- Desloratadine
-
Desloratadine 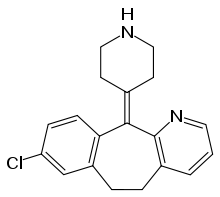

Systematic (IUPAC) name 8-chloro-6,11-dihydro-11-(4-piperdinylidene)- 5H-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridine Clinical data Trade names Clarinex AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a602002 Licence data EMA:Link, US FDA:link Pregnancy cat. B1(AU) C(US) Legal status POM (UK) ℞-only (US) Routes oral Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability Rapidly absorbed Protein binding 85% Metabolism Liver Half-life 27 hours Excretion 40% as conjugated metabolites into urine
Similar amount into the fecesIdentifiers CAS number 100643-71-8 
ATC code R06AX27 PubChem CID 124087 DrugBank APRD00324 ChemSpider 110575 
UNII FVF865388R 
KEGG D03693 
ChEBI CHEBI:291342 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1172 
Chemical data Formula C19H19ClN2 Mol. mass 310.82 SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Desloratadine is a drug used to treat allergies. It is marketed under several trade names such as NeoClarityn, Claramax, Clarinex, Larinex, Aerius, Dazit, Azomyr and Delot. It is an active metabolite of loratadine, which is also on the market.
Contents
Available forms
Desloratadine is available as tablets (including orally disintegrating and extended release) and as syrup.[1]
Mechanism of action
Desloratadine is a tricyclic antihistamine, which has a selective and peripheral H1-antagonist action. It is an antagonist at histamine H1 receptors, and an antagonist at all subtypes of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. It has a long-lasting effect and in moderate and low doses, does not cause drowsiness because it does not readily enter the central nervous system.[2]
Side effects
Most common side-effects are fatigue, dry mouth, headache, and gastrointestinal disturbances.
Desloratadine vs. loratadine
Desloratadine is the major metabolite of loratadine. There are no head-to-head randomised controlled trials of the two drugs. A survey of patients dissatisfied with loratadine published in August 2003 reported equal or better satisfaction with desloratadine,[3] concluding:
When severity of disease was controlled for in the analysis, a pattern emerged suggesting greater levels of satisfaction amongst loratadine dissatisfied patients who converted to desloratadine. Point estimates suggest a consistent pattern favoring desloratadine patient satisfaction, with statistically significant results reported for sum of adverse effects, nighttime awakening due to symptoms, symptom severity just prior to the next dose, and overall satisfaction (p < 0.05).
A November 2003 article published in the journal American Family Physician about the safety, tolerability, effectiveness, price, and simplicity of desloratadine concluded the following:[4]
Desloratadine is similar in effectiveness to fexofenadine and would be expected to produce results similar to loratadine and other nonsedating antihistamines. There is no clinical advantage to switching a patient from loratadine to desloratadine. However, it may be an option for patients whose medical insurance no longer covers loratadine if the co-pay is less than the cost of the over-the-counter product.
In Canada, desloratadine is available without a prescription, and as a generic. Prices are comparable to those of loratadine.
References
- ^ FDA Electronic Orange Book http://www.fda.gov/cder/ob/default.htm.
- ^ Mann R, Pearce G, Dunn N, Shakir S (2000). "Sedation with "non-sedating" antihistamines: four prescription-event monitoring studies in general practice". BMJ 320 (7243): 1184–6. doi:10.1136/bmj.320.7243.1184. PMC 27362. PMID 10784544. http://bmj.bmjjournals.com/cgi/content/full/320/7243/1184.
- ^ Glass D, Harper A (August 13, 2003). "Assessing satisfaction with desloratadine and fexofenadine in allergy patients who report dissatisfaction with loratadine". BMC Fam Pract 4: 10. doi:10.1186/1471-2296-4-10. PMC 194638. PMID 12917016. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=194638.
- ^ See S (2003). "Desloratadine for allergic rhinitis". Am Fam Physician 68 (10): 2015–6. PMID 14655812. http://www.aafp.org/afp/20031115/steps.html.
Tricyclics Classes Acridine • Anthracene • Dibenzazepine • Dibenzocycloheptene • Dibenzodiazepine • Dibenzothiazepine • Dibenzothiepin • Dibenzoxazepine • Dibenzoxepin • Phenothiazine • Pyridazinobenzoxazine • Pyridinobenzodiazepine • ThioxantheneAntidepressants 7-OH-Amoxapine • Amezepine • Amineptine • Amitriptyline • Amitriptylinoxide • Amoxapine • Aptazapine • Azepindole • Azipramine • Butriptyline • Cianopramine • Ciclazindol • Ciclopramine • Clomipramine • Cotriptyline • Cyanodothiepin • Demexiptiline • Depramine/Balipramine • Desipramine • Dibenzepin • Dimetacrine • Dosulepin/Dothiepin • Doxepin • Enprazepine • Esmirtazapine • Fluotracen • Hepzidine • Homopipramol • Imipramine • Imipraminoxide • Intriptyline • Iprindole • Ketipramine • Litracen • Lofepramine • Losindole • Loxapine • Maprotiline • Mariptiline • Mazindol • Melitracen • Metapramine • Mezepine • Mianserin • Mirtazapine • Naranol • Nitroxazepine • Nortriptyline • Noxiptiline • Octriptyline • Opipramol • Oxaprotiline • Pipofezine • Pirandamine • Propizepine • Protriptyline • Quinupramine • Setiptiline/Teciptiline • Tandamine • Tampramine • Tianeptine • Tienopramine • TrimipramineAntihistamines Alimemazine • Azatadine • Clobenzepam • Cyproheptadine • Dacemazine • Deptropine • Desloratadine • Epinastine • Etymemazine • Hydroxyethylpromethazine • Isopromethazine • Isothipendyl • Ketotifen • Latrepirdine • Loratadine • Mebhydrolin • Mequitazine • Methdilazine • Olopatadine • Oxomemazine • Phenindamine • Pimethixene • Promethazine • Propiomazine • Rupatadine • ThiazinamiumAntipsychotics Acetophenazine • Amoxapine • Asenapine • Butaclamol • Butaperazine • Carphenazine • Carpipramine • Chlorpromazine • Chlorprothixene • Ciclindole • Clocapramine • Clomacran • Clotiapine • Clozapine • Flucindole • Fluotracen • Flupentixol • Fluphenazine • Gevotroline • Homopipramol • Levomepromazine/Methotrimeprazine • Loxapine • Maroxepin • Mesoridazine • Metitepine/Methiothepin • Metoxepin • Mosapramine • Naranol • Olanzapine • Perazine • Perphenazine • Periciazine • Piperacetazine • Pipotiazine • Piquindone • Prochlorperazine • Promazine • Prothipendyl • Quetiapine • Sulforidazine • Thiethylperazine • Thiopropazate • Thioridazine • Thiothixene • Trifluoperazine • Triflupromazine • Zotepine • ZuclopenthixolOthers Atiprosin • Carbamazepine • Carvedilol • Cyclobenzaprine • Licarbazepine • Methylene Blue • Monatepil • Oxcarbazepine • Oxitriptyline • Pirenzepine • Pirolate • Pitrazepin • Pizotifen • ProfenamineCategories:- H1 receptor antagonists
- Schering-Plough
- Piperidines
- Benzocycloheptapyridines
- Organochlorides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
