- Dopamine receptor D1
-
Dopamine receptor D1, also known as DRD1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD1 gene.[1][2][3]
Contents
Function
This gene encodes the D1 subtype of the dopamine receptor. The D1 subtype is the most abundant dopamine receptor in the central nervous system. This G-protein-coupled receptor stimulates adenylyl cyclase and activates cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases. D1 receptors regulate neuronal growth and development, mediate some behavioral responses, and modulate dopamine receptor D2-mediated events[citation needed]. Alternate transcription initiation sites result in two transcript variants of this gene.[4]
Ligands
There are a number of ligands selective for the D1 receptors. They comprise almost exclusively of compounds derived from dihydrexidine and from the prototypical benzazepine SCH-23,390.[5] While the benzazepines are generally highly and fully selective for the D1 receptor over all other receptors, the dihydrexidine derivatives do not distinguish between the D1 and D5 receptors and therefore cannot be said to be truly selective.[5] The benzazepines are weak partial agonists/antagonists with low intrinsic activity, whereas the dihydrexidine derivatives function as full agonists with intrinsic activity equal to or greater than that elicited by dopamine itself.[5]
Agonists
- Dihydrexidine derivatives
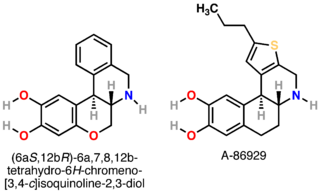
- A-86,929 - full agonist with 14-fold selectivity for D1-like receptors over D2[5][7][8]
- Dihydrexidine - full agonist with 10-fold selectivity for D1-like receptors over D2 that was being investigated for the treatment of Parkinson's disease but was discontinued due to intolerable side effects[5]
- Dinapsoline - full agonist with 5-fold selectivity for D1-like receptors over D2[5]
- Dinoxyline - full agonist with approximately equal affinity for D1-like and D2 receptors[5]
- Doxanthrine - full agonist with 168-fold selectivity for D1-like receptors over D2[5]
- Benzazepine derivatives
- SKF-81,297 - 200-fold selectivity for D1 over any other receptor[5]
- SKF-82,958 - 57-fold selectivity for D1 over D2[5]
- SKF-38,393 - very high selectivity for D1 with negligible affinity for any other receptor[5]
- Fenoldopam - highly selective peripheral D1 receptor partial agonist used clinically as an antihypertensive[5]
- 6-Br-APB - 90-fold selectivity for D1 over D2[5]
- Others
- A-68,930
- A-77,636
- CY-208,243 - partial agonist with moderate selectivity for D1-like over D2-like receptors, structurally most closely related to ergoline-based dopamine agonists like pergolide.
- SKF-89,145
- SKF-89,626
- 7,8-Dihydroxy-5-phenyl-octahydrobenzo[h]isoquinoline: extremely potent, high-affinity full agonist[9]
-
- Cabergoline - weak D1 agonism, highly selective for D2, and various serotonin receptors
- Pergolide - (similar to cabergoline) weak D1 agonism, highly selective for D2, and various serotonin receptors
Antagonists
- Benzazepine derivatives
- SCH-23,390 - 100-fold selectivity for D1 over D5[5]
- SKF-83,959 - 7-fold selectivity for D1 over D5 with negligible affinity for other receptors;[5] acts as an antagonist at D1 but as an agonist at D5
- Ecopipam (SCH-39,166) - a selective D1/D5 antagonist that was being developed as an anti-obesity medication but was discontinued[5]
Interactions
Dopamine receptor D1 has been shown to interact with COPG,[10] DNAJC14[11] and COPG2.[10]
See also
References
- ^ Dearry A, Gingrich JA, Falardeau P, Fremeau RT, Bates MD, Caron MG (September 1990). "Molecular cloning and expression of the gene for a human D1 dopamine receptor". Nature 347 (6288): 72–6. doi:10.1038/347072a0. PMID 2144334.
- ^ Zhou QY, Grandy DK, Thambi L, Kushner JA, Van Tol HH, Cone R, Pribnow D, Salon J, Bunzow JR, Civelli O (September 1990). "Cloning and expression of human and rat D1dopamine receptors". Nature 347 (6288): 76–80. doi:10.1038/347076a0. PMID 2168520.
- ^ Sunahara RK, Niznik HB, Weiner DM, Stormann TM, Brann MR, Kennedy JL, Gelernter JE, Rozmahel R, Yang YL, Israel Y, O'Dowd BF. (September 1990). "Human dopamine D1 receptor encoded by an intronless gene on chromosome 5". Nature 347 (6288): 80–3. doi:10.1038/347080a0. PMID 1975640.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: DRD1 dopamine receptor D1". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=1812.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Zhang J, Xiong B, Zhen X, Zhang A. (2009). "Dopamine D1 receptor ligands: where are we now and where are we going.". Med Res Rev. 29 (2): 272–294. doi:10.1002/med.20130. PMID 18642350.
- ^ Cueva JP, Giorgioni G, Grubbs RA, Chemel BR, Watts VJ, Nichols DE (November 2006). "trans-2,3-dihydroxy-6a,7,8,12b-tetrahydro-6H-chromeno[3,4-c]isoquinoline: synthesis, resolution, and preliminary pharmacological characterization of a new dopamine D1 receptor full agonist". J. Med. Chem. 49 (23): 6848–57. doi:10.1021/jm0604979. PMID 17154515.
- ^ a b Michaelides MR, Hong Y, DiDomenico S, Asin KE, Britton DR, Lin CW, Williams M, Shiosaki K (1995). "(5aR,11bS)-4,5,5a,6,7,11b-hexahydro-2-propyl-3-thia-5-azacyclopent-1- ena[c]-phenanthrene-9,10-diol (A-86929): a potent and selective dopamine D1agonist that maintains behavioral efficacy following repeated administration and characterization of its diacetyl prodrug (ABT-431)". J. Med. Chem. 38 (18): 3445–7. doi:10.1021/jm00018a002. PMID 7658429.
- ^ Yamashita M, Yamada K, Tomioka K (2004). "Construction of arene-fused-piperidine motifs by asymmetric addition of 2-trityloxymethylaryllithiums to nitroalkenes: the asymmetric synthesis of a dopamine D1 full agonist, A-86929". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126 (7): 1954–5. doi:10.1021/ja031760n. PMID 14971926.
- ^ PMID 20709559
- ^ a b Bermak, Jason C; Li Ming, Bullock Clayton, Weingarten Paul, Zhou Qun-Yong (Feb. 2002). "Interaction of gamma-COP with a transport motif in the D1 receptor C-terminus". Eur. J. Cell Biol. (Germany) 81 (2): 77–85. doi:10.1078/0171-9335-00222. ISSN 0171-9335. PMID 11893085.
- ^ Bermak, J C; Li M, Bullock C, Zhou Q Y (May. 2001). "Regulation of transport of the dopamine D1 receptor by a new membrane-associated ER protein". Nat. Cell Biol. (England) 3 (5): 492–8. doi:10.1038/35074561. ISSN 1465-7392. PMID 11331877.
Further reading
- Missale C, Nash SR, Robinson SW, et al. (1998). "Dopamine receptors: from structure to function.". Physiol. Rev. 78 (1): 189–225. PMID 9457173.
- Milligan G, White JH (2001). "Protein-protein interactions at G-protein-coupled receptors.". Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 22 (10): 513–8. doi:10.1016/S0165-6147(00)01801-0. PMID 11583808.
- Bermak JC, Zhou QY (2004). "Accessory proteins in the biogenesis of G protein-coupled receptors.". Mol. Interv. 1 (5): 282–7. PMID 14993367.
- Minowa MT, Minowa T, Monsma FJ, et al. (1992). "Characterization of the 5' flanking region of the human D1A dopamine receptor gene.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89 (7): 3045–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.7.3045. PMC 48800. PMID 1557411. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=48800.
- Tiberi M, Jarvie KR, Silvia C, et al. (1991). "Cloning, molecular characterization, and chromosomal assignment of a gene encoding a second D1 dopamine receptor subtype: differential expression pattern in rat brain compared with the D1A receptor.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88 (17): 7491–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.17.7491. PMC 52326. PMID 1831904. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=52326.
- Sunahara RK, Niznik HB, Weiner DM, et al. (1990). "Human dopamine D1 receptor encoded by an intronless gene on chromosome 5.". Nature 347 (6288): 80–3. doi:10.1038/347080a0. PMID 1975640.
- Grandy DK, Zhou QY, Allen L, et al. (1990). "A human D1 dopamine receptor gene is located on chromosome 5 at q35.1 and identifies an EcoRI RFLP.". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 47 (5): 828–34. PMC 1683700. PMID 1977312. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1683700.
- Dearry A, Gingrich JA, Falardeau P, et al. (1990). "Molecular cloning and expression of the gene for a human D1 dopamine receptor.". Nature 347 (6288): 72–6. doi:10.1038/347072a0. PMID 2144334.
- Zhou QY, Grandy DK, Thambi L, et al. (1990). "Cloning and expression of human and rat D1 dopamine receptors.". Nature 347 (6288): 76–80. doi:10.1038/347076a0. PMID 2168520.
- Frail DE, Manelli AM, Witte DG, et al. (1994). "Cloning and characterization of a truncated dopamine D1 receptor from goldfish retina: stimulation of cyclic AMP production and calcium mobilization.". Mol. Pharmacol. 44 (6): 1113–8. PMID 8264547.
- Ohara K, Ulpian C, Seeman P, et al. (1993). "Schizophrenia: dopamine D1 receptor sequence is normal, but has DNA polymorphisms.". Neuropsychopharmacology 8 (2): 131–5. PMID 8471124.
- Albrecht FE, Drago J, Felder RA, et al. (1996). "Role of the D1A dopamine receptor in the pathogenesis of genetic hypertension.". J. Clin. Invest. 97 (10): 2283–8. doi:10.1172/JCI118670. PMC 507308. PMID 8636408. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=507308.
- Lee SH, Minowa MT, Mouradian MM (1996). "Two distinct promoters drive transcription of the human D1A dopamine receptor gene.". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (41): 25292–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.41.25292. PMID 8810292.
- Mayerhofer A, Hemmings HC, Snyder GL, et al. (1999). "Functional dopamine-1 receptors and DARPP-32 are expressed in human ovary and granulosa luteal cells in vitro.". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 84 (1): 257–64. doi:10.1210/jc.84.1.257. PMID 9920093.
- Wong AC, Shetreat ME, Clarke JO, Rayport S (1999). "D1- and D2-like dopamine receptors are co-localized on the presynaptic varicosities of striatal and nucleus accumbens neurons in vitro.". Neuroscience 89 (1): 221–33. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(98)00284-X. PMID 10051231.
- Jin H, Xie Z, George SR, O'Dowd BF (2000). "Palmitoylation occurs at cysteine 347 and cysteine 351 of the dopamine D(1) receptor.". Eur. J. Pharmacol. 386 (2-3): 305–12. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(99)00727-X. PMID 10618483.
- Li M, Bermak JC, Wang ZW, Zhou QY (2000). "Modulation of dopamine D(2) receptor signaling by actin-binding protein (ABP-280).". Mol. Pharmacol. 57 (3): 446–52. PMID 10692483.
- Lezcano N, Mrzljak L, Eubanks S, et al. (2000). "Dual signaling regulated by calcyon, a D1 dopamine receptor interacting protein.". Science 287 (5458): 1660–4. doi:10.1126/science.287.5458.1660. PMID 10698743.
- Ginés S, Hillion J, Torvinen M, et al. (2000). "Dopamine D1 and adenosine A1 receptors form functionally interacting heteromeric complexes.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (15): 8606–11. doi:10.1073/pnas.150241097. PMC 26995. PMID 10890919. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=26995.
External links
- "Dopamine Receptors: D1". IUPHAR Database of Receptors and Ion Channels. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. http://www.iuphar-db.org/GPCR/ReceptorDisplayForward?receptorID=2252.
- MeSH Receptors,+Dopamine+D1
Metabolites and
signaling moleculesOtherBile acid · Cannabinoid (CB1, CB2, GPR (18, 55, 119)) · EBI2 · Estrogen · Free fatty acid (1, 2, 3, 4) · Lactate · Lysophosphatidic acid (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) · Lysophospholipid (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8) · Niacin (1, 2) · Oxoglutarate · PAF · Sphingosine-1-phosphate (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) · SuccinatePeptideOtherAnaphylatoxin (C3a, C5a) · Angiotensin (1, 2) · Apelin · Bombesin (BRS3, GRPR, NMBR) · Bradykinin (B1, B2) · Chemokine · Cholecystokinin (A, B) · Endothelin (A, B) · Formyl peptide (1, 2, 3) · FSH · Galanin (1, 2, 3) · GHB receptor · Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (1, 2) · Ghrelin · Kisspeptin · Luteinizing hormone/choriogonadotropin · MAS (1, 1L, D, E, F, G, X1, X2, X3, X4) · Melanocortin (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) · MCHR (1, 2) · Motilin · Opioid (Delta, Kappa, Mu, Nociceptin & Zeta, but not Sigma) · Orexin (1, 2) · Oxytocin · Prokineticin (1, 2) · Prolactin-releasing peptide · Relaxin (1, 2, 3, 4) · Somatostatin (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) · Tachykinin (1, 2, 3) · Thyrotropin · Thyrotropin-releasing hormone · Urotensin-II · Vasopressin (1A, 1B, 2)MiscellaneousGPR (1, 3, 4, 6, 12, 15, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 25, 26, 27, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 37, 39, 42, 44, 45, 50, 52, 55, 61, 62, 63, 65, 68, 75, 77, 78, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 87, 88, 92, 101, 103, 109A, 109B, 119, 120, 132, 135, 137B, 139, 141, 142, 146, 148, 149, 150, 151, 152, 153, 160, 161, 162, 171, 173, 174, 176, 177, 182, 183)OtherClass B: Secretin like OtherBrain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor (1, 2, 3) · Cadherin (1, 2, 3) · Calcitonin · CALCRL · CD97 · Corticotropin-releasing hormone (1, 2) · EMR (1, 2, 3) · Glucagon (GR, GIPR, GLP1R, GLP2R) · Growth hormone releasing hormone · PACAPR1 · GPR · Latrophilin (1, 2, 3, ELTD1) · Methuselah-like proteins · Parathyroid hormone (1, 2) · Secretin · Vasoactive intestinal peptide (1, 2)Class C: Metabotropic
glutamate / pheromoneOtherClass F:
Frizzled / SmoothenedFrizzledSmoothenedB trdu: iter (nrpl/grfl/cytl/horl), csrc (lgic, enzr, gprc, igsr, intg, nrpr/grfr/cytr), itra (adap, gbpr, mapk), calc, lipd; path (hedp, wntp, tgfp+mapp, notp, jakp, fsap, hipp, tlrp) Categories:- Human proteins
- Transmembrane receptor stubs
- G protein coupled receptors
- Dihydrexidine derivatives
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.