- Dimethoxyamphetamine
-
Dimethoxyamphetamine 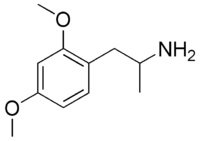
 2-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)propylamine
2-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)propylamineIdentifiers PubChem 91255 ChemSpider 82404 
ChEMBL CHEMBL280855 
Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- C1(=CC(=CC=C1CC(C)N)OC)OC
O(c1c(cccc1OC)CC(N)C)C
Properties Molecular formula C11H17NO2 Molar mass 195.26 g/mol  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references DMA, or dimethoxyamphetamine, is a series of lesser-known psychedelic drugs similar in structure to amphetamine and to trimethoxyamphetamine (TMA). They were first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and written up in his book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines i Have Known And Loved).[1] Very little data is known about their dangers or toxicity.
Contents
Positional isomers
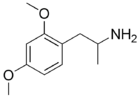
2,4-DMA
Dosage: 60 mg or greater
Duration: short
Effects: stimulative, amphetamine-like effects
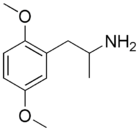
2,5-DMA
The DO analogue of 2C-H (DOH)
CAS Number: 2801-68-5
Dosage: 80–160 mg
Duration: 6–8 hours
Effects: Mydriasis, increase in heart rate
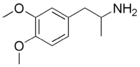
3,4-DMA
Dosage: unknown
Duration: unknown
Effects: Mescaline-like visuals
Note that two other positional isomers of dimethoxyamphetamine, 2,6-DMA and 3,5-DMA, have also been made, but these drugs have not been tested in humans and their effects are unknown. However, it is likely that these compounds would also produce amphetamine-like stimulation or possibly hallucinogenic effects.
See also
- 3-Methoxyamphetamine
- 4-Methoxyamphetamine
- Trimethoxyamphetamine
References
- ^ Shulgin, Alexander; Ann Shulgin (September 1991). PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story. Berkeley, California: Transform Press. ISBN 0-9630096-0-5. OCLC 25627628. http://www.erowid.org/library/books_online/pihkal/pihkal.shtml.
External links
- 2,4-DMA Entry in PiHKAL
- 2,4-DMA Entry in PiHKAL • info
- 2,5-DMA Entry in PiHKAL
- 2,5-DMA Entry in PiHKAL • info
- 3,4-DMA Entry in PiHKAL
- 3,4-DMA Entry in PiHKAL • info
Categories:- Amphetamines
- Phenol ethers
- C1(=CC(=CC=C1CC(C)N)OC)OC
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.