-Methyl-5-HT • α-MT • Bufotenin • DET • DiPT • DMT • DPT • Psilocin • Psilocybin; Others: AL-34662 • AL-37350A • Dimemebfe • Medifoxamine • Oxaflozane • PNU-22394 • RH-34
Antagonists: Atypical antipsychotics: Amperozide • Aripiprazole • Carpipramine • Clocapramine • Clozapine • Gevotroline • Iloperidone • Melperone • Mosapramine • Olanzapine • Paliperidone • Pimozide • Quetiapine • Risperidone • Sertindole • Ziprasidone • Zotepine; Typical antipsychotics: Loxapine • Pipamperone; Antidepressants: Amitriptyline • Amoxapine • Aptazapine • Etoperidone • Mianserin • Mirtazapine • Nefazodone • Teniloxazine • Trazodone; Others: 5-I-R91150 • AC-90179 • Adatanserin • Altanserin • AMDA • APD-215 • Blonanserin • Cinanserin • CSP-2503 • Cyproheptadine • Deramciclane • Dotarizine • Eplivanserin • Esmirtazapine • Fananserin • Flibanserin • Ketanserin • KML-010 • Lubazodone • Mepiprazole • Metitepine/Methiothepin • Nantenine • Pimavanserin • Pizotifen • Pruvanserin • Rauwolscine • Ritanserin • S-14,671 • Sarpogrelate • Setoperone • Spiperone • Spiramide • SR-46349B • Volinanserin • Xylamidine • YohimbineAgonists: Oxazolines: 4-Methylaminorex • Aminorex; Phenethylamines: Chlorphentermine • Cloforex • DOB • DOC • DOI • DOM • Fenfluramine • MDA • MDMA • Norfenfluramine; Tryptamines: 5-CT • 5-MT • α-Methyl-5-HT; Others: BW-723C86 • Cabergoline • mCPP • Pergolide • PNU-22394 • Ro60-0175
Antagonists: Agomelatine • Asenapine • EGIS-7625 • Ketanserin • Lisuride • LY-272,015 • Metitepine/Methiothepin • PRX-08066 • Rauwolscine • Ritanserin • RS-127,445 • Sarpogrelate • SB-200,646 • SB-204,741 • SB-206,553 • SB-215,505 • SB-221,284 • SB-228,357 • SDZ SER-082 • Tegaserod • YohimbineAgonists: Phenethylamines: 2C-B • 2C-E • 2C-I • 2C-T-2 • 2C-T-7 • 2C-T-21 • DOB • DOC • DOI • DOM • MDA • MDMA • Mescaline; Piperazines: Aripiprazole • mCPP • TFMPP; Tryptamines: 5-CT • 5-MeO-α-ET • 5-MeO-α-MT • 5-MeO-DET • 5-MeO-DiPT • 5-MeO-DMT • 5-MeO-DPT • 5-MT • α-ET • α-Methyl-5-HT • α-MT • Bufotenin • DET • DiPT • DMT • DPT • Psilocin • Psilocybin; Others: A-372,159 • AL-38022A • CP-809,101 • Dimemebfe • Lorcaserin• Medifoxamine • MK-212 • Org 12,962 • ORG-37,684 • Oxaflozane • PNU-22394 • Ro60-0175 • Ro60-0213 • Vabicaserin • WAY-629 • WAY-161,503 • YM-348
Antagonists: Atypical antipsychotics: Clozapine • Iloperidone • Melperone • Olanzapine • Paliperidone • Pimozide • Quetiapine • Risperidone • Sertindole • Ziprasidone • Zotepine; Typical antipsychotics: Chlorpromazine • Loxapine • Pipamperone; Antidepressants: Agomelatine • Amitriptyline • Amoxapine • Aptazapine • Etoperidone • Fluoxetine • Mianserin • Mirtazapine • Nefazodone • Nortriptyline • Tedatioxetine • Trazodone; Others: Adatanserin • Cinanserin • Cyproheptadine • Deramciclane • Dotarizine • Eltoprazine • Esmirtazapine • FR-260,010 • Ketanserin • Ketotifen • Latrepirdine • Metitepine/Methiothepin • Methysergide • Pizotifen • Ritanserin • RS-102,221 • S-14,671 • SB-200,646 • SB-206,553 • SB-221,284 • SB-228,357 • SB-242,084 • SB-243,213 • SDZ SER-082 • Xylamidine5-HT3, 5-HT4, 5-HT5, 5-HT6, 5-HT7 ligands Agonists: Piperazines: BZP • Quipazine; Tryptamines: 2-Methyl-5-HT • 5-CT; Others: Chlorophenylbiguanide • Butanol • Ethanol • Halothane • Isoflurane • RS-56812 • SR-57,227 • SR-57,227-A • Toluene • Trichloroethane • Trichloroethanol • Trichloroethylene • YM-31636
Antagonists: Antiemetics: AS-8112 • Alosetron • Azasetron • Batanopride • Bemesetron • Cilansetron • Dazopride • Dolasetron • Granisetron • Lerisetron • Ondansetron • Palonosetron • Ramosetron • Renzapride • Tropisetron • Zacopride • Zatosetron; Atypical antipsychotics: Clozapine • Olanzapine • Quetiapine; Tetracyclic antidepressants: Amoxapine • Mianserin • Mirtazapine; Others: CSP-2503 • ICS-205,930 • MDL-72,222 • Memantine • Nitrous Oxide • Ricasetron • Sevoflurane • Tedatioxetine • Thujone • Vortioxetine • XenonAgonists: Gastroprokinetic Agents: Cinitapride • Cisapride • Dazopride • Metoclopramide • Mosapride • Prucalopride • Renzapride • Tegaserod • Velusetrag • Zacopride; Others: 5-MT • BIMU8 • CJ-033,466 • PRX-03140 • RS-67333 • RS-67506 • SL65.0155 • Antagonists: GR-113,808 • GR-125,487 • L-Lysine • Piboserod • RS-39604 • RS-67532 • SB-203,186 • SB-204,070Agonists: Lysergamides: Ergotamine • LSD; Tryptamines: 5-CT; Others: Valerenic Acid
Antagonists: Asenapine • Latrepirdine • Metitepine/Methiothepin • Ritanserin • SB-699,551
* Note that the 5-HT5B receptor is not functional in humans.Agonists: Lysergamides: Dihydroergotamine • Ergotamine • Lisuride • LSD • Mesulergine • Metergoline • Methysergide; Tryptamines: 2-Methyl-5-HT • 5-BT • 5-CT • 5-MT • Bufotenin • E-6801 • E-6837 • EMD-386,088 • EMDT • LY-586,713 • Tryptamine; Others: WAY-181,187 • WAY-208,466
Antagonists: Antidepressants: Amitriptyline • Amoxapine • Clomipramine • Doxepin • Mianserin • Nortriptyline; Atypical antipsychotics: Aripiprazole • Asenapine • Clozapine • Fluperlapine • Iloperidone • Olanzapine • Tiospirone; Typical antipsychotics: Chlorpromazine • Loxapine; Others: BGC20-760 • BVT-5182 • BVT-74316 • Cerlapirdine • EGIS-12,233 • GW-742,457 • Ketanserin • Latrepirdine • Lu AE58054 • Metitepine/Methiothepin • MS-245 • PRX-07034 • Ritanserin • Ro04-6790 • Ro 63-0563 • SB-258,585 • SB-271,046 • SB-357,134 • SB-399,885 • SB-742,457Agonists: Lysergamides: LSD; Tryptamines: 5-CT • 5-MT • Bufotenin; Others: 8-OH-DPAT • AS-19 • Bifeprunox • E-55888 • LP-12 • LP-44 • RU-24,969 • Sarizotan
Antagonists: Lysergamides: 2-Bromo-LSD • Bromocriptine • Dihydroergotamine • Ergotamine • Mesulergine • Metergoline • Methysergide; Antidepressants: Amitriptyline • Amoxapine • Clomipramine • Imipramine • Maprotiline • Mianserin; Atypical antipsychotics: Amisulpride • Aripiprazole • Clozapine • Olanzapine • Risperidone • Sertindole • Tiospirone • Ziprasidone • Zotepine; Typical antipsychotics: Chlorpromazine • Loxapine; Others: Butaclamol • EGIS-12,233 • Ketanserin • LY-215,840 • Metitepine/Methiothepin • Pimozide • Ritanserin • SB-258,719 • SB-258,741 • SB-269,970 • SB-656,104 • SB-656,104-A • SB-691,673 • SLV-313 • SLV-314 • Spiperone • SSR-181,507Reuptake inhibitors Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): Alaproclate • Citalopram • Dapoxetine • Desmethylcitalopram • Desmethylsertraline • Escitalopram • Femoxetine • Fluoxetine • Fluvoxamine • Indalpine • Ifoxetine • Litoxetine • Lubazodone • Panuramine • Paroxetine • Pirandamine • RTI-353 • Seproxetine • Sertraline • Tedatioxetine • Vilazodone • Vortioxetine • Zimelidine; Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs): Bicifadine • Desvenlafaxine • Duloxetine • Eclanamine • Levomilnacipran • Milnacipran • Sibutramine • Venlafaxine; Serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors (SNDRIs): Brasofensine • Diclofensine • DOV-102,677 • DOV-21,947 • DOV-216,303 • NS-2359 • SEP-225289 • SEP-227,162 • Tesofensine; Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs): Amitriptyline • Butriptyline • Cianopramine • Clomipramine • Desipramine • Dosulepin • Doxepin • Imipramine • Lofepramine • Nortriptyline • Pipofezine • Protriptyline • Trimipramine; Tetracyclic antidepressants (TeCAs): Amoxapine; Piperazines: Nefazodone • Trazodone; Antihistamines: Brompheniramine • Chlorphenamine • Diphenhydramine • Mepyramine/Pyrilamine • Pheniramine • Tripelennamine; Opioids: Pethidine • Methadone • Propoxyphene; Others: Cocaine • CP-39,332 • Cyclobenzaprine • Dextromethorphan • Dextrorphan • EXP-561 • Fezolamine • Mesembrine • Nefopam • PIM-35 • Pridefine • Roxindole • SB-649,915 • ZiprasidoneReleasing agents Aminoindanes: 5-IAI • AMMI • ETAI • MDAI • MDMAI • MMAI • TAI; Aminotetralins: 6-CAT • 8-OH-DPAT • MDAT • MDMAT; Oxazolines: 4-Methylaminorex • Aminorex • Clominorex • Fluminorex; Phenethylamines (also Amphetamines, Cathinones, Phentermines, etc): 2-Methyl-MDA • 4-CAB • 4-FA • 4-FMA • 4-HA • 4-MTA • 5-APDB • 5-Methyl-MDA • 6-APDB • 6-Methyl-MDA • AEMMA • Amiflamine • BDB • BOH • Brephedrone • Butylone • Chlorphentermine • Cloforex • Amfepramone • Metamfepramone • DCA • DFMDA • DMA • DMMA • EBDB • EDMA • Ethylone • Etolorex • Fenfluramine (Dexfenfluramine) • Flephedrone • IAP • IMP • Lophophine • MBDB • MDA • MDEA • MDHMA • MDMA • MDMPEA • MDOH • MDPEA • Mephedrone • Methedrone • Methylone • MMA • MMDA • MMDMA • MMMA • NAP • Norfenfluramine • 4-TFMA • pBA • pCA • pIA • PMA • PMEA • PMMA • TAP; Piperazines: 2C-B-BZP • 2-BZP • 3-MeOPP • BZP • DCPP • MBZP • mCPP • MDBZP • MeOPP • Mepiprazole • pCPP • pFPP • pTFMPP • TFMPP; Tryptamines: 4-Methyl-αET • 4-Methyl-αMT • 5-CT • 5-MeO-αET • 5-MeO-αMT • 5-MT • αET • αMT • DMT • Tryptamine (itself); Others: Indeloxazine • Tramadol • ViqualineEnzyme inhibitors Nonselective: Benmoxin • Caroxazone • Echinopsidine • Furazolidone • Hydralazine • Indantadol • Iproclozide • Iproniazid • Isocarboxazid • Isoniazid • Linezolid • Mebanazine • Metfendrazine • Nialamide • Octamoxin • Paraxazone • Phenelzine • Pheniprazine • Phenoxypropazine • Pivalylbenzhydrazine • Procarbazine • Safrazine • Tranylcypromine; MAO-A Selective: Amiflamine • Bazinaprine • Befloxatone • Befol • Brofaromine • Cimoxatone • Clorgiline • Esuprone • Harmala alkaloids (Harmine, Harmaline, Tetrahydroharmine, Harman, Norharman, etc) • Methylene Blue • Metralindole • Minaprine • Moclobemide • Pirlindole • Sercloremine • Tetrindole • Toloxatone • TyrimaOthers Ferrous iron (Fe2+) • Magnesium (Mg2+) • Tetrahydrobiopterin • Vitamin B3 (Niacin, Nicotinamide → NADPH) • Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine, Pyridoxamine, Pyridoxal → Pyridoxal phosphate) • Vitamin B9 (Folic Acid → Tetrahydrofolic acid) • Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid) • Zinc (Zn2+)OthersCategories:- Antidepressants
- 5-HT2C antagonists
- Acetamides
- Naphthol ethers
- Servier
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.