- Ergine
-
Ergine 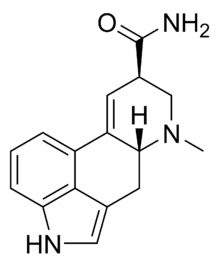
Systematic (IUPAC) name (8β)-9,10-didehydro-6-methyl-
ergoline-8-carboxamideClinical data Pregnancy cat. X [1] Legal status ? (UK) Schedule III (US) Routes Oral, Intramuscular Pharmacokinetic data Metabolism hepatic Excretion renal Identifiers CAS number 478-94-4 
ATC code None PubChem CID 442072 ChemSpider 390611 
ChEBI CHEBI:4819 
ChEMBL CHEMBL227213 
Synonyms LSA, d-lysergic acid amide, d-lysergamide, Ergine, and LA-111 Chemical data Formula C16H17N3O Mol. mass 267.326 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Ergine, also known as d-lysergic acid amide (LSA), d-lysergamide, and LA-111, is an alkaloid of the ergoline family that occurs in various species of vines of the Convolvulaceae and some species of fungi. As the dominant alkaloid in the hallucinogenic seeds of Rivea corymbosa (ololiuhqui), Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian baby woodrose) and Ipomoea tricolor (morning glories, tlitliltzin), it is often stated that ergine and/or isoergine (its epimer) is responsible for the psychedelic activity. In fact, the effects of synthetic LSA and iso-LSA are not particularly psychedelic, see Mixing the Kykeon below for a summary of human trials, and Chapter 17 and entry #26 of TiHKAL for further discussion. As a precursor to LSD, ergine is a DEA schedule III drug in the United States and a Class A drug in the UK.
Contents
History
A traditional use of morning glory seeds by Mexican Native Americans was first described by Richard Schultes in 1941 in a short report documenting their use going back to Aztec times (cited in TiHKAL by Alexander Shulgin). Further research was published in 1960, when Don Thomes MacDougall reported that the seeds of Ipomoea tricolor were used as sacraments by certain Zapotecs, sometimes in conjunction with the seeds of Rivea corymbosa, another species which has a similar chemical composition, with lysergol instead of ergometrine. Ergine was assayed for human activity by Albert Hofmann in self-trials in 1947, well before it was known to be a natural compound. Intramuscular administration of a 500 microgram dose led to a tired, dreamy state, with an inability to maintain clear thoughts. After a short period of sleep the effects were gone, and normal baseline was recovered within five hours.[2]
In 1956 the Central Intelligence Agency conducted research on the psychedelic properties of the ergine in the seeds of Rivea corymbosa, as Subproject 22 of MKULTRA.
Shamanic stories say ipomoea purpurea seeds, when swallowed or chewed, may incite a mild trip where synesthesia occurs and eye imagery is enhanced.[3]
Natural occurrence
Ergine has been found in high concentrations of 20 µg/g dry weight in the grass Stipa robusta (sleepygrass) infected with an Acremonium endophytic fungus together with other ergot alkaloids.[4]
It is also found in the seeds of several varieties of Morning Glories in concentrations of approximately 10 µg per seed, as well as Hawaiian Baby Woodrose seeds, at a concentration of around .3%.
Extraction
LSA can be extracted from morning glory (Ipomoea spp.) seeds[5] or Hawaiian baby woodrose.[6]
See also
- List of Entheogens
- Lysergic acid
- List of psychedelic plants
- Tlitliltzin (Ipomoea violacea)
References
Smith, Sydney; Timmis, Geoffrey M. (1932). "98. The Alkaloids of Ergot. Part III. Ergine, a New Base obtained by the Degradation of Ergotoxine and Ergotinine". J. Chem. Soc. 1932: 763–766. doi:10.1039/JR9320000763.
Powell, William (2002). The Anarchist Cookbook. Ozark Press,LLC. pp. 44. ISBN 0848811305.
References
- ^ Erowid (04-15-07). "Erowid Morning Glory Basics". http://www.erowid.org/plants/morning_glory/morning_glory_basics.shtml.
- ^ Alexander Shulgin. "TiHKAL #26". http://www.erowid.org/library/books_online/tihkal/tihkal26.shtml.
- ^ http://www.erowid.org/chemicals/lsd/lsd_faq2.shtml
- ^ Petroski RJ, Powell RG, Clay K (1992). "Alkaloids of Stipa robusta (sleepygrass) infected with an Acremonium endophyte". Nat. Toxins 1 (2): 84–88. doi:10.1002/nt.2620010205. PMID 1344912. http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/abstract/112640007/ABSTRACT.
- ^ "Ask Erowid". http://www.erowid.org/ask/ask.php?ID=121.
- ^ "LSA Extraction". http://nepenthes.lycaeum.org/Extraction/extract2.html.
External links
- Hofmann, A. Teonanácatl and Ololiuqui, two ancient magic drugs of Mexico Bulletin on Narcotics 1971 1 3
- Mixing the kykeon -- P. Webster, D. M. Perrine & C.A.P. Ruck
- TiHKAL (A & A Shulgin) #26
- Erowid's LSA Vault
Ergolines Lysergic acid derivatives 2-Bromo-LSD (BOL-148) • Bromocriptine • Cabergoline • Dihydroergocornine • Dihydroergocristine • Dihydroergocryptine • Dihydroergometrine (Dihydroergonovine, Dihydroergobasine) • Dihydroergotamine • Dihydroergotoxine • Ergine (LSA; LA-111; Lysergamide) • Ergocornine • Ergocristine • Ergocryptine • Ergoloid • Ergometrine (Ergonovine, Ergobasine) • Ergometrinine • Ergotamine • Ergotoxine • Ergovaline • Lisuride • LSD • LSH • Lysergic Acid • Lysergic acid cyclobutylamide • Lysergic acid cyclopentylamide • Lysergic Acid Methyl Ester • Lysergol • Mesulergine • Metergoline • Methergine (Methylergometrine, Methylergonovine, Methylergobasine) • Methysergide • Pergolide • SyntometrinePsychedelic lysergamides AL-LAD • ALD-52 • BU-LAD • CYP-LAD • DAL • DAM-57 • Ergonovine • ETH-LAD • IP-LAD • LAE-32 • LSD • LPD-824 • LSM-775 • LSH • LSD-Pip • Lysergic Acid 2-Butylamide • Lysergic Acid 2,4-Dimethylazetidide • Lysergic Acid 3-Pentylamide • Methylergonovine • Methylisopropyllysergamide • MLD-41 • PARGY-LAD • PRO-LADOther ergolines Natural sources Achnatherum robustum (Sleepy Grass) • Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian Baby Woodrose) • Claviceps spp. (Ergot) • Ipomoea spp. (Morning Glory, Tlitliltzin, Badoh Negro) • Rivea corymbosa (Coaxihuitl, Ololiúqui)Categories:- Alkaloids
- Lysergamides
- Serotonin receptor agonists
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
