- Glutethimide
-
Glutethimide 
Systematic (IUPAC) name 3-ethyl-3-phenyl-piperidine-2,6-dione Clinical data Pregnancy cat. C: (United States) Legal status Schedule II (US)
Schedule III internationalRoutes oral Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability Variable Metabolism Hepatic Half-life 10-12 hours Excretion Renal:2% Fecal:2% Identifiers CAS number 77-21-4 
ATC code N05CE01 PubChem CID 3487 DrugBank DB01437 ChemSpider 3367 
UNII C8I4BVN78E 
KEGG D00532 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1102 
Chemical data Formula C13H15NO2 Mol. mass 217.264 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Glutethimide is a hypnotic sedative that was introduced in 1954 as a safe alternative to barbiturates to treat insomnia. Before long, however, it had become clear that glutethimide was just as likely to cause addiction and caused similarly severe withdrawal symptoms. Doriden is the brand-name version of the drug; both the generic and brand-name forms are rarely prescribed today.

Contents
Long term use
In long term use rebound effects , which resembled those seen in withdrawal, have anecdotally been described in patients, who were still taking a stable dose of the drug. The symptoms included delirium, hallucinosis, convulsions and fever.[1]
Recreational use
Glutethimide is a CYP2D6 enzyme inducer. When taken with codeine, it enables the body to convert higher amounts of the codeine (higher than the average 5 - 10%) to morphine. The general sedative effect also adds to the effect of the combination.[2][3]
Legal status
Glutethimide is a Schedule II drug under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances.[4] It was originally a Schedule III drug in the United States under the Controlled Substances Act, but in 1991 it was upgraded to Schedule II[5], after it was discovered that misuse combined with codeine increased the effect of the codeine and deaths had resulted from the combination.[6][7]
Chemistry
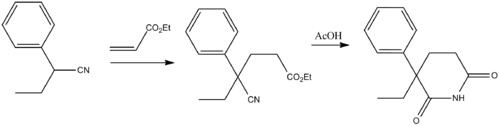
Glutethimide (2-ethyl-2-phenylgutarimide) is synthesized by addition of 2-phenylbutyronitrile to the methylacrylate (Michael reaction), and the subsequent alkaline hydrolysis of the nitrile group in the obtained compound into an amide group, and the subsequent acidic cyclization of the product into the desired glutethimide.[8]
See also
- Aminoglutethimide
- Piperidione
- Methyprylone
- Pyrithyldione
References
- ^ Cookson, J. C. (1995). "Rebound exacerbation of anxiety during prolonged tranquilizer ingestion". Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine 88 (9): 544. PMC 1295346. PMID 7562864. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1295346.
- ^ Popa, D.; Loghin, F.; Imre, S.; Curea, E. (2003). "The study of codeine-gluthetimide pharmacokinetic interaction in rats". Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis 32 (4–5): 867–877. PMID 12899973.
- ^ Khajawall, A. M.; Sramek Jr, J. J.; Simpson, G. M. (1982). "'Loads' Alert". The Western journal of medicine 137 (2): 166–168. PMC 1274052. PMID 7135952. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1274052.
- ^ "List of psychotropic substances under international control" (pdf). INCB. http://www.incb.org/pdf/e/list/green.pdf.
- ^ "Code of Federal Regulations Section 1308.12 Schedule II". DEA. http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/21cfr/cfr/1308/1308_12.htm.
- ^ Havier, R. G.; Lin, R. (1985). "Deaths as a result of a combination of codeine and glutethimide". Journal of forensic sciences 30 (2): 563–566. PMID 3998703.
- ^ Feuer, E.; French, J. (1984). "Descriptive epidemiology of mortality in New Jersey due to combinations of codeine and glutethimide". American journal of epidemiology 119 (2): 202–207. PMID 6695899.
- ^ Tagmann, E.; Sury, E.; Hoffmann, K. (1952). "Über Alkylenimin-Derivate. 2. Mitteilung". Helvetica Chimica Acta 35: 1541–1548. doi:10.1002/hlca.19520350516.
DE patent 950193, Hoffmann,K. & Tagmann,E., "Verfahren zur Herstellung neuer Dioxopiperidine"
US patent 2673205, Hoffmann,K. & Tagmann,E., "3-disubstituted dioxopiperidines and the manufacture thereof"
F. Salmon-Legagneur, C. Neveu, Compt. Rend., 234, 1060 (1952).
F. Salmon-Legagneur, C. Neveu, Bull. Soc. Chim. France, 70 (1953).
GABAergics Receptor
ligandsAgonists: Main site: Bamaluzole • Gaboxadol • Ibotenic acid • Isoguvacine • Isonipecotic acid • Muscimol (Amanita Muscaria) • Progabide • SL 75102 • Thiomuscimol • Tolgabide; Positive allosteric modulators: Barbiturates • Benzodiazepines • Carbamates • Chlormezanone • Clomethiazole • Ethanol (Alcohol) • Etomidate • Kavalactones (Kava) • Loreclezole • Metomidate • Neuroactive steroids • Nonbenzodiazepines (β-Carbolines, Cyclopyrrolones, Imidazopyridines, Pyrazolopyrimidines, etc.) • Phenols • Piperidinediones • Propanidid • Pyrazolopyridines • Quinazolinones • ROD-188 • Skullcap • Stiripentol • Valerenic acid (Valerian)
Antagonists: Main site: Bicuculline • Gabazine • Pitrazepin; Negative allosteric modulators: α5IA • Bilobalide • Cicutoxin • Cyclothiazide • DMCM • Flumazenil • Flurothyl • Furosemide • L-655,708 • Oenanthotoxin • Penicillin • Pentylenetetrazol • Picrotoxin • PWZ-029 • Ro15-4513 • Sarmazenil • Suritozole • Thujone (Absinthe) • Thiocolchicoside • ZK-93426
* See Template:GABAAergics for a full list of GABAA positive allosteric modulators.Agonists: Main site: CACA • CAMP • GABOB • N(4)-chloroacetylcytosine arabinoside • Progabide • Tolgabide
Antagonists: Main site: Bilobalide • TPMPAReuptake
inhibitorsPlasmalemmalGAT inhibitorsCI-966 • Deramciclane • EF-1502 • Gabaculine • Guvacine • Nipecotic acid • NNC 05-2090 • SKF-89976A • SNAP-5114 • TiagabineEnzyme
inhibitorsGAD inhibitorsAllylglycineGABA-T inhibitors3-Hydrazinopropionic acid • Aminooxyacetic acid • Gabaculine • Isoniazid • Phenelzine • Phenylethylidenehydrazine • Sodium valproate • Valnoctamide • Valproate pivoxil • Valproate semisodium (Divalproex sodium) • Valproic acid • Valpromide • VigabatrinOthers Glutamate • GlutamineOthersCategories:- Sedatives
- Glutarimides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.