- Cholinergic
-
The word choline generally refers to the various quaternary ammonium salts containing the N,N,N-trimethylethanolammonium cation. Found in most animal tissues, choline is a primary component of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine and functions with inositol as a basic constituent of lecithin. It prevents fat deposits in the liver and facilitates the movement of fats into the cells. The richest sources of choline are liver, kidneys, brains, wheat germ, brewer's yeast, and egg yolk. Therefore, cholinergic typically refers to acetylcholine in a neurological perspective.[1] The parasympathetic nervous system, which uses acetylcholine almost exclusively to send its messages, is said to be almost entirely cholinergic. Neuromuscular junctions, preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system, the basal forebrain, and brain stem complexes are also cholinergic. In addition, the receptor for the merocrine sweat glands are also cholinergic since acetylcholine is released from post ganglionic sympathetic neurons.
In neuroscience and related fields, the term cholinergic is used in the following related contexts:
- A substance (or ligand) is cholinergic if it is capable of producing, altering, or releasing acetylcholine ("indirect-acting") or mimicking its behaviour at one or more of the body's acetylcholine receptor types ("direct-acting").
- A receptor is cholinergic if it uses acetylcholine as its neurotransmitter.[2]
- A synapse is cholinergic if it uses acetylcholine as its neurotransmitter.
Contents
Cholinergic drug
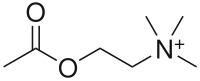
Main article: Parasympathomimetic drugStructure activity relationship for cholinergic drugs[3]
1. molecule must possess a nitrogen atom capable of bearing a positive charge, preferably a quaternary ammonium salt.
2. for maximum potency, the size of the alkyl groups substituted on the Nitrogen should not exceed the size of a methyl group.
3. The molecule should have an oxygen atom, preferably an ester-like oxygen capable of participating in a hydrogen bond.
4. There should be a two-carbon unit between the oxygen atom and the nitrogen atom.
A cholinergic drug, also known as a cholinergic agent, cholinergic agonist,[4] or a parasympathomimetic drug,[5] is any drug that functions to enhance the effects mediated by acetylcholine in the central nervous system, the peripheral nervous system, or both. These include acetylcholine's precursors and cofactors, acetylcholine receptor agonists,acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and cholinergic enzymes:
- Acetylcholine receptor agonists
- Alvameline
- Muscarine (muscarinic receptors)
- Nicotine (nicotinic receptors)
- Pilocarpine (M3 receptors)
- Suxamethonium (muscle type receptors)
- Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (abbreviated AChEIs)
See also
- Adrenergic
- Dopaminergic
- GABAergic
- Nootropic
- Serotonergic
- Glutamatergic
- Racetam
References
- ^ "Definition: cholinergic from Online Medical Dictionary". http://cancerweb.ncl.ac.uk/cgi-bin/omd?cholinergic.
- ^ "Dorlands Medical Dictionary:cholinergic receptors". http://www.mercksource.com/pp/us/cns/cns_hl_dorlands_split.jsp?pg=/ppdocs/us/common/dorlands/dorland/seven/000091035.htm.
- ^ Medicinal Chemistry of Adrenergics and Cholinergics
- ^ MeSH Cholinergic+Agonists
- ^ "Dorlands Medical Dictionary:cholinergic". http://www.mercksource.com/pp/us/cns/cns_hl_dorlands_split.jsp?pg=/ppdocs/us/common/dorlands/dorland/two/000020616.htm.
Cholinergics Receptor ligands Agonists: 77-LH-28-1 • AC-42 • AC-260,584 • Aceclidine • Acetylcholine • AF30 • AF150(S) • AF267B • AFDX-384 • Alvameline • AQRA-741 • Arecoline • Bethanechol • Butyrylcholine • Carbachol • CDD-0034 • CDD-0078 • CDD-0097 • CDD-0098 • CDD-0102 • Cevimeline • cis-Dioxolane • Ethoxysebacylcholine • LY-593,039 • L-689,660 • LY-2,033,298 • McNA343 • Methacholine • Milameline • Muscarine • NGX-267 • Ocvimeline • Oxotremorine • PD-151,832 • Pilocarpine • RS86 • Sabcomeline • SDZ 210-086 • Sebacylcholine • Suberylcholine • Talsaclidine • Tazomeline • Thiopilocarpine • Vedaclidine • VU-0029767 • VU-0090157 • VU-0152099 • VU-0152100 • VU-0238429 • WAY-132,983 • Xanomeline • YM-796
Antagonists: 3-Quinuclidinyl Benzilate • 4-DAMP • Aclidinium Bromide • Anisodamine • Anisodine • Atropine • Atropine Methonitrate • Benactyzine • Benzatropine (Benztropine) • Benzydamine • BIBN 99 • Biperiden • Bornaprine • CAR-226,086 • CAR-301,060 • CAR-302,196 • CAR-302,282 • CAR-302,368 • CAR-302,537 • CAR-302,668 • CS-27349 • Cyclobenzaprine • Cyclopentolate • Darifenacin • DAU-5884 • Dimethindene • Dexetimide • DIBD • Dicyclomine (Dicycloverine) • Ditran • EA-3167 • EA-3443 • EA-3580 • EA-3834 • Elemicin • Etanautine • Etybenzatropine (Ethylbenztropine) • Flavoxate • Himbacine • HL-031,120 • Ipratropium bromide • J-104,129 • Hyoscyamine • Mamba Toxin 3 • Mamba Toxin 7 • Mazaticol • Mebeverine • Methoctramine • Metixene • Myristicin • N-Ethyl-3-Piperidyl Benzilate • N-Methyl-3-Piperidyl Benzilate • Orphenadrine • Otenzepad • Oxybutynin • PBID • PD-102,807 • PD-0298029 • Phenglutarimide • Phenyltoloxamine • Pirenzepine • Piroheptine • Procyclidine • Profenamine • RU-47,213 • SCH-57,790 • SCH-72,788 • SCH-217,443 • Scopolamine (Hyoscine) • Solifenacin • Telenzepine • Tiotropium bromide • Tolterodine • Trihexyphenidyl • Tripitamine • Tropatepine • Tropicamide • WIN-2299 • Xanomeline • Zamifenacin; Others: 1st Generation Antihistamines (Brompheniramine, chlorphenamine, cyproheptadine, dimenhydrinate, diphenhydramine, doxylamine, mepyramine/pyrilamine, phenindamine, pheniramine, tripelennamine, triprolidine, etc) • Tricyclic Antidepressants (Amitriptyline, doxepin, trimipramine, etc) • Tetracyclic Antidepressants (Amoxapine, maprotiline, etc) • Typical Antipsychotics (Chlorpromazine, thioridazine, etc) • Atypical Antipsychotics (Clozapine, olanzapine, quetiapine, etc)Agonists: 5-HIAA • A-84,543 • A-366,833 • A-582,941 • A-867,744 • ABT-202 • ABT-418 • ABT-560 • ABT-894 • Acetylcholine • Altinicline • Anabasine • Anatoxin-a • AR-R17779 • Butyrylcholine • Carbachol • Cotinine • Cytisine • Decamethonium • Desformylflustrabromine • Dianicline • Dimethylphenylpiperazinium • Epibatidine • Epiboxidine • Ethanol • Ethoxysebacylcholine • EVP-4473 • EVP-6124 • Galantamine • GTS-21 • Ispronicline • Lobeline • MEM-63,908 (RG-3487) • Nicotine • NS-1738 • PHA-543,613 • PHA-709,829 • PNU-120,596 • PNU-282,987 • Pozanicline • Rivanicline • Sazetidine A • Sebacylcholine • SIB-1508Y • SIB-1553A • SSR-180,711 • Suberylcholine • TC-1698 • TC-1734 • TC-1827 • TC-2216 • TC-5214 • TC-5619 • TC-6683 • Tebanicline • Tropisetron • UB-165 • Varenicline • WAY-317,538 • XY-4083
Antagonists: 18-Methoxycoronaridine • α-Bungarotoxin • α-Conotoxin • Alcuronium • Amantadine • Anatruxonium • Atracurium • Bupropion (Amfebutamone) • Chandonium • Chlorisondamine • Cisatracurium • Coclaurine • Coronaridine • Dacuronium • Decamethonium • Dextromethorphan • Dextropropoxyphene • Dextrorphan • Diadonium • DHβE • Dimethyltubocurarine (Metocurine) • Dipyrandium • Dizocilpine (MK-801) • Doxacurium • Duador • Esketamine • Fazadinium • Gallamine • Hexafluronium • Hexamethonium (Benzohexonium) • Ibogaine • Isoflurane • Ketamine • Kynurenic acid • Laudexium (Laudolissin) • Levacetylmethadol • Malouetine • Mecamylamine • Memantine • Methadone • Methorphan (Racemethorphan) • Methyllycaconitine • Metocurine • Mivacurium • Morphanol (Racemorphanol) • Neramexane • Nitrous Oxide • Pancuronium • Pempidine • Pentamine • Pentolinium • Phencyclidine • Pipecuronium • Radafaxine • Rapacuronium • Rocuronium • Surugatoxin • Suxamethonium (Succinylcholine) • Thiocolchicoside • Toxiferine • Trimethaphan • Tropeinium • Tubocurarine • Vecuronium • XenonReuptake inhibitors PlasmalemmalCHT InhibitorsHemicholinium-3 (Hemicholine; HC3) • TriethylcholineVAChT InhibitorsEnzyme inhibitors ChAT inhibitors1-(-Benzoylethyl)pyridinium • 2-(α-Naphthoyl)ethyltrimethylammonium • 3-Chloro-4-stillbazole • 4-(1-Naphthylvinyl)pyridine • Acetylseco hemicholinium-3 • Acryloylcholine • AF64A • B115 • BETA • CM-54,903 • CatabolismAChE inhibitorsReversible: Carbamates: Aldicarb • Bendiocarb • Bufencarb • Carbaryl • Carbendazim • Carbetamide • Carbofuran • Chlorbufam • Chloropropham • Ethienocarb • Ethiofencarb • Fenobucarb • Fenoxycarb • Formetanate • Furadan • Ladostigil • Methiocarb • Methomyl • Miotine • Oxamyl • Phenmedipham • Pinmicarb • Pirimicarb • Propamocarb • Propham • Propoxur; Stigmines: Ganstigmine • Neostigmine • Phenserine • Physostigmine • Pyridostigmine • Rivastigmine; Others: Acotiamide • Ambenonium • Donepezil • Edrophonium • Galantamine • Huperzine A • Minaprine • Tacrine • Zanapezil
Irreversible: Organophosphates: Acephate • Azinphos-methyl • Bensulide • Cadusafos • Chlorethoxyfos • Chlorfenvinphos • Chlorpyrifos • Chlorpyrifos-Methyl • Coumaphos • Cyclosarin (GF) • Demeton • Demeton-S-Methyl • Diazinon • Dichlorvos • Dicrotophos • Diisopropyl fluorophosphate (Guthion) • Diisopropylphosphate • Dimethoate • Dioxathion • Disulfoton • EA-3148 • Echothiophate • Ethion • Ethoprop • Fenamiphos • Fenitrothion • Fenthion • Fosthiazate • GV • Isofluorophate • Isoxathion • Malaoxon • Malathion • Methamidophos • Methidathion • Metrifonate • Mevinphos • Monocrotophos • Naled • Novichok agent • Omethoate • Oxydemeton-Methyl • Paraoxon • Parathion • Parathion-Methyl • Phorate • Phosalone • Phosmet • Phostebupirim • Phoxim • Pirimiphos-Methyl • Sarin (GB) • Soman (GD) • Tabun (GA) • Temefos • Terbufos • Tetrachlorvinphos • Tribufos • Trichlorfon • VE • VG • VM • VR • VX; Others: Demecarium • Onchidal (Onchidella binneyi)BChE inhibitorsCymserine * Many of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitors listed above act as butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors.Others Choline (Lecithin) • Citicoline • Cyprodenate • Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE, deanol) • Glycerophosphocholine • Meclofenoxate (Centrophenoxine) • Phosphatidylcholine • Phosphatidylethanolamine • Phosphorylcholine • PirisudanolOthersAcetylcholine releasing agents: α-Latrotoxin • β-Bungarotoxin; Acetylcholine release inhibitors: Botulinum toxin (Botox); Acetylcholinesterase reactivators: Asoxime • Obidoxime • PralidoximeCategories:- Parasympathetic nervous system
- Neurochemistry
- Sympathomimetics
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
cholinergic — [kō΄lin ʉr′jik] adj. [< CHOLINE + Gr ergon, WORK + IC] 1. having the properties of acetylcholine 2. releasing or stimulated by acetylcholine … English World dictionary
cholinergic — adjective Etymology: International Scientific Vocabulary Date: 1934 1. liberating, activated by, or involving acetylcholine < cholinergic nerve fiber > < cholinergic functions > 2. resembling acetylcholine especially in physiologic action … New Collegiate Dictionary
cholinergic — cho•lin•er•gic [[t]ˌkoʊ ləˈnɜr dʒɪk, ˌkɒl ə [/t]] adj. 1) biochem. pha resembling acetylcholine in physiological effect: a cholinergic drug[/ex] 2) biochem. releasing acetylcholine: a cholinergic neuron[/ex] 3) cbl activated by acetylcholine: a… … From formal English to slang
cholinergic — Relating to nerve cells or fibers that employ acetylcholine as their neurotransmitter. Cf.:adrenergic. [choline + G. ergon, work] * * * cho·lin·er·gic .kō lə nər jik adj 1) of autonomic nerve fibers liberating, activated by, or involving… … Medical dictionary
cholinergic — adj. 1) describing nerve fibres that release acetylcholine as a neurotransmitter. 2) describing receptors at which acetylcholine acts to pass on messages from cholinergic nerve fibres. 3) describing drugs that mimic the actions of acetylcholine… … The new mediacal dictionary
cholinergic — adjective releasing or activated by acetylcholine or a related compound • Ant: ↑anticholinergic * * * cholinergic, a. (kɒlɪˈnɜːdʒɪk) [f. cholinee + Gr. ἔργ ον work + ic.] Of the synapses or nerve fibres: liberating acetylcholine; also, stimulated … Useful english dictionary
Cholinergic urticaria — Classification and external resources ICD 10 L50.5 … Wikipedia
Cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 1 — (muscle) Rendering based on PDB 1Y5P … Wikipedia
Cholinergic crisis — A cholinergic crisis is an over stimulation at a neuromuscular junction due to an excess of acetylcholine (ACh), as of a result of the inactivity (perhaps even inhibition) of the AChE enzyme, which normally breaks down acetylcholine. This is a… … Wikipedia
Cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway — The Cholinergic Anti inflammatory Pathway regulates the innate immune response (Innate immunity) to injury, pathogens, and tissue ischemia. It is the efferent, or motor arm of the Inflammatory Reflex, the neural circuit that responds to and… … Wikipedia