- Lysergic acid
-
Lysergic acid 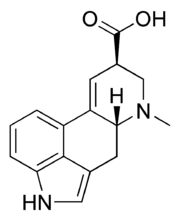
 7-Methyl- 4,6,6a,7,8,9- hexahydro- indolo [4,3-fg] quinoline- 9-carboxylic acidOther names6-Methyl- 9,10- didehydroergoline- 8-carboxylic acid
7-Methyl- 4,6,6a,7,8,9- hexahydro- indolo [4,3-fg] quinoline- 9-carboxylic acidOther names6-Methyl- 9,10- didehydroergoline- 8-carboxylic acidIdentifiers CAS number 82-58-6  ,
,
[478-95-5],
[6915-32-8],
[23953-76-6],
[68985-97-7],
[68985-98-8]ChemSpider 6461 
ChEBI CHEBI:6604 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C(O)[C@@H]3/C=C2/c4cccc1c4c(cn1)C[C@H]2N(C3)C
- InChI=1S/C16H16N2O2/c1-18-8-10(16(19)20)5-12-11-3-2-4-13-15(11)9(7-17-13)6-14(12)18/h2-5,7,10,14,17H,6,8H2,1H3,(H,19,20)/t10-,14-/m1/s1

Key: ZAGRKAFMISFKIO-QMTHXVAHSA-N
InChI=1/C16H16N2O2/c1-18-8-10(16(19)20)5-12-11-3-2-4-13-15(11)9(7-17-13)6-14(12)18/h2-5,7,10,14,17H,6,8H2,1H3,(H,19,20)/t10-,14-/m1/s1
Key: ZAGRKAFMISFKIO-QMTHXVAHBD
Properties Molecular formula C16H16N2O2 Molar mass 268.31 g mol−1 Melting point 238 - 240 °C
 acid (verify) (what is:
acid (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Lysergic acid, also known as D-lysergic acid and (+)-lysergic acid, is a precursor for a wide range of ergoline alkaloids that are produced by the ergot fungus and some plants. Amides of lysergic acid, lysergamides, are widely used as pharmaceuticals and as psychedelic drugs (LSD). Lysergic acid received its name as it was a product of the lysis of various ergot alkaloids [1].
Contents
Synthesis
Lysergic acid is generally produced by hydrolysis[2] of natural lysergamides, but can also be synthesized in the laboratory by a complex total synthesis for example by Woodward's team in 1956 [3]. Lysergic acid monohydrate crystallizes in very thin hexagonal leaflets when recrystallized from water. Lysergic acid monohydrate, when dried (140 °C at 2 mmHg or 270 Pa) forms anhydrous lysergic acid. The biosynthetic route is based on the alkylation of the amino acid Tryptophan with dimethylallyl diphosphate (isoprene derived from 3R-mevalonic acid) giving 4-dimethylallyl-L-tryptophan which is N-methylated with S-adenosyl-L-methionine. Oxidative ring closure followed by decarboxylation, reduction, cyclization, oxidation, and allylic isomerization yields D-(+)-lysergic acid.[1]
Isomers
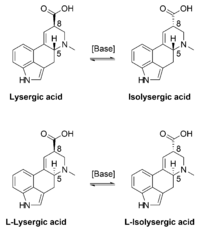
Lysergic acid is a chiral compound with two stereocenters. The isomer with inverted configuration at carbon atom 8 close to the carboxy group is called isolysergic acid. Inversion at carbon 5 close to the nitrogen atom leads to L-lysergic acid and L-isolysergic acid, respectively. Lysergic acid is listed as a Table I precursor under the United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances.[4]
See also
- Lysergic acid diethylamide (also known as LSD/Acid)
- Lysergic acid amide (LSA/Ergine)
- Ergoline
- Lysergamides
References
- ^ a b Schiff PL (2006 Oct 15). "Ergot and its alkaloids". Am J Pharm Educ. 70 (5): 98. PMID 17149427.
- ^ Martínková L, Kren V, Cvak L, Ovesná M, Prepechalová I (2001 Nov 17). "Hydrolysis of lysergamide to lysergic acid by Rhodococcus equi A4". J Biotechnol. 84 (1): 63-6.
- ^ Edmund C. Kornfeld, E.J. Fornefeld, G. Bruce Kline, Marjorie J. Mann, Dwight E. Morrison, Reuben G. Jones and R.B. Woodward (1956). "The Total Synthesis of Lysergic Acid". Journal of the American Chemical Society 78: 3087-3114.
- ^ List of Precursors and Chemicals Frequently Used in the Illicit Manufacture of Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Under International Control, International Narcotics Control Board
Ergolines Lysergic acid derivatives 2-Bromo-LSD (BOL-148) • Bromocriptine • Cabergoline • Dihydroergocornine • Dihydroergocristine • Dihydroergocryptine • Dihydroergometrine (Dihydroergonovine, Dihydroergobasine) • Dihydroergotamine • Dihydroergotoxine • Ergine (LSA; LA-111; Lysergamide) • Ergocornine • Ergocristine • Ergocryptine • Ergoloid • Ergometrine (Ergonovine, Ergobasine) • Ergometrinine • Ergotamine • Ergotoxine • Ergovaline • Lisuride • LSD • LSH • Lysergic Acid • Lysergic acid cyclobutylamide • Lysergic acid cyclopentylamide • Lysergic Acid Methyl Ester • Lysergol • Mesulergine • Metergoline • Methergine (Methylergometrine, Methylergonovine, Methylergobasine) • Methysergide • Pergolide • SyntometrinePsychedelic lysergamides AL-LAD • ALD-52 • BU-LAD • CYP-LAD • DAL • DAM-57 • Ergonovine • ETH-LAD • IP-LAD • LAE-32 • LSD • LPD-824 • LSM-775 • LSH • LSD-Pip • Lysergic Acid 2-Butylamide • Lysergic Acid 2,4-Dimethylazetidide • Lysergic Acid 3-Pentylamide • Methylergonovine • Methylisopropyllysergamide • MLD-41 • PARGY-LAD • PRO-LADOther ergolines Natural sources Achnatherum robustum (Sleepy Grass) • Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian Baby Woodrose) • Claviceps spp. (Ergot) • Ipomoea spp. (Morning Glory, Tlitliltzin, Badoh Negro) • Rivea corymbosa (Coaxihuitl, Ololiúqui)Categories:- Ergolines
- Carboxylic acids
- Hallucinogen stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.