- Stimulant
-
Stimulants (also referred to as psychostimulants) are psychoactive drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both. Examples of these kinds of effects may include enhanced alertness, wakefulness, and locomotion, among others. Due to their effects typically having an "up" quality to them, stimulants are also occasionally referred to as "uppers". Depressants or "downers", which decrease mental and/or physical function, are in stark contrast to stimulants and are considered to be their functional opposites. Stimulants are widely used throughout the world as prescription medicines and as illicit substances of recreational use or abuse.
Contents
Effects
Stimulants (analeptics) produce a variety of different kinds of effects by enhancing the activity of the central and peripheral nervous systems. Common effects, which vary depending on the substance in question, may include enhanced alertness, awareness, wakefulness, endurance, productivity, and motivation, increased arousal, locomotion, heart rate, and blood pressure, and the perception of a diminished requirement for food and sleep. Many stimulants are also capable of improving mood and relieving anxiety, and some can even induce feelings of euphoria. It should be noted, however, that many of these drugs are also capable of causing anxiety and heart failure, even the ones that may paradoxically reduce it to a degree at the same time. Stimulants exert their effects through a number of different pharmacological mechanisms, the most prominent of which include facilitation of norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and/or dopamine activity (e.g., via monoamine transporter inhibition or reversal[1]), adenosine receptor antagonism, and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonism.
Indications
Stimulants are used both individually and clinically for therapeutic purposes in the treatment of a number of indications, including the following:
- To counteract lethargy and fatigue throughout the day while at work or while doing other activities.
- To reduce sleepiness and to keep the person awake when necessary, as well as to treat narcolepsy.
- To decrease appetite and promote weight loss, as well as to treat obesity.
- To improve concentration and focus while at work or school, especially for those with attentional disorders such as ADHD.
- Occasionally, they are also used off label to treat clinical depression, more particularly, non-typical depression and treatment-resistant depression.
Types
Xanthines
Theobromine
Theophylline
Caffeine
Caffeine is a mild stimulant compound that is found naturally in coffee, tea, and to a lesser degree, in cocoa or chocolate. It is included in many soft drinks, as well as a larger amount in energy drinks. Caffeine is the world's most widely used psychoactive drug and by far the most common stimulant. The vast majority (over 85%) of people in the United States consume caffeine on a daily basis. Few jurisdictions restrict its sale and use. Caffeine is also included in some medications, usually for the purpose of enhancing the effect of the primary ingredient, or reducing one of its side effects (especially drowsiness). Tablets containing standardized doses of caffeine are also widely available.
Nicotine
Nicotine is the active chemical constituent in tobacco, which is available in many forms, including cigarettes, cigars, chewing tobacco, and smoking cessation aids such as nicotine patches and nicotine gum. Nicotine is used widely throughout the world for its stimulating effects.
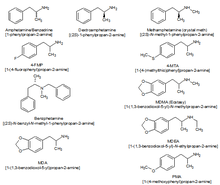
Amphetamines
Amphetamines are a group of phenylethylamine stimulants such as amphetamine and methamphetamine. Like NDRIs, amphetamine increases the levels of norepinephrine and dopamine in the brain via reuptake inhibition; however, the more important mechanism by which amphetamines cause stimulation is through the direct release of these catecholamines from storage vesicles in cells. Amphetamines are known to cause elevated mood and euphoria as well as rebound depression and anxiety.[2]
Amphetamines are often used for their therapeutic effects; physicians occasionally prescribe amphetamines to treat major depression, where subjects do not respond well to traditional SSRI medications, and numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of drugs such as Adderall in controlling symptoms associated with ADD/ADHD. In rare cases, ADD/ADHD patients who are not responding sufficiently to traditional amphetamines are prescribed dextrorotary methamphetamine.[3] Due to their availability and fast-acting effects, amphetamines are prime candidates for abuse.[4]
MDMA ("Ecstasy")
Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), known by its common street name "Ecstasy", is an illicit substance that typically comes in either tablet, capsule, or powder/crystal form. It had a medical application as a treatment for depression until 1985 when the DEA placed MDMA into schedule 1, prohibiting most medical studies and applications. Notably, MDMA is also unique and very popular for its entactogenic properties. The stimulant effects of MDMA include hypertension, anorexia (appetite loss), euphoria, social disinhibition, insomnia (or enhanced wakefulness), improved energy, increased arousal, and increased perspiration, among others.
Cocaine
Cocaine is made from the leaves of the coca shrub, which grows in the mountain regions of South American countries such as Bolivia, Colombia, and Peru. In Europe, North America, and in some parts of Asia, the most common form of cocaine is a white crystalline powder. Cocaine is a stimulant but is not normally prescribed therapeutically for its stimulant properties, although it sees clinical use as a local anesthetic, particularly in ophthalmology. Most cocaine use is recreational and its abuse potential is high, and so its sale and possession are strictly controlled in most jurisdictions. Other tropane derivative drugs related to cocaine are also known such as troparil and lometopane but have not been widely sold or used recreationally.[5]
NRIs & NDRIs
These drugs inhibit the reuptake of norepinephrine and/or dopamine, resulting in increased extracellular levels and therefore enhanced neurotransmission, ultimately producing a stimulant effect. Many of these compounds are used as ADHD medications and antidepressants. The best-known NDRI is bupropion (Wellbutrin, Zyban), and the two best-known NRIs are atomoxetine (Strattera) and reboxetine (Edronax). Many of these drugs have a considerably lower abuse potential in comparison to other stimulants like the amphetamines and cocaine.
Methylphenidate
Methylphenidate (MPH; Ritalin, Concerta, Metadate, or Methylin) is a drug approved for treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, and narcolepsy. It belongs to the piperidine class of compounds and increases the levels of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain through reuptake inhibition of the monoamine transporters. It also increases the release of dopamine and norepinephrine. MPH possesses structural similarities to amphetamine, and, though it is less potent, its pharmacological effects are even more closely related to those of cocaine.[6][7][8]
Modafinil, Adrafinil, and Armodafinil
Modafinil (Provigil/Alertec/Modavigil) is an analeptic drug approved by the (FDA) for the treatment of narcolepsy, shift work sleep disorder, and excessive daytime sleepiness associated with obstructive sleep apnea.
Modafinil, like other stimulants, increases the release of monoamines but also elevates hypothalamic histamine levels, leading some researchers to consider Modafinil a "wakefulness promoting agent" rather than a classic amphetamine-like stimulant.
Modafinil has been shown to be effective in the treatment of Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), depression, cocaine addiction, Parkinson's Disease, schizophrenia, shift workers' sleep disorder and disease-related fatigue.
Adrafinil is the prodrug of Modafinil, and is metabolized into it in about one hour, when taken on an empty stomach.
Armodafinil is a new version of Modafinil.
Ampakines
Recently, there have been improvements in the area of stimulant pharmacology, producing a class of chemicals known as ampakines, or eugeroics, (good arousal). These stimulants tend to increase alertness without the peripheral (body) effects or addiction/tolerance/abuse potential of the traditional stimulants. They have minimal effect on sleep structure, and do not cause rebound hypersomnolence or "come down" effects. Ampakines such as ampalex and CX717 have been developed but are still in clinical trials and have not yet been sold commercially. Another compound with similar effects to these drugs is carphedon, which is sold as a general stimulant in Russia under the brand name Phenotropil.
Yohimbine
Yohimbine is a psychoactive drug of the tryptamine chemical class with stimulant and aphrodisiac effects. Yohimbine is sometimes used to remedy Type-2 Diabetes in animals and humans that carry the polymorphisms of the α2A-adrenergic receptor gene.[9]
Abuse
Abuse of central nervous system stimulants is common. Addiction to CNS stimulants can quickly lead to medical, psychiatric and psychosocial deterioration. Drug tolerance, dependence, sensitisation as well as a withdrawal syndrome can occur.[10]
Testing
The presence of stimulants in the body may be tested by a variety of procedures. Serum and urine are the common sources of testing material although saliva is sometimes used. Commonly used tests include chromatography, immunologic assay and mass spectrometry.[11]
See also
- Pentorex
- Depressants
- Hallucinogens
References
- ^ Riddle EL, Fleckenstein AE, Hanson GR (2005). "Role of monoamine transporters in mediating psychostimulant effects". The AAPS journal 7 (4): E847–51. doi:10.1208/aapsj070481. PMC 2750953. PMID 16594636. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2750953.
- ^ P Knapp (1952). "Amphetamine and addiction". Journal of Nervous and Mental Disorders 115: 406–409.
- ^ Huffman, JC; Stern, TA (2004). "Using Psychostimulants to Treat Depression in the Medically Ill". Primary care companion to the Journal of clinical psychiatry 6 (1): 44–46. PMC 427614. PMID 15486600. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=427614.
- ^ Efforts of the National Institute on Drug Abuse to Prevent and Treat Prescription Drug Abuse, Testimony Before the Subcommittee on Criminal Justice, Drug Policy, and Human Resources Committee on Government Reform, United States House of Representatives, July 26, 2006
- ^ AJ Giannini, WC Price (1986). "Contemporary drugs of abuse". American Family Physician 33: 207–213.
- ^ "Ritalin & Cocaine: The Connection and the Controversy"
- ^ "Psychiatric nursing: contemporary practice"
- ^ "Why isn't methylphenidate more addictive?"[dead link]
- ^ Rosengren, A. H.; Jokubka, R.; Tojjar, D.; Granhall, C.; Hansson, O.; Li, D.-Q.; Nagaraj, V.; Reinbothe, T. M. et al. (2009). "Overexpression of Alpha2A-Adrenergic Receptors Contributes to Type 2 Diabetes". Science 327 (5962): 217–20. doi:10.1126/science.1176827. PMID 19965390.
- ^ Dackis CA, Gold MS (1990). "Addictiveness of central stimulants". Adv Alcohol Subst Abuse 9 (1–2): 9–26. doi:10.1300/J251v09n01_02. PMID 1974121.
- ^ AJ Giannini. Drug Abuse. Los Angeles, Health Information Press, 1999, pp.203-208
External links
- Long Island Council on Alcohol & Drug Dependence - About Drugs - Stimulants
- Online - Publications - Drugs of Abuse - Stimulants
- Asia & Pacific Amphetamine-Type Stimulants Information Centre (APAIC)
Stimulants (N06B) Adamantanes Adaphenoxate • Adapromine • Amantadine • Bromantane • Chlodantane • Gludantane • Memantine • Midantane
Adenosine antagonists 8-Chlorotheophylline • 8-Cyclopentyltheophylline • 8-Phenyltheophylline • Aminophylline • Caffeine • CGS-15943 • Dimethazan • Paraxanthine • SCH-58261 • Theobromine • TheophyllineAlkylamines Arylcyclohexylamines Benocyclidine • Dieticyclidine • Esketamine • Eticyclidine • Gacyclidine • Ketamine • Phencyclamine • Phencyclidine • Rolicyclidine • Tenocyclidine • Tiletamine
Benzazepines 6-Br-APB • SKF-77434 • SKF-81297 • SKF-82958
Cholinergics A-84543 • A-366,833 • ABT-202 • ABT-418 • AR-R17779 • Altinicline • Anabasine • Arecoline • Cotinine • Cytisine • Dianicline • Epibatidine • Epiboxidine • GTS-21 • Ispronicline • Nicotine • PHA-543,613 • PNU-120,596 • PNU-282,987 • Pozanicline • Rivanicline • Sazetidine A • SIB-1553A • SSR-180,711 • TC-1698 • TC-1827 • TC-2216 • TC-5619 • Tebanicline • UB-165 • Varenicline • WAY-317,538
Convulsants Anatoxin-a • Bicuculline • DMCM • Flurothyl • Gabazine • Pentetrazol • Picrotoxin • Strychnine • Thujone
Eugeroics Adrafinil • Armodafinil • CRL-40941 • Modafinil
Oxazolines 4-Methylaminorex • Aminorex • Clominorex • Cyclazodone • Fenozolone • Fluminorex • Pemoline • Thozalinone
Phenethylamines 1-(4-Methylphenyl)-2-aminobutane • 1-Phenyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)pentan-3-one • 1-Methylamino-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)propane • 2-Fluoroamphetamine • 2-Fluoromethamphetamine • 2-OH-PEA • 2-Phenyl-3-aminobutane • 2-Phenyl-3-methylaminobutane • 2,3-MDA • 3-Fluoroamphetamine • 3-Fluoroethamphetamine • 3-Fluoromethcathinone • 3-Methoxyamphetamine • 3-Methylamphetamine • 3,4-DMMC • 4-BMC • 4-Ethylamphetamine • 4-FA • 4-FMA • 4-MA • 4-MMA • 4-MTA • 6-FNE • Alfetamine • α-Ethylphenethylamine • Amfecloral • Amfepentorex • Amfepramone • Amidephrine • Amphetamine (Dextroamphetamine, Levoamphetamine) • Amphetaminil • Arbutamine • β-Methylphenethylamine • β-Phenylmethamphetamine • Benfluorex • Benzedrone • Benzphetamine • BDB (J) • BOH (Hydroxy-J) • BPAP • Buphedrone • Bupropion (Amfebutamone) • Butylone • Cathine • Cathinone • Chlorphentermine • Cinnamedrine • Clenbuterol • Clobenzorex • Cloforex • Clortermine • D-Deprenyl • Denopamine • Dimethoxyamphetamine • Dimethylamphetamine • Dimethylcathinone (Dimethylpropion, Metamfepramone) • Dobutamine • DOPA (Dextrodopa, Levodopa) • Dopamine • Dopexamine • Droxidopa • EBDB (Ethyl-J) • Ephedrine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Epinine (Deoxyepinephrine) • Etafedrine • Ethcathinone (Ethylpropion) • Ethylamphetamine (Etilamfetamine) • Ethylnorepinephrine (Butanefrine) • Ethylone • Etilefrine • Famprofazone • Fenbutrazate • Fencamine • Fenethylline • Fenfluramine (Dexfenfluramine) • Fenmetramide • Fenproporex • Flephedrone • Fludorex • Furfenorex • Gepefrine • HMMA • Hordenine • Ibopamine • IMP • Indanylamphetamine • Isoetarine • Isoethcathinone • Isoprenaline (Isoproterenol) • L-Deprenyl (Selegiline) • Lefetamine • Lisdexamfetamine • Lophophine (Homomyristicylamine) • Manifaxine • MBDB (Methyl-J; "Eden") • MDA (Tenamfetamine) • MDBU • MDEA ("Eve") • MDMA ("Ecstasy", "Adam") • MDMPEA (Homarylamine) • MDOH • MDPR • MDPEA (Homopiperonylamine) • Mefenorex • Mephedrone • Mephentermine • Metanephrine • Metaraminol • Methamphetamine (Desoxyephedrine, Methedrine; Dextromethamphetamine, Levomethamphetamine) • Methoxamine • Methoxyphenamine • MMA • Methcathinone (Methylpropion) • Methedrone • Methoxyphenamine • Methylone • MMDA • MMDMA • MMMA • Morazone • N-Benzyl-1-phenethylamine • N,N-Dimethylphenethylamine • Naphthylamphetamine • Nisoxetine • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Norfenefrine • Norfenfluramine • Normetanephrine • Octopamine • Orciprenaline • Ortetamine • Oxilofrine • Paredrine (Norpholedrine, Oxamphetamine, Mycadrine) • PBA • PCA • PHA • Pargyline • Pentorex (Phenpentermine) • Pentylone • Phendimetrazine • Phenmetrazine • Phenpromethamine • Phentermine • Phenylalanine • Phenylephrine (Neosynephrine) • Phenylpropanolamine • Pholedrine • PIA • PMA • PMEA • PMMA • PPAP • Prenylamine • Propylamphetamine • Pseudoephedrine • Radafaxine • Ropinirole • Salbutamol (Albuterol; Levosalbutamol) • Sibutramine • Synephrine (Oxedrine) • Theodrenaline • Tiflorex (Flutiorex) • Tranylcypromine • Tyramine • Tyrosine • Xamoterol • Xylopropamine • Zylofuramine
Piperazines Piperidines 1-Benzyl-4-(2-(diphenylmethoxy)ethyl)piperidine • 1-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-1-(piperidin-2-yl)butane • 2-Benzylpiperidine • 2-Methyl-3-phenylpiperidine • 3,4-Dichloromethylphenidate • 4-Benzylpiperidine • 4-Methylmethylphenidate • Desoxypipradrol • Difemetorex • Diphenylpyraline • Ethylphenidate • Methylnaphthidate • Methylphenidate (Dexmethylphenidate) • N-Methyl-3β-propyl-4β-(4-chlorophenyl)piperidine • Nocaine • Phacetoperane • Pipradrol • SCH-5472
Pyrrolidines 2-Diphenylmethylpyrrolidine • α-PPP • α-PBP • α-PVP • Diphenylprolinol • MDPPP • MDPBP • MDPV • MPBP • MPHP • MPPP • MOPPP • Naphyrone • PEP • Prolintane • Pyrovalerone
Tropanes 3-CPMT • 3'-Chloro-3α-(diphenylmethoxy)tropane • 3-Pseudotropyl-4-fluorobenzoate • 4'-Fluorococaine • AHN-1055 • Altropane (IACFT) • Brasofensine • CFT (WIN 35,428) • β-CIT (RTI-55) • Cocaethylene • Cocaine • Dichloropane (RTI-111) • Difluoropine • FE-β-CPPIT • FP-β-CPPIT • Ioflupane (123I) • Norcocaine • PIT • PTT • RTI-31 • RTI-32 • RTI-51 • RTI-105 • RTI-112 • RTI-113 • RTI-117 • RTI-120 • RTI-121 (IPCIT) • RTI-126 • RTI-150 • RTI-154 • RTI-171 • RTI-177 • RTI-183 • RTI-193 • RTI-194 • RTI-199 • RTI-202 • RTI-204 • RTI-229 • RTI-241 • RTI-336 • RTI-354 • RTI-371 • RTI-386 • Salicylmethylecgonine • Tesofensine • Troparil (β-CPT, WIN 35,065-2) • Tropoxane • WF-23 • WF-33 • WF-60
Others 1-(Thiophen-2-yl)-2-aminopropane • 2-Amino-1,2-dihydronaphthalene • 2-Aminoindane • 2-Aminotetralin • 2-MDP • 2-Phenylcyclohexylamine • 2-Phenyl-3,6-dimethylmorpholine • 3-Benzhydrylmorpholine • 3,3-Diphenylcyclobutanamine • 5-(2-Aminopropyl)indole • 5-Iodo-2-aminoindane • AL-1095 • Amfonelic acid • Amineptine • Amiphenazole • Atipamezole • Atomoxetine (Tomoxetine) • Bemegride • Benzydamine • BTQ • BTS 74,398 • Carphedon • Ciclazindol • Cilobamine • Clofenciclan • Cropropamide • Crotetamide • Cypenamine • D-161 • Diclofensine • Dimethocaine • Efaroxan • Etamivan • EXP-561 • Fencamfamine • Fenpentadiol • Feprosidnine • G-130 • Gamfexine • Gilutensin • GSK1360707F • GYKI-52895 • Hexacyclonate • Idazoxan • Indanorex • Indatraline • JNJ-7925476 • JZ-IV-10 • Lazabemide • Leptacline • Levopropylhexedrine • Lomevactone • LR-5182 • Mazindol • Meclofenoxate • Medifoxamine • Mefexamide • Mesocarb • Methastyridone • Methiopropamine • N-Methyl-3-phenylnorbornan-2-amine • Nefopam • Nikethamide • Nomifensine • O-2172 • Oxaprotiline • Phthalimidopropiophenone • PNU-99,194 • Propylhexedrine • PRC200-SS • Rasagiline • Rauwolscine • Rubidium chloride • Setazindol • Tametraline • Tandamine • Trazium • UH-232 • Yohimbine
See also Sympathomimetic aminesPsychostimulants, agents used for ADHD, and nootropics (N06B) Centrally acting sympathomimetics Xanthine derivatives Glutamate receptor CX-516 • CX-546 • CX-614 • CX-691 • CX-717 • IDRA-21 • LY-404,187 • LY-503,430 • PEPA • S-18986 • Sunifiram • UnifiramEugeroics / Benzhydryl compounds Histamine H3 receptor antagonists GABAA α5 inverse agonists Dopamine D1 receptor agonists α7 nicotinic agonists / PAMs AR-R17779 • PNU-282,987 • SSR-180,711Prolyl endopeptidase inhibitors S-17092Alpha-adrenergic agonists Other psychostimulants and nootropics Acetylcarnitine • Adafenoxate • Bifemelane • Carbenoxolone • Citicoline • Cyprodenate • Ensaculin • Idebenone • Ispronicline • Deanol • Dimebon • Fipexide • Leteprinim • Linopirdine • Meclofenoxate • Nizofenone • P7C3 • Pirisudanol • Pyritinol • Rubidium • Sulbutiamine • Taltirelin • Tricyanoaminopropene • VinpocetineAntidepressants (N06A) Specific reuptake inhibitors (RIs), enhancers (REs), and releasing agents (RAs) Alaproclate • Citalopram • Escitalopram • Femoxetine • Fluoxetine# • Fluvoxamine • Indalpine • Ifoxetine • Litoxetine • Lubazodone • Panuramine • Paroxetine • Pirandamine • Seproxetine • Sertraline# • Vilazodone • Zimelidine‡Bicifadine • Clovoxamine • Desvenlafaxine • Duloxetine • Levomilnacipran • Eclanamine • Milnacipran • Sibutramine • VenlafaxineSerotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitors (SNDRIs)Brasofensine • BTS-74,398 • Cocaine • Diclofensine • DOV-21,947 • DOV-102,677 • DOV-216,303 • EXP-561 • Fezolamine • JNJ-7925476 • NS-2359 • PRC200-SS • Pridefine • SEP-225,289 • SEP-227,162 • TesofensineAmedalin • Atomoxetine/Tomoxetine • Binedaline • Ciclazindol • Daledalin • Esreboxetine • Lortalamine • Mazindol • Nisoxetine • Reboxetine • Talopram • Talsupram • Tandamine • ViloxazineDopamine reuptake inhibitors (DRIs)Amineptine • Bupropion/Amfebutamone# • Cilobamine • Manifaxine • Methylphenidate • Nomifensine • Radafaxine • TametralineNorepinephrine-dopamine releasing agents (NDRAs)Serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine releasing agents (SNDRAs)OthersReceptor antagonists and/or reuptake inhibitors Serotonin antagonists and reuptake inhibitors (SARIs)Serotonin modulators and stimulators (SMSs)VortioxetineTricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants (TCAs/TeCAs) TricyclicsAmezepine • Amineptine • Amitriptyline# • Amitriptylinoxide • Azepindole • Butriptyline • Cianopramine • Clomipramine • Cotriptyline • Cyanodothiepin • Demexiptiline • Depramine/Balipramine • Desipramine • Dibenzepin • Dimetacrine • Dosulepin/Dothiepin • Doxepin • Enprazepine • Fluotracen • Hepzidine • Homopipramol • Imipramine • Imipraminoxide • Intriptyline • Iprindole • Ketipramine • Litracen • Lofepramine • Losindole • Mariptiline • Melitracen • Metapramine • Mezepine • Naranol • Nitroxazepine • Nortriptyline • Noxiptiline • Octriptyline • Opipramol • Pipofezine • Propizepine • Protriptyline • Quinupramine • Tampramine • Tianeptine • Tienopramine • Trimipramine;7-OH-Amoxapine • Amoxapine • Aptazapine • Azipramine • Ciclazindol • Ciclopramine • Esmirtazapine • Loxapine • Maprotiline • Mazindol • Mianserin • Mirtazapine • Oxaprotiline • Setiptiline/TeciptilineMonoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) NonselectiveIrreversible: Benmoxin • Echinopsidine • Iproclozide • Iproniazid • Isocarboxazid • Mebanazine • Metfendrazine • Nialamide • Octamoxin • Phenelzine • Pheniprazine • Phenoxypropazine • Pivalylbenzhydrazine • Safrazine • Tranylcypromine; Reversible: Caroxazone • Paraxazone;MAOA-SelectiveIrreversible: Clorgiline; Reversible: Amiflamine • Bazinaprine • Befloxatone • Befol • Brofaromine • Cimoxatone • Esuperone • Harmala Alkaloids (Harmine, Harmaline, Tetrahydroharmine, Harman, Norharman, etc) • Methylene Blue • Metralindole • Minaprine • Moclobemide • Pirlindole • Sercloremine • Tetrindole • Toloxatone • Tyrima;MAOB-SelectiveIrreversible: Ladostigil • Mofegiline • Pargyline • Rasagiline • Selegiline; Reversible: Lazabemide • MilacemideAzapirones and other 5-HT1A receptor agonists Alnespirone • Aripiprazole • Befiradol • Buspirone • Eptapirone • Flesinoxan • Flibanserin • Gepirone • Ipsapirone • Oxaflozane • Tandospirone • Vilazodone • ZalospironeAnxiolytics (N05B) GABAA PAMs Adinazolam • Alprazolam • Bretazenil • Bromazepam • Camazepam • Chlordiazepoxide • Clobazam • Clonazepam • Clorazepate • Clotiazepam • Cloxazolam • Diazepam • Ethyl Loflazepate • Etizolam • Fludiazepam • Halazepam • Imidazenil • Ketazolam • Lorazepam • Medazepam • Nordazepam • Oxazepam • Pinazepam • PrazepamAbecarnil • Adipiplon • Alpidem • CGS-8216 • CGS-9896 • CGS-13767 • CGS-20625 • Divaplon • ELB-139 • Fasiplon • GBLD-345 • Gedocarnil • L-838,417 • NS-2664 • NS-2710 • Ocinaplon • Pagoclone • Panadiplon • Pipequaline • RWJ-51204 • SB-205,384 • SL-651,498 • Taniplon • TP-003 • TP-13 • TPA-023 • Y-23684 • ZK-93423PyrazolopyridinesOthersChlormezanone • Ethanol (Alcohol) • Etifoxine • Kavalactones (Kava Kava) • Skullcap • Valerenic Acid (Valerian)α2δ VDCC Blockers 5-HT1A Agonists H1 Antagonists Diphenylmethanes: Captodiame • Hydroxyzine; Others: Brompheniramine • Chlorpheniramine • PheniramineCRH1 Antagonists NK2 Antagonists MCH1 antagonists ATC-0175 • SNAP-94847mGluR2/3 Agonists mGluR5 NAMs TSPO agonists σ1 agonists Afobazole • OpipramolOthers Benzoctamine • Carbetocin • Demoxytocin • Mephenoxalone • Mepiprazole • Oxanamide • Oxytocin • Promoxolane • Tofisopam • Trimetozine • WAY-267,464Pharmacology: major drug groups Gastrointestinal tract/metabolism (A) stomach acid (Antacids, H2 antagonists, Proton pump inhibitors) • Antiemetics • Laxatives • Antidiarrhoeals/Antipropulsives • Anti-obesity drugs • Anti-diabetics • Vitamins • Dietary mineralsBlood and blood forming organs (B) Cardiovascular system (C) cardiac therapy/antianginals (Cardiac glycosides, Antiarrhythmics, Cardiac stimulants)
Antihypertensives • Diuretics • Vasodilators • Beta blockers • Calcium channel blockers • renin-angiotensin system (ACE inhibitors, Angiotensin II receptor antagonists, Renin inhibitors)
Antihyperlipidemics (Statins, Fibrates, Bile acid sequestrants)Skin (D) Genitourinary system (G) Endocrine system (H) Hypothalamic-pituitary hormones • Corticosteroids (Glucocorticoids, Mineralocorticoids) • Sex hormones • Thyroid hormones/Antithyroid agentsInfections and infestations (J, P, QI) Antimicrobials: Antibacterials (Antimycobacterials) • Antifungals • Antivirals • Antiparasitics (Antiprotozoals, Anthelmintics, Ectoparasiticides) • IVIG • VaccinesMalignant disease (L01-L02) Immune disease (L03-L04) Muscles, bones, and joints (M) Brain and nervous system (N) Analgesics • Anesthetics (General, Local) • Anorectics • Anti-ADHD Agents • Antiaddictives • Anticonvulsants • Antidementia Agents • Antidepressants • Antimigraine Agents • Antiparkinson's Agents • Antipsychotics • Anxiolytics • Depressants • Entactogens • Entheogens • Euphoriants • Hallucinogens (Psychedelics, Dissociatives, Deliriants) • Hypnotics/Sedatives • Mood Stabilizers • Neuroprotectives • Nootropics • Neurotoxins • Orexigenics • Serenics • Stimulants • Wakefulness-Promoting AgentsRespiratory system (R) Sensory organs (S) Other ATC (V) Recreational drug use Major recreational drugs StimulantsAmphetamine · Arecoline (Areca) · Betel · Caffeine (Coffee · Tea) · Cathinone (Khat) · Cocaine (Coca) · Ephedrine (Ephedra) · Mephedrone · Methamphetamine · Methylphenidate · Nicotine (Tobacco) · Theobromine (Cocoa)EntactogensHallucinogensBufotenin ( Psychoactive toads · Vilca · Yopo) · DMT (Ayahuasca) · LSA · LSD-25 · Mescaline (Peruvian Torch · Peyote · San Pedro) · Psilocybin / Psilocin (Psilocybin mushrooms)DXM · Inhalants (Nitrous oxide · alkyl nitrites – poppers, such as amyl nitrite) · Ketamine · Methoxetamine · Muscimol (Amanita muscaria) · PCP · Salvinorin A (Salvia divinorum)Atropine and Scopolamine (Datura · Deadly Nightshade · Henbane · Mandrake) · Dimenhydrinate · DiphenhydramineCannabinoids
Drug subculture 420 · Cannabis cultivation · Cannabis smoking · Legal history of cannabis in the United States · Legality of cannabis · Marijuana Policy Project · Medical cannabis · NORML · Religious and spiritual use of cannabis · Stoner filmOtherProblems with drug use Abuse · Dependence (Prevention · Opioid replacement therapy · Rehabilitation · Responsible use) · Drug-related crime · Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder · Illegal drug trade · Long-term effects of cannabis · Neurotoxicity · OverdoseLegality of drug use InternationalState levelDrug policy
by countryAustralia · Canada · Germany · Netherlands · Portugal · Sweden · Switzerland · Soviet Union · United States (Just Say No · Office of National Drug Control Policy · School district drug policies · California · Colorado · Maryland · Virginia)OtherLists of countries by... Alcohol consumption · Cannabis legality (Annual use · Lifetime use) · Cigarette consumption · Cocaine use · Opiates useCategories:- Stimulants
- Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.