- Fenoldopam
-
Fenoldopam 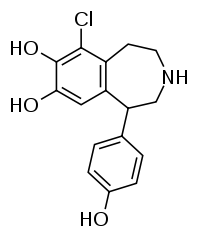
Systematic (IUPAC) name (RS)-6-chloro-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-3-benzazepine-7,8-diol Clinical data Trade names Corlopam AHFS/Drugs.com monograph Pregnancy cat. B Legal status ? Routes IV Pharmacokinetic data Metabolism Hepatic (CYP not involved) Half-life 5 minutes Excretion Renal (90%) and fecal (10%) Identifiers CAS number 67227-57-0 
ATC code C01CA19 PubChem CID 3341 DrugBank APRD00969 ChemSpider 3224 
UNII HA3R0MY016 
KEGG D07946 
ChEBI CHEBI:5002 
ChEMBL CHEMBL588 
Chemical data Formula C16H16ClNO3 Mol. mass 305.76 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Fenoldopam (Corlopam) is a drug and synthetic benzazepine derivative which acts as a peripheral selective D1 receptor weak partial agonist/antagonist and is used as an antihypertensive.[1] It was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in September 1997. [2]
Contents
Indications
Fenoldopam is used as an antihypertensive agent postoperatively, and also via IV to treat hypertensive crisis.[3] Since fenoldopam is the only intravenous agent that improves renal perfusion, it may be exceptionally beneficial in hypertensive patients with concomitant renal insufficiency. [4]
Pharmacology
By activating peripheral D1 receptors, fenoldopam causes arterial/arteriolar vasodilation leading to a decrease in blood pressure. It is particularly effective in dilating the renal, mesenteric, and coronary arteries, where D1.receptors are found.[3] It decreases afterload and also through specific dopamine receptors along the nephron promoting sodium excretion.[citation needed] In contrast to dopamine, it is a selective D1 receptor agonist with no effect on alpha or beta receptors. D1 receptor stimulation activates adenylyl cyclase and raises intracellular cyclic AMP, resulting in vasodilation of most arterial beds, especially renal, mesenteric, and coronary beds. The main effect is a significant reduction in systemic vascular resistance. Stimulation of dopamine-receptors in the kidneys not only improves renal blood flow, but also leads to increased sodium and water excretion. Thus fenoldopam is the only available intravenous agent that improves renal perfusion while it lowers blood pressure.[5] Fenoldopam has a rapid onset of action (4 minutes) and short duration of action (< 10 minutes) and a linear dose response relationship at usual clinical doses. [6]
Side effects
Adverse effects include headache, flushing, angina, hypotension, reflex tachycardia, and increased intraocular pressure.[3]
Contraindications
Contraindicated with patients who suffer from glaucoma.
References
- ^ Oliver WC, Nuttall GA, Cherry KJ, Decker PA, Bower T, Ereth MH (October 2006). "A comparison of fenoldopam with dopamine and sodium nitroprusside in patients undergoing cross-clamping of the abdominal aorta". Anesth. Analg. 103 (4): 833–40. doi:10.1213/01.ane.0000237273.79553.9e. PMID 17000789. http://www.anesthesia-analgesia.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=17000789.
- ^ http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/drugsatfda/index.cfm?fuseaction=Search.Label_ApprovalHistory accessed November 14, 2011
- ^ a b c Shen, Howard (2008). Illustrated Pharmacology Memory Cards: PharMnemonics. Minireview. p. 9. ISBN 1-59541-101-1.
- ^ USMLE WORLD 2009 Step1 QBanks, Pharmacology, Pharma50q, Q NO 18
- ^ USMLE WORLD 2009 Step1 QBanks, Pharmacology, Pharma50q, Q NO 18
- ^ Epstein, Murray MD, "Diagnosis and Management of Hypertensive Emergencies," clinical Cornerstone. Hypertension Vol2. No 1.
Sympatholytic (and closely related) antihypertensives (C02) Sympatholytics
(antagonize α-adrenergic
vasoconstriction)CentralAdrenergic release inhibitorsBethanidine • Bretylium • Debrisoquine • Guanadrel • Guanazodine • Guanethidine • Guanoclor • Guanoxan • Guanazodine • Guanoxabenz • GuanoxanImidazoline receptor agonistMecamylamine • Pentolinium • TrimethaphanPeripheralIndirectTyrosine hydroxylase inhibitorDirectNon-selective α blockerOther antagonists Endothelin antagonist (for PH)Dopaminergics Reuptake inhibitors PlasmalemmalDAT inhibitorsPiperazines: DBL-583 • GBR-12,935 • Nefazodone • Vanoxerine; Piperidines: BTCP • Desoxypipradrol • Dextromethylphenidate • Difemetorex • Ethylphenidate • Methylnaphthidate • Methylphenidate • Phencyclidine • Pipradrol; Pyrrolidines: Diphenylprolinol • Methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) • Naphyrone • Prolintane • Pyrovalerone; Tropanes: β-CPPIT • Altropane • Brasofensine • CFT • Cocaine • Dichloropane • Difluoropine • FE-β-CPPIT • FP-β-CPPIT • Ioflupane (123I) • Iometopane • RTI-112 • RTI-113 • RTI-121 • RTI-126 • RTI-150 • RTI-177 • RTI-229 • RTI-336 • Tenocyclidine • Tesofensine • Troparil • Tropoxane • WF-11 • WF-23 • WF-31 • WF-33; Others: Adrafinil • Armodafinil • Amfonelic acid • Amineptine • Benzatropine (Benztropine) • Bromantane • BTQ • BTS-74,398 • Bupropion (Amfebutamone) • Ciclazindol • Diclofensine • Dimethocaine • Diphenylpyraline • Dizocilpine • DOV-102,677 • DOV-21,947 • DOV-216,303 • Etybenzatropine (Ethylbenztropine) • EXP-561 • Fencamine • Fencamfamine • Fezolamine • GYKI-52,895 • Indatraline • Ketamine • Lefetamine • Levophacetoperane • LR-5182 • Manifaxine • Mazindol • Medifoxamine • Mesocarb • Modafinil • Nefopam • Nomifensine • NS-2359 • O-2172 • Pridefrine • Propylamphetamine • Radafaxine • SEP-225,289 • SEP-227,162 • Sertraline • Sibutramine • Tametraline • TripelennamineVMAT inhibitorsReleasing agents Morpholines: Fenbutrazate • Morazone • Phendimetrazine • Phenmetrazine; Oxazolines: 4-Methylaminorex (4-MAR, 4-MAX) • Aminorex • Clominorex • Cyclazodone • Fenozolone • Fluminorex • Pemoline • Thozalinone; Phenethylamines (also amphetamines, cathinones, phentermines, etc): 2-Hydroxyphenethylamine (2-OH-PEA) • 4-CAB • 4-Methylamphetamine (4-MA) • 4-Methylmethamphetamine (4-MMA) • Alfetamine • Amfecloral • Amfepentorex • Amfepramone • Amphetamine (Dextroamphetamine, Levoamphetamine) • Amphetaminil • β-Methylphenethylamine (β-Me-PEA) • Benzodioxolylbutanamine (BDB) • Benzodioxolylhydroxybutanamine (BOH) • Benzphetamine • Buphedrone • Butylone • Cathine • Cathinone • Clobenzorex • Clortermine • D-Deprenyl • Dimethoxyamphetamine (DMA) • Dimethoxymethamphetamine (DMMA) • Dimethylamphetamine • Dimethylcathinone (Dimethylpropion, metamfepramone) • Ethcathinone (Ethylpropion) • Ethylamphetamine • Ethylbenzodioxolylbutanamine (EBDB) • Ethylone • Famprofazone • Fenethylline • Fenproporex • Flephedrone • Fludorex • Furfenorex • Hordenine • Lophophine (Homomyristicylamine) • Mefenorex • Mephedrone • Methamphetamine (Desoxyephedrine, Methedrine; Dextromethamphetamine, Levomethamphetamine) • Methcathinone (Methylpropion) • Methedrone • Methoxymethylenedioxyamphetamine (MMDA) • Methoxymethylenedioxymethamphetamine (MMDMA) • Methylbenzodioxolylbutanamine (MBDB) • Methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA, tenamfetamine) • Methylenedioxyethylamphetamine (MDEA) • Methylenedioxyhydroxyamphetamine (MDOH) • Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) • Methylenedioxymethylphenethylamine (MDMPEA, homarylamine) • Methylenedioxyphenethylamine (MDPEA, homopiperonylamine) • Methylone • Ortetamine • Parabromoamphetamine (PBA) • Parachloroamphetamine (PCA) • Parafluoroamphetamine (PFA) • Parafluoromethamphetamine (PFMA) • Parahydroxyamphetamine (PHA) • Paraiodoamphetamine (PIA) • Paredrine (Norpholedrine, Oxamphetamine) • Phenethylamine (PEA) • Pholedrine • Phenpromethamine • Prenylamine • Propylamphetamine • Tiflorex (Flutiorex) • Tyramine (TRA) • Xylopropamine • Zylofuramine; Piperazines: 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-bromobenzylpiperazine (2C-B-BZP) • Benzylpiperazine (BZP) • Methoxyphenylpiperazine (MeOPP, paraperazine) • Methylbenzylpiperazine (MBZP) • Methylenedioxybenzylpiperazine (MDBZP, piperonylpiperazine); Others: 2-Amino-1,2-dihydronaphthalene (2-ADN) • 2-Aminoindane (2-AI) • 2-Aminotetralin (2-AT) • 4-Benzylpiperidine (4-BP) • 5-IAI • Clofenciclan • Cyclopentamine • Cypenamine • Cyprodenate • Feprosidnine • Gilutensin • Heptaminol • Hexacyclonate • Indanylaminopropane (IAP) • Indanorex • Isometheptene • Methylhexanamine • Naphthylaminopropane (NAP) • Octodrine • Phthalimidopropiophenone • Propylhexedrine (Levopropylhexedrine) • Tuaminoheptane (Tuamine)Enzyme inhibitors PAH inhibitors3,4-DihydroxystyreneTH inhibitorsNonselective: Benmoxin • Caroxazone • Echinopsidine • Furazolidone • Hydralazine • Indantadol • Iproclozide • Iproniazid • Isocarboxazid • Isoniazid • Linezolid • Mebanazine • Metfendrazine • Nialamide • Octamoxin • Paraxazone • Phenelzine • Pheniprazine • Phenoxypropazine • Pivalylbenzhydrazine • Procarbazine • Safrazine • Tranylcypromine; MAO-A selective: Amiflamine • Bazinaprine • Befloxatone • Befol • Brofaromine • Cimoxatone • Clorgiline • Esuprone • Harmala alkaloids • Methylene Blue • Metralindole • Minaprine • Moclobemide • Pirlindole • Sercloremine • Tetrindole • Toloxatone • Tyrima; MAO-B selective: D-Deprenyl • L-Deprenyl (Selegiline) • Ladostigil • Lazabemide • Milacemide • Pargyline • Rasagiline • SafinamideDBH inhibitorsOthers L-Phenylalanine → L-Tyrosine → L-DOPA (Levodopa)Ferrous iron (Fe2+) • Tetrahydrobiopterin • Vitamin B3 (Niacin, Nicotinamide → NADPH) • Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine, Pyridoxamine, Pyridoxal → Pyridoxal phosphate) • Vitamin B9 (Folic acid → Tetrahydrofolic acid) • Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid) • Zinc (Zn2+)OthersActivity enhancers: Benzofuranylpropylaminopentane (BPAP) • Phenylpropylaminopentane (PPAP); Toxins: Oxidopamine (6-Hydroxydopamine)List of dopaminergic drugs
This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
