- Metiamide
-
Metiamide 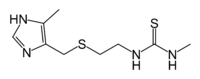 N-methyl-N'-(2-{[(4-methyl-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methyl]thio}ethyl)thiourea
N-methyl-N'-(2-{[(4-methyl-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methyl]thio}ethyl)thioureaIdentifiers PubChem 1548992 ChemSpider 1265996 
DrugBank DB08805 ChEMBL CHEMBL275446 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - S=C(NC)NCCSCc1ncnc1C
Properties Molecular formula C9H16N4S2 Molar mass 244.38 g mol−1  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Metiamide is a histamine H2-receptor antagonist developed from another H2 antagonist, burimamide.[1] It was an intermediate compound in the development of the successful anti-ulcer drug cimetidine (Tagamet).[2]
Development of metiamide from burimamide
After discovering that burimamide is largely inactive at physiological pH, due to the presence of its electron donating side chain, the following steps were undertaken to stabilse burimamide:
- addition of a sulfide group close to the imidazole ring, giving thiaburimamide
- addition of methyl group to the 4- position on the imidazole ring to favour the tautomer of thiaburimamide which binds better to the H2-receptor
These changes increased the bioavailability metiamide so that it is 10 times more potent than burimamide in inhibiting histamine-stimulated release of gastric acid.[2] The clinical trials that began in 1973 demonstrated the ability of metiamide to provide symptomatic relief for ulcerous patients by increasing healing rate of peptic ulcers. However, during these trials, an unacceptable number of patients dosed with metiamide developed agranulocytosis (decreased white blood cell count).[2]
Modification of metiamide to cimetidine
It was determined that the thiourea group was the cause of the agranulocytosis. Therefore replacement of the =S in the thiourea group was suggested:
- with =O or =NH resulted in a compound with much less activity (20 times less than metiamide)
- however, the NH form (the guanidine analogue of metiamide) did not show agonistic effects
- to prevent the guanidine group being protonated at physiological pH, electron-withdrawing groups were added
- adding a -C≡N or -NO2 group prevented the guanidine group being protonated and did not cause agranulocytosis
The nitro and cyano groups are sufficiently electronegative to reduce the pKa of the neighbouring nitrogens to the same acidity of the thiourea group, hence preserving the activity of the drug in a physiological environment.
References
- ^ Clayden, Jonathan; Greeves, Nick; Warren, Stuart; Wothers, Peter (2001). Organic Chemistry (1st ed.). Oxford University Press. pp. 204–206, 586-588. ISBN 978-0-19-850346-0.
- ^ a b c "Tagamet: A medicine that changed people's lives". American Chemical Society. 2004. http://acswebcontent.acs.org/landmarks/tagamet/tagamet.html. Retrieved 2009-09-06.
This drug article relating to the gastrointestinal system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
