- Dimethylethanolamine
-
Dimethylethanolamine 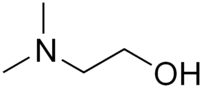 2-(Dimethylamino)ethanolOther namesDimethylamino ethanol
2-(Dimethylamino)ethanolOther namesDimethylamino ethanol
DeanolIdentifiers Abbreviations DMAE CAS number 108-01-0 
ChemSpider 13835861 
UNII 2N6K9DRA24 
EC number 7902 ChEMBL CHEMBL122588 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - CC(C)(N)CO
Properties Molecular formula C4H11NO Molar mass 89.14 g mol−1 Density 0.89 g/mL Melting point -70 °C, 203 K, -94 °F
Boiling point 133–134 °C
 (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Dimethylaminoethanol, also known as DMAE or dimethylethanolamine, is an organic compound. This compound also goes by the names of N,N-dimethyl-2-aminoethanol, beta-dimethylaminoethyl alcohol, beta-hydroxyethyldimethylamine and Deanol. It is a clear, pale-yellow liquid.
Contents
Industrial uses
Dimethylaminoethanol is used as a curing agent for polyurethanes and epoxy resins. It is also used in mass quantities for water treatment, and to some extent in the coatings industry. It is used in the synthesis of dyestuffs, textile auxiliaries, pharmaceuticals, emulsifiers, and corrosion inhibitors. It is also an additive to paint removers, boiler water and amino resins. It forms a number of salts with melting points below room temperature (ionic liquids) such as N,N-dimethylethanolammonium acetate and N,N-dimethylethanolammonium octanoate, which have been used as alternatives to conventional solvents.[1]
2-Dimethylaminoethyl chloride hydrochloride is an intermediate made from dimethylaminoethanol that is widely used for the manufacture of pharmaceuticals.[2]
Biochemical precursor
Dimethylaminoethanol is related to choline and may be a biochemical precursor to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, although this conclusion has been disputed.[3] It is believed that dimethylaminoethanol is methylated to produce choline in the brain.[3] It is known that dimethylaminoethanol is processed by the liver into choline; however, the choline molecule is charged and cannot pass the blood-brain barrier.[3]
Research
Short-term studies have shown an increase in vigilance and alertness with a positive influence on mood following administration of DMAE, vitamins, and minerals in individuals suffering from borderline emotional disturbance.[4] Research for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) has been promising, though inconclusive.[5] Long-term studies are equivocal. Some showed dimethylaminoethanol to increase the lifespan of animals in which it was tested, while others indicate a possible reduction in the average life span of quail.[6]
See also
- Ethanolamine
- Methylethanolamine
- Choline
References
- ^ Sanders MW, Wright L, Tate L, Fairless G, Crowhurst L, Bruce NC, Walker AJ, Hembury GA, Shimizu S (September 2009). "Unexpected preferential dehydration of artemisinin in ionic liquids". J. Phys. Chem. A 113 (38): 10143–45. doi:10.1021/jp906436e. PMID 19722599. http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jp906436e.
- ^ Ashford's Dictionary of Industrial Chemicals, 3rd edition, 2011, ISBN: 978-0-9522674-3-0, page 3294
- ^ a b c Zahniser NR, Chou D, Hanin I (March 1977). "Is 2-dimethylaminoethanol (deanol) indeed a precursor of brain acetylcholine? A gas chromatographic evaluation". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 200 (3): 545–59. PMID 850128. http://jpet.aspetjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=850128.
- ^ Dimpfel W, Wedekind W, Keplinger I (May 2003). "Efficacy of dimethylaminoethanol (DMAE) containing vitamin-mineral drug combination on EEG patterns in the presence of different emotional states". Eur. J. Med. Res. 8 (5): 183–91. PMID 12844472.
- ^ Knobel M (1974). "Approach to a combined pharmacologic therapy of childhood hyperkinesis". Behav Neuropsychiatry 6 (1–12): 87–90. PMID 4619768.
- ^ Cherkin A, Exkardt MJ (January 1977). "Effects of dimethylaminoethanol upon life-span and behavior of aged Japanese quail". J Gerontol 32 (1): 38–45. PMID 830732. http://geronj.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=830732.
Studies
- Earliest research
- Pfeiffer CC, Jenney EH, Gallagher W, et al. (September 1957). "Stimulant effect of 2-dimethylaminoethanol; possible precursor of brain acetylcholine". Science 126 (3274): 610–1. doi:10.1126/science.126.3274.610. PMID 13467254. http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=13467254.
- As a treatment for tardive dyskinesia
- Haug BA, Holzgraefe M (1991). "Orofacial and respiratory tardive dyskinesia: potential side effects of 2-dimethylaminoethanol (deanol)?". Eur. Neurol. 31 (6): 423–5. doi:10.1159/000116708. PMID 1756771.
- As an unsuccessful treatment for Alzheimer's disease
- Fisman M, Mersky H, Helmes E (July 1981). "Double-blind trial of 2-dimethylaminoethanol in Alzheimer's disease". Am J Psychiatry 138 (7): 970–2. PMID 7020434. http://ajp.psychiatryonline.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=7020434.
Nootropics (N06B) Acetylcholinesterases Ampakines CX-516 • CX-546 • CX-614 • CX-691 • CX-717 • IDRA-21 • LY-404,187 • LY-503,430 • PEPA • Sunifiram • UnifiramD1 Agonists Eugeroics GABAA α5 Inverse Agonists H3 Antagonists mACh Agonists Alvameline • Arecoline • Cevimeline • CI-1017 • Milameline • Sabcomeline • Talsaclidine • Tazomeline • XanomelinenACh Agonists Racetams Others Acetylcarnitine • Adafenoxate • Bifemelane • Bilobalide (Ginkgo Biloba) • Carbenoxolone • Cerlapirdine • Choline (Lecithin) • Citicoline • Cyprodenate • Dimethylethanolamine • Ensaculin • Fipexide • Idebenone • Indeloxazine • Latrepirdine • Leteprinim • Linopirdine • Meclofenoxate • Nizofenone • Pirisudanol • Pyritinol • S-17092 • Sulbutiamine • Taltirelin • Teniloxazine • Tricyanoaminopropene • VinpocetineCholinergics Receptor ligands Agonists: 77-LH-28-1 • AC-42 • AC-260,584 • Aceclidine • Acetylcholine • AF30 • AF150(S) • AF267B • AFDX-384 • Alvameline • AQRA-741 • Arecoline • Bethanechol • Butyrylcholine • Carbachol • CDD-0034 • CDD-0078 • CDD-0097 • CDD-0098 • CDD-0102 • Cevimeline • cis-Dioxolane • Ethoxysebacylcholine • LY-593,039 • L-689,660 • LY-2,033,298 • McNA343 • Methacholine • Milameline • Muscarine • NGX-267 • Ocvimeline • Oxotremorine • PD-151,832 • Pilocarpine • RS86 • Sabcomeline • SDZ 210-086 • Sebacylcholine • Suberylcholine • Talsaclidine • Tazomeline • Thiopilocarpine • Vedaclidine • VU-0029767 • VU-0090157 • VU-0152099 • VU-0152100 • VU-0238429 • WAY-132,983 • Xanomeline • YM-796
Antagonists: 3-Quinuclidinyl Benzilate • 4-DAMP • Aclidinium Bromide • Anisodamine • Anisodine • Atropine • Atropine Methonitrate • Benactyzine • Benzatropine (Benztropine) • Benzydamine • BIBN 99 • Biperiden • Bornaprine • CAR-226,086 • CAR-301,060 • CAR-302,196 • CAR-302,282 • CAR-302,368 • CAR-302,537 • CAR-302,668 • CS-27349 • Cyclobenzaprine • Cyclopentolate • Darifenacin • DAU-5884 • Dimethindene • Dexetimide • DIBD • Dicyclomine (Dicycloverine) • Ditran • EA-3167 • EA-3443 • EA-3580 • EA-3834 • Elemicin • Etanautine • Etybenzatropine (Ethylbenztropine) • Flavoxate • Himbacine • HL-031,120 • Ipratropium bromide • J-104,129 • Hyoscyamine • Mamba Toxin 3 • Mamba Toxin 7 • Mazaticol • Mebeverine • Methoctramine • Metixene • Myristicin • N-Ethyl-3-Piperidyl Benzilate • N-Methyl-3-Piperidyl Benzilate • Orphenadrine • Otenzepad • Oxybutynin • PBID • PD-102,807 • PD-0298029 • Phenglutarimide • Phenyltoloxamine • Pirenzepine • Piroheptine • Procyclidine • Profenamine • RU-47,213 • SCH-57,790 • SCH-72,788 • SCH-217,443 • Scopolamine (Hyoscine) • Solifenacin • Telenzepine • Tiotropium bromide • Tolterodine • Trihexyphenidyl • Tripitamine • Tropatepine • Tropicamide • WIN-2299 • Xanomeline • Zamifenacin; Others: 1st Generation Antihistamines (Brompheniramine, chlorphenamine, cyproheptadine, dimenhydrinate, diphenhydramine, doxylamine, mepyramine/pyrilamine, phenindamine, pheniramine, tripelennamine, triprolidine, etc) • Tricyclic Antidepressants (Amitriptyline, doxepin, trimipramine, etc) • Tetracyclic Antidepressants (Amoxapine, maprotiline, etc) • Typical Antipsychotics (Chlorpromazine, thioridazine, etc) • Atypical Antipsychotics (Clozapine, olanzapine, quetiapine, etc)Agonists: 5-HIAA • A-84,543 • A-366,833 • A-582,941 • A-867,744 • ABT-202 • ABT-418 • ABT-560 • ABT-894 • Acetylcholine • Altinicline • Anabasine • Anatoxin-a • AR-R17779 • Butyrylcholine • Carbachol • Cotinine • Cytisine • Decamethonium • Desformylflustrabromine • Dianicline • Dimethylphenylpiperazinium • Epibatidine • Epiboxidine • Ethanol • Ethoxysebacylcholine • EVP-4473 • EVP-6124 • Galantamine • GTS-21 • Ispronicline • Lobeline • MEM-63,908 (RG-3487) • Nicotine • NS-1738 • PHA-543,613 • PHA-709,829 • PNU-120,596 • PNU-282,987 • Pozanicline • Rivanicline • Sazetidine A • Sebacylcholine • SIB-1508Y • SIB-1553A • SSR-180,711 • Suberylcholine • TC-1698 • TC-1734 • TC-1827 • TC-2216 • TC-5214 • TC-5619 • TC-6683 • Tebanicline • Tropisetron • UB-165 • Varenicline • WAY-317,538 • XY-4083
Antagonists: 18-Methoxycoronaridine • α-Bungarotoxin • α-Conotoxin • Alcuronium • Amantadine • Anatruxonium • Atracurium • Bupropion (Amfebutamone) • Chandonium • Chlorisondamine • Cisatracurium • Coclaurine • Coronaridine • Dacuronium • Decamethonium • Dextromethorphan • Dextropropoxyphene • Dextrorphan • Diadonium • DHβE • Dimethyltubocurarine (Metocurine) • Dipyrandium • Dizocilpine (MK-801) • Doxacurium • Duador • Esketamine • Fazadinium • Gallamine • Hexafluronium • Hexamethonium (Benzohexonium) • Ibogaine • Isoflurane • Ketamine • Kynurenic acid • Laudexium (Laudolissin) • Levacetylmethadol • Malouetine • Mecamylamine • Memantine • Methadone • Methorphan (Racemethorphan) • Methyllycaconitine • Metocurine • Mivacurium • Morphanol (Racemorphanol) • Neramexane • Nitrous Oxide • Pancuronium • Pempidine • Pentamine • Pentolinium • Phencyclidine • Pipecuronium • Radafaxine • Rapacuronium • Rocuronium • Surugatoxin • Suxamethonium (Succinylcholine) • Thiocolchicoside • Toxiferine • Trimethaphan • Tropeinium • Tubocurarine • Vecuronium • XenonReuptake inhibitors PlasmalemmalCHT InhibitorsVAChT InhibitorsEnzyme inhibitors ChAT inhibitors1-(-Benzoylethyl)pyridinium • 2-(α-Naphthoyl)ethyltrimethylammonium • 3-Chloro-4-stillbazole • 4-(1-Naphthylvinyl)pyridine • Acetylseco hemicholinium-3 • Acryloylcholine • AF64A • B115 • BETA • CM-54,903 • CatabolismAChE inhibitorsReversible: Carbamates: Aldicarb • Bendiocarb • Bufencarb • Carbaryl • Carbendazim • Carbetamide • Carbofuran • Chlorbufam • Chloropropham • Ethienocarb • Ethiofencarb • Fenobucarb • Fenoxycarb • Formetanate • Furadan • Ladostigil • Methiocarb • Methomyl • Miotine • Oxamyl • Phenmedipham • Pinmicarb • Pirimicarb • Propamocarb • Propham • Propoxur; Stigmines: Ganstigmine • Neostigmine • Phenserine • Physostigmine • Pyridostigmine • Rivastigmine; Others: Acotiamide • Ambenonium • Donepezil • Edrophonium • Galantamine • Huperzine A • Minaprine • Tacrine • Zanapezil
Irreversible: Organophosphates: Acephate • Azinphos-methyl • Bensulide • Cadusafos • Chlorethoxyfos • Chlorfenvinphos • Chlorpyrifos • Chlorpyrifos-Methyl • Coumaphos • Cyclosarin (GF) • Demeton • Demeton-S-Methyl • Diazinon • Dichlorvos • Dicrotophos • Diisopropyl fluorophosphate (Guthion) • Diisopropylphosphate • Dimethoate • Dioxathion • Disulfoton • EA-3148 • Echothiophate • Ethion • Ethoprop • Fenamiphos • Fenitrothion • Fenthion • Fosthiazate • GV • Isofluorophate • Isoxathion • Malaoxon • Malathion • Methamidophos • Methidathion • Metrifonate • Mevinphos • Monocrotophos • Naled • Novichok agent • Omethoate • Oxydemeton-Methyl • Paraoxon • Parathion • Parathion-Methyl • Phorate • Phosalone • Phosmet • Phostebupirim • Phoxim • Pirimiphos-Methyl • Sarin (GB) • Soman (GD) • Tabun (GA) • Temefos • Terbufos • Tetrachlorvinphos • Tribufos • Trichlorfon • VE • VG • VM • VR • VX; Others: Demecarium • Onchidal (Onchidella binneyi)BChE inhibitorsCymserine * Many of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitors listed above act as butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors.Others Choline (Lecithin) • Citicoline • Cyprodenate • Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE, deanol) • Glycerophosphocholine • Meclofenoxate (Centrophenoxine) • Phosphatidylcholine • Phosphatidylethanolamine • Phosphorylcholine • PirisudanolOthersAcetylcholine releasing agents: α-Latrotoxin • β-Bungarotoxin; Acetylcholine release inhibitors: Botulinum toxin (Botox); Acetylcholinesterase reactivators: Asoxime • Obidoxime • PralidoximeCategories:- Amines
- Alcohols
- Nootropics
- Corrosion inhibitors
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
dimethylethanolamine — noun Dimethylaminoethanol … Wiktionary
Choline — The N,N,N trimethylethanolammonium cation, with an undefined counteranion, X− Choline is a water soluble essential nutrient.[1][ … Wikipedia
Cyprodenate — Systematic (IUPAC) name 2 dimethylaminoethyl 3 cyclohexylpropanoate Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com … Wikipedia
Meclofenoxate — Systematic (IUPAC) name 2 Dimethylaminoethyl (4 chlorophenoxy)acetate Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com … Wikipedia
Phosphatidylcholine — Phosphatidylcholines (PC) are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup. They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources such as egg yolk or soy… … Wikipedia
Cotinine — Not to be confused with cotinin. Cotinine Systematic (IUPAC) name (5S) 1 methyl 5 (3 pyridyl)pyrrolidin 2 one Clinical data … Wikipedia
N-Methylethanolamine — N Methylethanolamine[1] IUPAC name … Wikipedia
Galantamine — Systematic (IUPAC) name (4aS,6R,8aS) 5,6,9,10,11,12 hexahydro 3 methoxy 11 methyl 4aH [1]benzofuro[3a,3,2 ef] [2] benzazepin 6 ol Clinical data … Wikipedia
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor — Acetylcholine … Wikipedia
Cytisine — Not to be confused with cytosine, cysteine, or cystine. Cytisine IUPAC name … Wikipedia
