- Promethazine
-
Promethazine 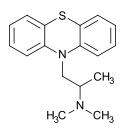
Systematic (IUPAC) name (RS)-N,N-dimethyl-1-(10H-phenothiazin-10-yl)propan-2-amine Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a682284 Pregnancy cat. C(AU) C(US) Legal status P (UK) ℞-only (US)
(injection POM(UK))Routes Oral, rectal, IV, IM, topical Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability 88% absorbed but after first-pass metabolism reduced to 25% absolute bioavailability Protein binding 93% Metabolism Hepatic glucuronidation and sulfoxidation Half-life 16-19 hours Excretion Renal and biliary Identifiers CAS number 60-87-7 
58-33-3 (hydrochloride)ATC code D04AA10 R06AD02, R06AD05 PubChem CID 4926 DrugBank APRD00602 ChemSpider 4759 
UNII FF28EJQ494 
KEGG D00494 
ChEBI CHEBI:8461 
ChEMBL CHEMBL643 
Chemical data Formula C17H20N2S Mol. mass 284.42 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Promethazine is a first-generation H1 receptor antagonist of the phenothiazine chemical class used medically as an antihistamine. It has a strong sedative effect and in some countries is prescribed for insomnia when benzodiazepines are contraindicated. It is available over the counter in the United Kingdom, Australia, Switzerland, and many other countries, but by prescription in the United States (brand names Phenergan, Promethegan, Romergan, Fargan, Farganesse, Prothiazine, Avomine, Atosil, Receptozine, Lergigan, and Sominex in the UK).[1]
Contents
Chemistry
 The enantiomers of promethazine
The enantiomers of promethazine
Chemically, promethazine hydrochloride appears as a white to faint yellow crystalline powder that is practically odorless. Slow oxidation may occur upon prolonged exposure to air usually causing blue discoloration. Promethazine as the hydrochloride salt is freely soluble in water and somewhat soluble in alcohol. Promethazine is a chiral compound, occurring as a mixture of enantiomers (pictured).[2]
Promethazine, 10-(2-dimethylaminopropyl)phenothiazine, is synthesized by alkylating phenothiazine with 1-dimethylamino-2-propylchloride.
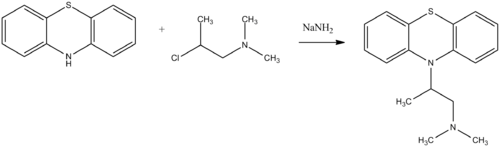
- P. Charpentier, U.S. Patent 2,530,451 (1950).
- S.B. Sidney, J.A. Nicholson, U.S. Patent 2,607,773 (1952).
Indications
- As a sedative[3]
- For preoperative sedation and to counteract postnarcotic nausea[3]
- As antiallergic medication to combat hay fever (allergic rhinitis), etc. To treat allergic reactions it can be given alone or in combination with oral decongestants like pseudoephedrine.[3]
- As an adjunct treatment for anaphylactoid conditions (IM/IV route preferred)[3]
- Together with codeine or dextromethorphan against cough
- As a motion sickness or seasickness remedy when used with Ephedrine or Pseudoephedrine[3]
- To combat moderate to severe morning sickness and hyperemesis gravidarum. In the UK promethazine is drug of first choice, being preferred as an older drug with which there is a greater experience of use in pregnancy (second line being metoclopramide or prochlorperazine).[4]
- Previously it was used as an antipsychotic,[5] although it is generally not administered for this purpose now; promethazine has only approximately 1/10 of the antipsychotic strength of chlorpromazine.
- Also used to potentiate any opiates. Commonly combined with pethidine (AKA, meperidine, or Demerol) in a brand called Mepergan, a meperidine/promethazine combination. Also frequently used in conjunction with codeine, in a syrup form. The combination leads to more powerful euphoric effects than with codeine alone.
Mechanism of action
- Promethazine is a phenothiazine derivative that competitively and potently blocks histamine H1 receptors without blocking the secretion of histamine. It also is a moderate muscarinic acetylcholine antagonist and a very weak dopamine antagonist.[6][7]
- It has sedative, anti-motion-sickness, anti-emetic, and anti-cholinergic effects.[citation needed]
Side effects
Some common side effects include:
- Tardive dyskinesia
- Confusion in the elderly
- Drowsiness, dizziness, fatigue, more rarely vertigo
- Dry mouth
- Respiratory depression in patients under age of 2 and in those with severely compromised pulmonal function
- Constipation
- Chest Discomfort/Pressure. (typically in cases when patient is already taking medication for high blood pressure)
- Euphoria (very rare, except with high IV doses and/or coadministration with opioids/CNS depressants)
- Akathisia [8]
- Paresthesia
- Short temper/Irritability
Extremely rare side effects include:
- Seizures
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
IV administration: Dilute with 0.9% NaCl or D5W. CONCENTRATION: Doses should not exceed a concentration of 25 mg/ml. Administer through a large-bore vein through a running IV line into the most distal port. Slight yellow color does not alter potency. Do not administer if precipitate is present. RATE: Administer each 25 mg slowly, over at least 10-15min. Rapid administration may produce a transient fall in blood pressure. [9] Serious complications including those listed above have resulted from improper parenteral administration, including those requiring surgical intervention and amputation.
Because of potential for more severe side effects, this drug is on the list to avoid in the elderly. (See NCQA’s HEDIS Measure: Use of High Risk Medications in the Elderly).
Product liability lawsuit
Main article: Wyeth v. LevineIn 2009, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled on a product liability case involving promethazine. Diana Levine, a woman suffering from a migraine, was administered Wyeth's Phenergan via IV push. The drug was injected improperly resulting in gangrene and subsequent amputation of her right forearm below the elbow. A state jury awarded her $6 million in punitive damages.
The case was appealed to the Supreme Court on grounds of federal preemption and substantive due process.[10] The Supreme Court upheld the lower courts' rulings stating that "Wyeth could have unilaterally added a stronger warning about IV-push administration" without acting in opposition to federal law.[11] In effect, this means that drug manufacturers can be held liable for injuries if warnings of potential adverse effects (approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, "FDA") are deemed insufficient by state courts.
On September 9, 2009, the FDA made the decision that a black box warning for injection be put on promethazine stating the contraindication for subcutaneous administration. The preferred administrative route is intramuscular (IM) which reduces risk of surrounding muscle and tissue damage [12]
References
- ^ RxList: Promethazine
- ^ http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic/phenergan.htm RxList: Promethazine Description
- ^ a b c d e RxList Indications for Promethazine.
- ^ British National Formulary (March 2001). "4.6 Drugs used in nausea and Vertigo - Vomiting of pregnancy". BNF (45 ed.)..
- ^ [1].
- ^ David J. McCann and Brett Roth, Toxicity, Antihistamine, eMedicine Toxicology, updated June 21, 2007
- ^ http://www.mywhatever.com/cifwriter/library/70/4938.html
- ^ Cordingley Neurology
- ^ Davis Drug Guide for Nurses Eleventh Edition pgs. 1017-1020
- ^ Liptak, Adam (2001-09-18). "Drug Label, Maimed Patient and Crucial Test for Justices". The New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2008/09/19/us/19scotus.html?n=Top/Reference/Times%20Topics/Organizations/S/Supreme%20Court&_r=1&adxnnl=1&oref=slogin&adxnnlx=1225505895-T2aivHeTdvJTT7b+uEsK1Q. Retrieved 2008-10-31.
- ^ Stout, David (2009-03-04). "Drug Approval Is Not a Shield From Lawsuits, Justices Rule". The New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2009/03/05/washington/05scotus.html. Retrieved 2009-03-04.
- ^ http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/PostmarketDrugSafetyInformationforPatientsandProviders/DrugSafetyInformationforHeathcareProfessionals/ucm182169.htm
See Also
- Purple drank, a recreational drug concoction containing Promethazine.
External links
- "Promethazine". U.S. National Library of Medicine and National Institutes of Health. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/medmaster/a682284.html.
Antiemetics (A04) 5-HT3 Antagonists Alosetron • Azasetron • Bemesetron • Cilansetron • Clozapine • Dazopride • Dolasetron • Granisetron • Lerisetron • Metoclopramide • Mianserin • Mirtazapine • Olanzapine • Ondansetron • Palonosetron • Ramosetron • Ricasetron • Tropisetron • ZatosetronCB1 Agonists (Cannabinoids) D2/D3 Antagonists H1 Antagonists (Antihistamines) mACh Antagonists (Anticholinergics) NK1 Antagonists Others Antipruritics (D04) Antihistamines for topical use Thonzylamine - Mepyramine - Thenalidine - Tripelennamine - Chloropyramine - Promethazine - Tolpropamine - Dimetindene - Clemastine - Bamipine - Isothipendyl - Diphenhydramine - ChlorphenoxamineAnesthetics for topical use Cholinergics Receptor ligands Agonists: 77-LH-28-1 • AC-42 • AC-260,584 • Aceclidine • Acetylcholine • AF30 • AF150(S) • AF267B • AFDX-384 • Alvameline • AQRA-741 • Arecoline • Bethanechol • Butyrylcholine • Carbachol • CDD-0034 • CDD-0078 • CDD-0097 • CDD-0098 • CDD-0102 • Cevimeline • cis-Dioxolane • Ethoxysebacylcholine • LY-593,039 • L-689,660 • LY-2,033,298 • McNA343 • Methacholine • Milameline • Muscarine • NGX-267 • Ocvimeline • Oxotremorine • PD-151,832 • Pilocarpine • RS86 • Sabcomeline • SDZ 210-086 • Sebacylcholine • Suberylcholine • Talsaclidine • Tazomeline • Thiopilocarpine • Vedaclidine • VU-0029767 • VU-0090157 • VU-0152099 • VU-0152100 • VU-0238429 • WAY-132,983 • Xanomeline • YM-796
Antagonists: 3-Quinuclidinyl Benzilate • 4-DAMP • Aclidinium Bromide • Anisodamine • Anisodine • Atropine • Atropine Methonitrate • Benactyzine • Benzatropine (Benztropine) • Benzydamine • BIBN 99 • Biperiden • Bornaprine • CAR-226,086 • CAR-301,060 • CAR-302,196 • CAR-302,282 • CAR-302,368 • CAR-302,537 • CAR-302,668 • CS-27349 • Cyclobenzaprine • Cyclopentolate • Darifenacin • DAU-5884 • Dimethindene • Dexetimide • DIBD • Dicyclomine (Dicycloverine) • Ditran • EA-3167 • EA-3443 • EA-3580 • EA-3834 • Elemicin • Etanautine • Etybenzatropine (Ethylbenztropine) • Flavoxate • Himbacine • HL-031,120 • Ipratropium bromide • J-104,129 • Hyoscyamine • Mamba Toxin 3 • Mamba Toxin 7 • Mazaticol • Mebeverine • Methoctramine • Metixene • Myristicin • N-Ethyl-3-Piperidyl Benzilate • N-Methyl-3-Piperidyl Benzilate • Orphenadrine • Otenzepad • Oxybutynin • PBID • PD-102,807 • PD-0298029 • Phenglutarimide • Phenyltoloxamine • Pirenzepine • Piroheptine • Procyclidine • Profenamine • RU-47,213 • SCH-57,790 • SCH-72,788 • SCH-217,443 • Scopolamine (Hyoscine) • Solifenacin • Telenzepine • Tiotropium bromide • Tolterodine • Trihexyphenidyl • Tripitamine • Tropatepine • Tropicamide • WIN-2299 • Xanomeline • Zamifenacin; Others: 1st Generation Antihistamines (Brompheniramine, chlorphenamine, cyproheptadine, dimenhydrinate, diphenhydramine, doxylamine, mepyramine/pyrilamine, phenindamine, pheniramine, tripelennamine, triprolidine, etc) • Tricyclic Antidepressants (Amitriptyline, doxepin, trimipramine, etc) • Tetracyclic Antidepressants (Amoxapine, maprotiline, etc) • Typical Antipsychotics (Chlorpromazine, thioridazine, etc) • Atypical Antipsychotics (Clozapine, olanzapine, quetiapine, etc)Agonists: 5-HIAA • A-84,543 • A-366,833 • A-582,941 • A-867,744 • ABT-202 • ABT-418 • ABT-560 • ABT-894 • Acetylcholine • Altinicline • Anabasine • Anatoxin-a • AR-R17779 • Butyrylcholine • Carbachol • Cotinine • Cytisine • Decamethonium • Desformylflustrabromine • Dianicline • Dimethylphenylpiperazinium • Epibatidine • Epiboxidine • Ethanol • Ethoxysebacylcholine • EVP-4473 • EVP-6124 • Galantamine • GTS-21 • Ispronicline • Lobeline • MEM-63,908 (RG-3487) • Nicotine • NS-1738 • PHA-543,613 • PHA-709,829 • PNU-120,596 • PNU-282,987 • Pozanicline • Rivanicline • Sazetidine A • Sebacylcholine • SIB-1508Y • SIB-1553A • SSR-180,711 • Suberylcholine • TC-1698 • TC-1734 • TC-1827 • TC-2216 • TC-5214 • TC-5619 • TC-6683 • Tebanicline • Tropisetron • UB-165 • Varenicline • WAY-317,538 • XY-4083
Antagonists: 18-Methoxycoronaridine • α-Bungarotoxin • α-Conotoxin • Alcuronium • Amantadine • Anatruxonium • Atracurium • Bupropion (Amfebutamone) • Chandonium • Chlorisondamine • Cisatracurium • Coclaurine • Coronaridine • Dacuronium • Decamethonium • Dextromethorphan • Dextropropoxyphene • Dextrorphan • Diadonium • DHβE • Dimethyltubocurarine (Metocurine) • Dipyrandium • Dizocilpine (MK-801) • Doxacurium • Duador • Esketamine • Fazadinium • Gallamine • Hexafluronium • Hexamethonium (Benzohexonium) • Ibogaine • Isoflurane • Ketamine • Kynurenic acid • Laudexium (Laudolissin) • Levacetylmethadol • Malouetine • Mecamylamine • Memantine • Methadone • Methorphan (Racemethorphan) • Methyllycaconitine • Metocurine • Mivacurium • Morphanol (Racemorphanol) • Neramexane • Nitrous Oxide • Pancuronium • Pempidine • Pentamine • Pentolinium • Phencyclidine • Pipecuronium • Radafaxine • Rapacuronium • Rocuronium • Surugatoxin • Suxamethonium (Succinylcholine) • Thiocolchicoside • Toxiferine • Trimethaphan • Tropeinium • Tubocurarine • Vecuronium • XenonReuptake inhibitors PlasmalemmalCHT InhibitorsHemicholinium-3 (Hemicholine; HC3) • TriethylcholineVAChT InhibitorsEnzyme inhibitors ChAT inhibitors1-(-Benzoylethyl)pyridinium • 2-(α-Naphthoyl)ethyltrimethylammonium • 3-Chloro-4-stillbazole • 4-(1-Naphthylvinyl)pyridine • Acetylseco hemicholinium-3 • Acryloylcholine • AF64A • B115 • BETA • CM-54,903 • CatabolismAChE inhibitorsReversible: Carbamates: Aldicarb • Bendiocarb • Bufencarb • Carbaryl • Carbendazim • Carbetamide • Carbofuran • Chlorbufam • Chloropropham • Ethienocarb • Ethiofencarb • Fenobucarb • Fenoxycarb • Formetanate • Furadan • Ladostigil • Methiocarb • Methomyl • Miotine • Oxamyl • Phenmedipham • Pinmicarb • Pirimicarb • Propamocarb • Propham • Propoxur; Stigmines: Ganstigmine • Neostigmine • Phenserine • Physostigmine • Pyridostigmine • Rivastigmine; Others: Acotiamide • Ambenonium • Donepezil • Edrophonium • Galantamine • Huperzine A • Minaprine • Tacrine • Zanapezil
Irreversible: Organophosphates: Acephate • Azinphos-methyl • Bensulide • Cadusafos • Chlorethoxyfos • Chlorfenvinphos • Chlorpyrifos • Chlorpyrifos-Methyl • Coumaphos • Cyclosarin (GF) • Demeton • Demeton-S-Methyl • Diazinon • Dichlorvos • Dicrotophos • Diisopropyl fluorophosphate (Guthion) • Diisopropylphosphate • Dimethoate • Dioxathion • Disulfoton • EA-3148 • Echothiophate • Ethion • Ethoprop • Fenamiphos • Fenitrothion • Fenthion • Fosthiazate • GV • Isofluorophate • Isoxathion • Malaoxon • Malathion • Methamidophos • Methidathion • Metrifonate • Mevinphos • Monocrotophos • Naled • Novichok agent • Omethoate • Oxydemeton-Methyl • Paraoxon • Parathion • Parathion-Methyl • Phorate • Phosalone • Phosmet • Phostebupirim • Phoxim • Pirimiphos-Methyl • Sarin (GB) • Soman (GD) • Tabun (GA) • Temefos • Terbufos • Tetrachlorvinphos • Tribufos • Trichlorfon • VE • VG • VM • VR • VX; Others: Demecarium • Onchidal (Onchidella binneyi)BChE inhibitorsCymserine * Many of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitors listed above act as butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors.Others Choline (Lecithin) • Citicoline • Cyprodenate • Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE, deanol) • Glycerophosphocholine • Meclofenoxate (Centrophenoxine) • Phosphatidylcholine • Phosphatidylethanolamine • Phosphorylcholine • PirisudanolOthersAcetylcholine releasing agents: α-Latrotoxin • β-Bungarotoxin; Acetylcholine release inhibitors: Botulinum toxin (Botox); Acetylcholinesterase reactivators: Asoxime • Obidoxime • PralidoximeHistaminergics Receptor
ligandsAgonists: 2-Pyridylethylamine • Betahistine • Histamine • HTMT • UR-AK49
Antagonists: 1st generation: 4-Methyldiphenhydramine • Alimemazine • Antazoline • Azatadine • Bamipine • Benzatropine (Benztropine) • Bepotastine • Bromazine • Brompheniramine • Buclizine • Captodiame • Carbinoxamine • Chlorcyclizine • Chloropyramine • Chlorothen • Chlorphenamine • Chlorphenoxamine • Cinnarizine • Clemastine • Clobenzepam • Clocinizine • Cyclizine • Cyproheptadine • Dacemazine • Deptropine • Dexbrompheniramine • Dexchlorpheniramine • Dimenhydrinate • Dimetindene • Diphenhydramine • Diphenylpyraline • Doxylamine • Embramine • Etybenzatropine (Ethylbenztropine) • Etymemazine • Histapyrrodine • Homochlorcyclizine • Hydroxyethylpromethazine • Hydroxyzine • Isopromethazine • Isothipendyl • Meclozine • Mepyramine (Pyrilamine) • Mequitazine • Methafurylene • Methapyrilene • Methdilazine • Moxastine • Niaprazine • Orphenadrine • Oxatomide • Oxomemazine • Phenindamine • Pheniramine • Phenyltoloxamine • Pimethixene • Piperoxan • Promethazine • Propiomazine • Pyrrobutamine • Talastine • Thenalidine • Thenyldiamine • Thiazinamium • Thonzylamine • Tolpropamine • Tripelennamine • Triprolidine; 2nd generation: Acrivastine • Astemizole • Azelastine • Cetirizine • Clemizole • Clobenztropine • Ebastine • Emedastine • Epinastine • Ketotifen • Latrepirdine • Levocabastine • Loratadine • Mebhydrolin • Mizolastine • Olopatadine • Rupatadine • Setastine • Terfenadine; "3rd generation": Desloratadine • Fexofenadine • Levocetirizine; Miscellaneous: Tricyclic antidepressants (Amitriptyline, Doxepin, Trimipramine, etc) • Tetracyclic antidepressants (Mianserin, Mirtazapine, etc) • Serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitors (Trazodone, Nefazodone) • Typical antipsychotics (Chlorpromazine, Thioridazine, etc) • Atypical antipsychotics (Clozapine, Olanzapine, Quetiapine, etc)Agonists: Amthamine • Betazole • Dimaprit • Histamine • HTMT • Impromidine • UR-AK49
Antagonists: Burimamide • Cimetidine • Ebrotidine • Famotidine • Lafutidine • Lavoltidine/Loxtidine • Lupitidine • Metiamide • Niperotidine • Nizatidine • Oxmetidine • Ranitidine • RoxatidineAgonists: α-Methylhistamine • Cipralisant • Histamine • Imetit • Immepip • Immethridine • Methimepip • Proxyfan
Antagonists: A-349,821 • A-423,579 • ABT-239 • Betahistine • Burimamide • Ciproxifan • Clobenpropit • Conessine • GSK-189,254 • Impentamine • Iodophenpropit • JNJ-5,207,852 • MK-0249 • NNC-38-1,049 • PF-03654746 • Pitolisant • SCH-79,687 • Thioperamide • VUF-5,681Agonists: 4-Methylhistamine • Histamine • VUF-8,430
Antagonists: JNJ-7,777,120 • Thioperamide • VUF-6,002Reuptake
inhibitorsVMAT inhibitorsEnzyme
inhibitorsHDC inhibitorsCatechin • Meciadanol • Naringenin • TritoqualineHNMT inhibitorsDAO inhibitorsAminoguanidineOthers L-HistidineTricyclics Classes Acridine • Anthracene • Dibenzazepine • Dibenzocycloheptene • Dibenzodiazepine • Dibenzothiazepine • Dibenzothiepin • Dibenzoxazepine • Dibenzoxepin • Phenothiazine • Pyridazinobenzoxazine • Pyridinobenzodiazepine • ThioxantheneAntidepressants 7-OH-Amoxapine • Amezepine • Amineptine • Amitriptyline • Amitriptylinoxide • Amoxapine • Aptazapine • Azepindole • Azipramine • Butriptyline • Cianopramine • Ciclazindol • Ciclopramine • Clomipramine • Cotriptyline • Cyanodothiepin • Demexiptiline • Depramine/Balipramine • Desipramine • Dibenzepin • Dimetacrine • Dosulepin/Dothiepin • Doxepin • Enprazepine • Esmirtazapine • Fluotracen • Hepzidine • Homopipramol • Imipramine • Imipraminoxide • Intriptyline • Iprindole • Ketipramine • Litracen • Lofepramine • Losindole • Loxapine • Maprotiline • Mariptiline • Mazindol • Melitracen • Metapramine • Mezepine • Mianserin • Mirtazapine • Naranol • Nitroxazepine • Nortriptyline • Noxiptiline • Octriptyline • Opipramol • Oxaprotiline • Pipofezine • Pirandamine • Propizepine • Protriptyline • Quinupramine • Setiptiline/Teciptiline • Tandamine • Tampramine • Tianeptine • Tienopramine • TrimipramineAntihistamines Alimemazine • Azatadine • Clobenzepam • Cyproheptadine • Dacemazine • Deptropine • Desloratadine • Epinastine • Etymemazine • Hydroxyethylpromethazine • Isopromethazine • Isothipendyl • Ketotifen • Latrepirdine • Loratadine • Mebhydrolin • Mequitazine • Methdilazine • Olopatadine • Oxomemazine • Phenindamine • Pimethixene • Promethazine • Propiomazine • Rupatadine • ThiazinamiumAntipsychotics Acetophenazine • Amoxapine • Asenapine • Butaclamol • Butaperazine • Carphenazine • Carpipramine • Chlorpromazine • Chlorprothixene • Ciclindole • Clocapramine • Clomacran • Clotiapine • Clozapine • Flucindole • Fluotracen • Flupentixol • Fluphenazine • Gevotroline • Homopipramol • Levomepromazine/Methotrimeprazine • Loxapine • Maroxepin • Mesoridazine • Metitepine/Methiothepin • Metoxepin • Mosapramine • Naranol • Olanzapine • Perazine • Perphenazine • Periciazine • Piperacetazine • Pipotiazine • Piquindone • Prochlorperazine • Promazine • Prothipendyl • Quetiapine • Sulforidazine • Thiethylperazine • Thiopropazate • Thioridazine • Thiothixene • Trifluoperazine • Triflupromazine • Zotepine • ZuclopenthixolOthers Atiprosin • Carbamazepine • Carvedilol • Cyclobenzaprine • Licarbazepine • Methylene Blue • Monatepil • Oxcarbazepine • Oxitriptyline • Pirenzepine • Pirolate • Pitrazepin • Pizotifen • ProfenamineCategories:- Antiemetics
- H1 receptor antagonists
- Hypnotics
- Phenothiazines
- World Health Organization essential medicines
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Prométhazine — Énantiomère R de la prométhazine (en haut) et S prométhazine (en bas) Général … Wikipédia en Français
prométhazine — ● prométhazine nom féminin Antihistaminique de synthèse utilisé dans le traitement des maladies allergiques et du mal des transports … Encyclopédie Universelle
promethazine — /proh meth euh zeen , zin/, n. Pharm. a phenothiaxine derivative, C17H20N2S, used for the symptomatic relief of allergies and in the management of motion sickness. [1950 55; PROPYL + (di)meth(ylamine) + (PHENOTHI)AZINE, components of its chemical … Universalium
promethazine — pro·meth·a·zine ( )prō meth ə .zēn n a crystalline antihistamine drug derived from phenothiazine and used chiefly in the form of its hydrochloride C17H20N2S·HCl see PHENERGAN * * * n. a powerful antihistamine drug used to treat allergic… … Medical dictionary
promethazine — n. a powerful antihistamine drug used to treat allergic conditions and – because of its sedative action – insomnia; it is also used as an antiemetic. Promethazine is administered by mouth or injection; side effects include drowsiness, dizziness,… … The new mediacal dictionary
promethazine — noun A first generation H1 receptor antagonist, antihistamine and antiemetic medication with strong sedative effects … Wiktionary
promethazine — [prə(ʊ) mɛθəzi:n] noun Medicine a synthetic antihistamine drug taken chiefly for allergies and motion sickness. Origin 1950s: from pro(pyl) + meth(yl) + (phenothi)azine … English new terms dictionary
promethazine — pro·methazine … English syllables
promethazine — n. an antihistamine drug used to treat allergies, motion sickness, etc. Etymology: PROPYL + di methylamine + phenothi azine … Useful english dictionary
promethazine hydrochloride — An antihistaminic with antiemetic properties, often used to enhance the efficacy of narcotics. * * * pro·meth·a·zine hy·dro·chlo·ride (pro methґə zēn) [USP] a phenothiazine derivative having marked antihistaminic activity as well as… … Medical dictionary
