- Ethchlorvynol
-
Ethchlorvynol 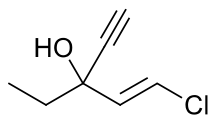
Systematic (IUPAC) name 1-chloro-3-ethylpent-1-en-4-yn-3-ol Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status Schedule IV[1] Routes Oral Pharmacokinetic data Protein binding 35–50% Identifiers CAS number 113-18-8 
ATC code N05CM08 PubChem CID 5281077 DrugBank DB00189 ChemSpider 4444534 
UNII 6EIM3851UZ 
KEGG D00704 
ChEMBL CHEMBL591 
Chemical data Formula C7H9ClO Mol. mass 144.598 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Ethchlorvynol is a sedative and hypnotic medication developed by Pfizer in the 1950s[2]. It has been used to treat insomnia, but has been largely superseded and is only offered where an intolerance or allergy to other drugs exists.
Along with expected sedative effects of relaxation and drowsiness, ethchlorvynol can cause skin rashes, faintness, restlessness and euphoria. Early adjustment side effects can include nausea and vomiting, numbness, blurred vision, stomach pains and temporary dizziness. An overdose is marked by confusion, fever, peripheral numbness and weakness, reduced coordination and muscle control, slurred speech, reduced heartbeat.
It is addictive and after prolonged use can cause withdrawal symptoms including convulsions, hallucinations, and memory loss. Due to these problems, it is unusual for ethchlorvynol to be prescribed for periods exceeding seven days. During the late 1970s, ethchlorvynol was sometimes over-prescribed causing a minor epidemic of persons who became addicted to this powerful drug. Occasional deaths would occur when addicted persons would try to inject the drug directly into a vein or an artery. Ethchlorvynol is not compatible with intravenous injection and serious injury or death can occur when it is used in this manner.
Ethchlorvynol is a member of the class of sedative-hypnotic tertiary carbinols, which includes methylparafynol and tert-amyl alcohol. It is not a barbituric acid derivative. The systematic name of ethchlorvynol is usually given as ethyl 2-chlorovinyl ethynyl carbinol or 1-chloro-3-ethyl-1-penten-4-yl-3-ol. Its empirical formula is C7H9ClO. In the United States Abbott Laboratories used to sell it under the tradename Placidyl. During their heyday, they were known on the street as "jelly-bellies".[3] Since Abbott and Banner Pharmacaps, which manufactured the generic version, discontinued production in 1999, ethchlorvynol is no longer available in the United States.

Production
Ethchlorvynol is synthesized by the reaction of lithium acetylide with 1-chloro-1-penten-3-one in liquid ammonia, followed by acidic work-up.[4][5]

Notes
- ^ Green List: Annex to the annual statistical report on psychotropic substances (form P) 23rd edition. August 2003. International Narcotics Board, Vienna International Centre. Accessed 1 September 2005 (UTC)
- ^ US Patent 2746900 – Hypnotic Agent and Method of Making the Same
- ^ "William H. Rehnquist: Supreme Court stoner". CelebStoner. 4 January 2007. http://www.celebstoner.com/2007010578/news/celebstoner-news/william-h-rehnquist-supreme-court-stoner.html. Retrieved 2009-09-04.[dead link]
- ^ A. Bavley, W.M. McLamore, U.S. Patent 2,746,900 (1956)
- ^ McLamore, W. M.; P'an, S. Y.; Bavley, A. (1955). Journal of Organic Chemistry 20: 109. doi:10.1021/jo01119a018.
References
- Electronic Orange Book: Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations Food and Drug Administration. Accessed 12 December 2005 (UTC)
Categories:- Sedatives
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
