- Ayahuasca
-
- This entry focuses on the Ayahuasca brew; for information on the vine of the same name, see Banisteriopsis caapi
Ayahuasca (ayawaska pronounced [ajaˈwaska] in the Quechua language) is any of various psychoactive infusions or decoctions prepared from the Banisteriopsis spp. vine, usually mixed with the leaves of dimethyltryptamine-containing species of shrubs from the Psychotria genus. The brew, first described academically in the early 1950s by Harvard ethnobotanist Richard Evans Schultes, who found it employed for divinatory and healing purposes by the native peoples of the Amazonian Colombia, is known by a number of different names (see below). It has been noted that effects can be had from imbibing the Caapi vine alone, but that DMT-containing plants remain inactive when drunk as a brew without an MAO inhibitor (such as Caapi). How indigenous peoples discovered the synergistic properties of the ayahuasca brew remains unknown.[1]
Contents
Nomenclature
In Ecuador, Bolivia and Peru, Colombia and to a lesser extent in Brazil, "ayahuasca" or "ayawaska" is Quechua for "spirit vine" or "vine of the souls"; aya means "spirit" while huasca or waska means "vine". The spelling of ayahuasca is the hispanicized version of the name; many Quechua or Aymara speakers would prefer the spelling ayawaska. The name is properly that of the plant B. caapi, one of the primary sources of beta-carbolines for the brew. Other terms include:
- cipó (generic vine, liana), "caapi", "hoasca", "vegetal", "daime" or "santo daime" in Brazil
- natem amongst the indigenous Shuar[2] and Achuar people[3] of Peru and Ecuador
- yagé or yajé (both pronounced [jaˈhe]) in Tucanoan[4]
- shori among the Nahua people of Peru[5]
Chemistry
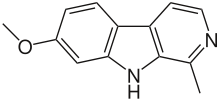
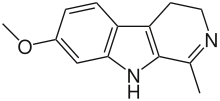
Harmine compounds are of beta-carboline origin. The three most studied beta-carboline compounds found in the B. caapi vine are harmine, harmaline and tetrahydroharmine. Harmine and harmaline are selective and reversible inhibitors of MAO-A, while tetrahydroharmine is a weak serotonin uptake inhibitor.[6] This inhibition of MAO-A allows DMT to diffuse unmetabolized past the membranes in the stomach and small intestine and eventually get through the blood-brain barrier (which, by itself, requires no MAO-A inhibition) to activate receptor sites in the brain. Without RIMAs or the MAOI of MAO-A, DMT would be metabolized in the digestive tract and would not have an effect when taken orally.[7]
Individual polymorphisms in the cytochrome P450-2D6 enzyme affect the ability of individuals to metabolize harmine.[8] Some natural tolerance to habitual use of ayahuasca (roughly once weekly) may develop through upregulation of the serotonergic system.[6][9] A phase 1 pharmacokinetic study on ayahuasca (as Hoasca) with 15 volunteers was conducted in 1993, during the Hoasca Project.[6] A review of the Hoasca Project has been published.[10]
Preparation
Sections of Banisteriopsis caapi vine are macerated and boiled alone or with leaves from any of a number of other plants, including Psychotria viridis (chacruna) or Diplopterys cabrerana (also known as chaliponga). The resulting brew contains the powerful hallucinogenic alkaloid N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT), and MAO inhibiting harmala alkaloids, which are necessary to make the DMT orally active.
Brews can also be made with no DMT-containing plants; Psychotria viridis being substituted by plants such as Justicia pectoralis, Brugmansia, or sacred tobacco, also known as Mapacho (Nicotiana rustica), or sometimes left out with no replacement. The potency of this brew varies radically from one batch to the next, both in potency and psychoactive effect, based mainly on the skill of the shaman or brewer, as well as other admixtures sometimes added and the intent of the ceremony. Natural variations in plant alkaloid content and profiles also affect the final concentration of alkaloids in the brew, and the physical act of cooking may also serve to modify the alkaloid profile of harmala alkaloids.[11][12]
Traditional brew
Traditional ayahuasca brews are often made with Banisteriopsis caapi as a MAOI, although Dimethyltryptamine sources and other admixtures vary from region to region. There are several varieties of caapi, often known as different "colors", with varying effects, potencies, and uses.
DMT admixtures:
- Psychotria viridis (Chacruna)[13] - leaves
- Diplopterys cabrerana (Chaliponga, Banisteriopsis rusbyana)[13] - leaves
- Psychotria carthagenensis (Amyruca)[13] - leaves
- Acacia maidenii (Maiden's Wattle), Acacia phlebophylla, and other Acacias, most commonly employed in Australia - bark
- Anadenanthera peregrina, A. colubrina, A. excelsa, A. macrocarpa
- Mimosa hostilis (Jurema) - root bark - not traditionally employed with ayahuasca by any existing cultures, though likely it was in the past. Popular in Europe and North America.
MAOI:
- Harmal (Peganum harmala, Syrian Rue) - seeds
- Passion flower
- synthetic MAOIs
Other common admixtures:
- Justicia pectoralis
- Brugmansia (Toé)[13]
- Nicotiana rustica[13] (Mapacho, variety of tobacco)
- Ilex guayusa,[13] a relative of yerba mate
Common admixtures with their associated ceremonial values and spirits:
- Ayahuma[13] bark
Dead Head Tree. Provides protection and is used in healing susto (soul loss from spiritual fright or trauma). Head spirit is a headless giant.
- Capirona[13] bark
Provides cleansing and protection. It is noted for its smooth bark, white flowers, and hard wood. Head spirits look Caucasian.
- Chullachaki Caspi[13] bark
Provides cleansing to the physical body. Used to transcend physical body ailments. Head spirits look Caucasian.
- Lopuna Blanca bark
Provides protection. Head spirits take the form of giants.
- Punga Amarilla bark
Yellow Punga. Provides protection. Used to pull or draw out negative spirits or energies. Head spirit is the yellow anaconda.
- Remo Caspi[13] bark
Oar Tree. Used to move dense or dark energies. Head spirit is a native warrior.
- Wyra (huaira) Caspi[13] bark
Air Tree. Used to create purging, transcend gastro/intestinal ailments, calm the mind, and bring tranquility. Head spirit looks African.
- Shiwawaku bark
Brings purple medicine to the ceremony. Provides healing and protection.
- Camu camu Gigante:
Head spirit comes in the form of a large dark skinned giant. He provides medicine and protection in the form of warding off dark and demonic spirits.
- Tamamuri:
Head spirit looks like an old Asian warrior with a long white wispy beard. He carries a staff and manages thousands of spirits to protect the ceremony and send away energies that are purged from the participants.
- Uchu Sanango
Head of the sanango plants. Provides power, strength, and protection. Head doctor spirit is a grandfather with a long, gray-white beard.
- Huacapurana:
Giant tree of the amazon with very hard bark. Its head spirits come in the form of Amazonian giants and provide a strong grounding presence in the ceremony.
Usage
Ayahuasca is used largely as a religious sacrament. Users of ayahuasca in non-traditional contexts often align themselves with the philosophies and cosmologies associated with ayahuasca shamanism, as practiced among indigenous peoples like the Urarina of Peruvian Amazonia.[14] While non-native users know of the spiritual applications of ayahuasca, a less well-known traditional usage focuses on the medicinal properties of ayahuasca. When used for its medicinal purposes ayahuasca affects the human consciousness for less than six hours beginning half an hour after consumption, and peaking after two hours. The remedy also has cardiovascular effects, moderately increasing both heart rate and diastolic blood pressure. The psychedelic effects of ayahuasca include visual and auditory stimulation, the mixing of sensory modaltities, and psychological introspection that may lead to great elation, fear, or illumination. Its purgative properties are important (known as la purga or "the purge"). The intense vomiting and occasional diarrhea it induces can clear the body of worms and other tropical parasites,[15] and harmala alkaloids themselves have been shown to be anthelmintic[16] Thus, this action is twofold; a direct action on the parasites by these harmala alkaloids (particularly harmine in ayahuasca) works to kill the parasites, and parasites are expelled through the increased intestinal motility that is caused by these alkaloids.
 Urarina shaman, 1988
Urarina shaman, 1988
Dietary taboos are often associated with the use of ayahuasca.[17] In the rainforest, these tend towards the purification of one's self - abstaining from spicy and heavily-seasoned foods, excess fat, salt, caffeine, acidic foods (such as citrus) and sex before, after, or during a ceremony. A diet low in foods containing tyramine has been recommended, as the speculative interaction of tyramine and MAOIs could lead to a hypertensive crisis. However, evidence indicates that harmala alkaloids act only on MAO-A, in a reversible way similar to moclobemide (an antidepressant that does not require dietary restrictions). Psychonautic experiments and the absence of dietary restrictions in the highly urban Brazilian ayahuasca church União do Vegetal also suggest that the risk is much lower than perceived, and probably non-existent.[17]
The name 'ayahuasca' specifically refers to a botanical decoction that contains Banisteriopsis caapi. A synthetic version, known as pharmahuasca is a combination of an appropriate MAOI and typically DMT. In this usage, the DMT is generally considered the main psychoactive active ingredient, while the MAOI merely preserves the psychoactivity of orally ingested DMT, which would otherwise be destroyed in the gut before it could be absorbed in the body. Thus, ayahuasqueros and most others working with the brew maintain that the B. caapi vine is the defining ingredient, and that this beverage is not ayahuasca unless B. caapi is in the brew. The vine is considered to be the "spirit" of ayahuasca, the gatekeeper and guide to the otherworldly realms.
In some areas[specify], it is even said that the chakruna or chaliponga admixtures are added only to make the brew taste sweeter. This is a strong indicator of the often wildly divergent intentions and cultural differences between the native ayahuasca-using cultures and psychedelics enthusiasts in other countries.
In modern Europe and North America, ayahuasca analogues are often prepared using non-traditional plants which contain the same alkaloids. For example, seeds of the Syrian rue plant can be used as a substitute for the ayahuasca vine, and the DMT-rich Mimosa hostilis is used in place of chakruna. Australia has several indigenous plants which are popular among modern ayahuasqueros there, such as various DMT-rich species of Acacia.
A visitor who wishes to become a "dietero" or "dietera", that is, a male or female apprentice-shaman learning the way of the teacher plants, undergoes a rigorous initiation. This can involve spending up to a year or more in the jungle. This initiation challenges and trains the initiate through extreme circumstances involving a special diet and numerous different plant medicines to complement the ayahuasca, the lack of western food and conveniences, the harsh environmental conditions of heavy rains, storms, intense heat, insects, and poisonous animals. The initiate is also tested for their unwavering commitment to ayahuasca and the shaman who oversees the training.
Non-traditional usage
Around the end of the 1990s, ayahuasca use spread to Europe. The first ayahuasca ‘Churches’ affiliated to the Brazilian Santo Daime were established in the Netherlands. A legal case was filed against two of the Church's leaders, Hans Bogers (one of the original founders of the Dutch Santo Daime community) and Geraldine Fijneman (the head of the Amsterdam Santo Daime community). Bogers and Fijneman were charged with distributing a scheduled substance (DMT), however the prosecution was unable to prove that the use of ayahuasca by members of the Santo Daime constituted a sufficient threat to public health and order that it warranted denying their rights to religious freedom under ECHR Article 9. The 2001 verdict of the Amsterdam district court is an important precedent. Since then groups that are not affiliated to the Santo Daime have used ayahuasca, and a number of different 'styles' have been developed, such as the non-religious approach developed by Daniel Waterman in 2001,[18] popularly termed Ayahuasca Open Style (AOS).[19]
Due to the legal status of ayahuasca, those who have been exploring its therapeutic potential are unable to do so openly. The therapeutic use of ayahuasca is not protected by covenants on religious freedom.
History
In the 16th century, Christian missionaries from Spain and Portugal first encountered indigenous peoples using ayahuasca in South America; their earliest reports described it as the work of the devil.[20] In the 20th century, the active chemical constituent of B. caapi was named telepathine, but it was found to be identical to a chemical already isolated from Peganum harmala and was given the name harmaline. Beat writer William Burroughs read a paper by Richard Evans Schultes on the subject and sought out yagé in the early 1950s while traveling through South America in the hopes that it could relieve or cure opiate addiction (see The Yage Letters). Ayahuasca became more widely known when the McKenna brothers published their experience in the Amazon in True Hallucinations. Dennis McKenna later studied the pharmacology, botany, and chemistry of ayahuasca and oo-koo-he, which became the subject of his master's thesis.
In Brazil, a number of modern religious movements based on the use of ayahuasca have emerged, the most famous of them being Santo Daime and the União do Vegetal (or UDV), usually in an animistic context that may be shamanistic or, more often (as with Santo Daime and the UDV), integrated with Christianity. Both Santo Daime and União do Vegetal now have members and churches throughout the world. Similarly, the US and Europe have started to see new religious groups develop in relation to increased ayahuasca use.[21] Some Westerners have teamed up with shamans in the Amazon rainforest regions, forming ayahuasca healing retreats that claim to be able to cure mental and physical illness and allow communication with the spirit world. Some reports and scientific studies affirm that ritualized use of ayahuasca may improve mental and physical health.[22]
In recent years, the tea has been popularized by Wade Davis (The Serpent and The Rainbow), Chilean novelist Isabel Allende,[23] writer Kira Salak,[24][25]author Jeremy Narby (The Cosmic Serpent), author Jay Griffiths ("Wild: An Elemental Journey"), and radio personality Robin Quivers.[26]
Legal status
Internationally, DMT is a Schedule I drug under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances. The Commentary on the Convention on Psychotropic Substances notes, however, that the plants containing it are not subject to international control:[27]
The cultivation of plants from which psychotropic substances are obtained is not controlled by the Vienna Convention. . . . Neither the crown (fruit, mescal button) of the Peyote cactus nor the roots of the plant Mimosa hostilis nor Psilocybe mushrooms themselves are included in Schedule 1, but only their respective principles, mescaline, DMT and psilocin.
A fax from the Secretary of the International Narcotics Control Board to the Netherlands Ministry of Public Health sent in 2001 goes on to state that "Consequently, preparations (e.g.decoctions) made of these plants, including ayahuasca, are not under international control and, therefore, not subject to any of the articles of the 1971 Convention."[28]
The legal status in the United States of DMT-containing plants is somewhat questionable. Ayahuasca plants and preparations are legal, as they contain no scheduled chemicals. However, brews made using DMT containing plants are illegal since DMT is a Schedule I drug. That said, some people are challenging this, using arguments similar to those used by peyotist religious sects, such as the Native American Church. A court case allowing União do Vegetal to use the tea for religious purposes in the United States, Gonzales v. O Centro Espirita Beneficente Uniao do Vegetal, was heard by the U.S. Supreme Court on November 1, 2005; the decision, released February 21, 2006, allows the UDV to use the tea in its ceremonies pursuant to the Religious Freedom Restoration Act. In a similar case an Ashland, Oregon based Santo Daime church sued for their right to import and consume ayahuasca tea. In March 2009, U.S. District Court Judge Panner ruled in favor of the Santo Daime, acknowledging its protection from prosecution under the Religious Freedom Restoration Act.[29]
Religious use in Brazil was legalized after two official inquiries into the tea in the mid-1980s, which concluded that ayahuasca is not a recreational drug and has valid spiritual uses.[30]
In France, Santo Daime won a court case allowing them to use the tea in early 2005; however, they were not allowed an exception for religious purposes, but rather for the simple reason that they did not perform chemical extractions to end up with pure DMT and harmala and the plants used were not scheduled.[31] Four months after the court victory, the common ingredients of ayahuasca as well as harmala were declared stupéfiants, or narcotic schedule I substances, making the tea and its ingredients illegal to use or possess.[32]
Research
Charles Grob directed the first major study of the effects of ayahuasca on humans with the Hoasca Project in 1993. The project studied members of the União do Vegetal (UDV) church in Brazil who use ayahuasca as a sacrament.[24]
The Institute of Medical Psychology at the University Hospital in Heidelberg, Germany has set up a Research Department Ayahuasca / Santo Daime,[33] which in May 2008 held a 3-day conference under the title The globalization of Ayahuasca - An Amazonian psychoactive and its users.[34] There are also the investigations of the human pharmacology of ayahuasca done by Jordi Riba [7][35][36][37][38][39][40][41][42][43] and the work of Rafael G. dos Santos.[44][45][46][47][48][49][50][51]
See also
Icaro
Notes
- ^ "Ayahuasca.com - Overviews Shamanism - On The Origin of Ayahuasca". http://www.ayahuasca.com/ayahuasca-overviews/on-the-origins-of-ayahuasca/. Retrieved August, 2010.
- ^ Incayawar, Mario; Lise Bouchard, Ronald Wintrob, Goffredo Bartocci (2009). Psychiatrists and Traditional Healers: Unwitting Partners in Global Mental Health. Wiley. p. 69. ISBN 978-0-470-51683-6.
- ^ Descola, Philippe (1996). In the Society of Nature: A Native Ecology in Amazonia. Cambridge University Press. pp. 99–100, 163. ISBN 9780521574679.
- ^ This term was popularized in English in the 1960s by the beat generation writers William S. Burroughs and Allen Ginsberg in The Yage Letters. The letters were originally written in the 1950s.
- ^ Siskind, Janet (1973). To Hunt in the Morning. Oxford University Press. p. 130. ISBN 0195018915.
- ^ a b c Callaway JC, McKenna DJ, Grob CS, Brito GS, Raymon LP, Poland RE, Andrade EN, Andrade EO (1999). "Pharmacokinetics of Hoasca alkaloids in healthy humans". Journal of Ethnopharmacology 65 (3): 243–256. doi:10.1016/S0378-8741(98)00168-8. PMID 10404423.
- ^ a b RIBA, J. Human Pharmacology of Ayahuasca. Doctoral Thesis: Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, 2003.
- ^ Callaway JC (June 2005). "Fast and slow metabolizers of Hoasca". J Psychoactive Drugs 37 (2): 157–61. PMID 16149329.
- ^ Callaway JC, Airaksinen MM, McKenna DJ, Brito GS, Grob CS (November 1994). "Platelet serotonin uptake sites increased in drinkers of ayahuasca". Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 116 (3): 385–7. doi:10.1007/BF02245347. PMID 7892432.
- ^ McKenna DJ, Callaway JC, Grob CS (1998). "The scientific investigation of ayahuasca: A review of past and current research". The Heffter Review of Psychedelic Research 1: 65–77. http://www.scribd.com/doc/3937611/The-Scientific-Investigation-of-Ayahuasca-A-Review-of-Past-and-Current-Research-.
- ^ Callaway JC (June 2005). "Various alkaloid profiles in decoctions of Banisteriopsis caapi". J Psychoactive Drugs 37 (2): 151–5. PMID 16149328.
- ^ Callaway JC, Brito GS, Neves ES (June 2005). "Phytochemical analyses of Banisteriopsis caapi and Psychotria viridis". J Psychoactive Drugs 37 (2): 145–50. PMID 16149327.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Ratsch 2005, pp. 704–708
- ^ Dean, Bartholomew (2009). Urarina Society, Cosmology, and History in Peruvian Amazonia. Gainesville: University Press of Florida. ISBN 978-0-8130-3378-5. http://www.upf.com/book.asp?id=DEANXS07.
- ^ Andritzky W (1989). "Sociopsychotherapeutic functions of ayahuasca healing in Amazonia". J Psychoactive Drugs 21 (1): 77–89. PMID 2656954.
- ^ Hassan, I. (1967). "Some folk uses of Peganum harmala in India and Pakistan". Economic Botany 21 (3): 384. doi:10.1007/BF02860378.
- ^ a b Ott, J. (1994). Ayahuasca Analogues: Pangaean Entheogens. Kennewick, WA: Natural Books. ISBN 978-0961423445.
- ^ Who We Are at a-keys.nl
- ^ Introduction to Ayahuasca at a-keys.nl
- ^ Reichel-Dolmatoff 1975, p. 48 as cited in Soibelman 1995, p. 14.
- ^ Labate, B.C.; Rose, I.S. & Santos, R.G. (2009). Ayahuasca Religions: a comprehensive bibliography and critical essays. Santa Cruz: Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies - MAPS. ISBN 978-0979862212.
- ^ See research by Doctor John Halpern in New Scientist
- ^ Elsworth, Catherine (2008-03-21). "Isabel Allende: kith and tell". The Daily Telegraph (London). http://www.telegraph.co.uk/arts/main.jhtml?xml=/arts/2008/03/23/st_isabelallende.xml. Retrieved 2010-04-26.
- ^ a b Salak, Kira. "Hell And Back". http://www.kirasalak.com/Peru.html. Retrieved 29 December 2010.
- ^ Salak, Kira. "Ayahuasca Healing in Peru". http://www.kirasalak.com/Ayahuasca.html. Retrieved 27 December 2010.
- ^ http://www.wcqj.com/
- ^ MAPS: DMT - UN report
- ^ Erowid Ayahuasca Vault : Law : UNDCP's Ayahuasca Fax, Jan 17 2001
- ^ Ruling by District Court Judge Panner in Santo Daime case in Oregon
- ^ More on the legal status of ayahuasca can be found in the Erowid vault on the legality of ayahuasca.
- ^ Cour d'appel de Paris, 10ème chambre, section B, dossier n° 04/01888. Arrêt du 13 janvier 2005 [Court of Appeal of Paris, 10th Chamber, Section B, File No. 04/01888. Judgement of 13 January 2005]. PDF of this document may be obtained from Ayahuasca - Santo Daime Library.
- ^ JO, 2005-05-03. Arrêté du 20 avril 2005 modifiant l'arrêté du 22 février 1990 fixant la liste des substances classées comme stupéfiants (PDF) [Decree of 20 April 2005 amending the decree of 22 February 1990 establishing the list of substances scheduled as narcotics].
- ^ 'Research Department Ayahuasca / Santo Daime' at the University Hospital in Heidelberg, Germany
- ^ Conference schedule "The globalization of Ayahuasca" (May 2008, Heidelberg, Germany)
- ^ Riba J, Barbanoj MJ (June 2005). "Bringing ayahuasca to the clinical research laboratory". J Psychoactive Drugs 37 (2): 219–30. PMID 16149336.
- ^ Riba, J. & Barbanoj, M.J. Ayahuasca (2006). Peris, J.C., Zurián, J.C., Martínez, G.C. & Valladolid, G.R.. ed. Tratado SET de Transtornos Adictivos. Madrid: Ed. Médica Panamericana. pp. 321–324. ISBN 9788479031640. http://books.google.com/books?id=bnV6Tx6hD5cC.
- ^ Riba J, Rodríguez-Fornells A, Strassman RJ, Barbanoj MJ (May 2001). "Psychometric assessment of the Hallucinogen Rating Scale". Drug Alcohol Depend 62 (3): 215–23. doi:10.1016/S0376-8716(00)00175-7. PMID 11295326.
- ^ Riba J, Rodríguez-Fornells A, Urbano G, et al. (February 2001). "Subjective effects and tolerability of the South American psychoactive beverage Ayahuasca in healthy volunteers". Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 154 (1): 85–95. doi:10.1007/s002130000606. PMID 11292011.
- ^ Riba J, Anderer P, Morte A, et al. (June 2002). "Topographic pharmaco-EEG mapping of the effects of the South American psychoactive beverage ayahuasca in healthy volunteers". Br J Clin Pharmacol 53 (6): 613–28. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2125.2002.01609.x. PMC 1874340. PMID 12047486. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1874340.
- ^ Riba, J., Rodriguez–Fornells, A., & Barbanoj, M.j. (2002). "Effects of ayahuasca sensory and sensorimotor gating in humans as measured by P50 suppression and prepulse inhibition of the startle reflex, respectively.". Psychopharmacology (Berl) 165 (1): 18–28. doi:10.1007/s00213-002-1237-5.
- ^ Riba J, Valle M, Urbano G, Yritia M, Morte A, Barbanoj MJ (July 2003). "Human pharmacology of ayahuasca: subjective and cardiovascular effects, monoamine metabolite excretion, and pharmacokinetics". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 306 (1): 73–83. doi:10.1124/jpet.103.049882. PMID 12660312.
- ^ Riba J, Anderer P, Jané F, Saletu B, Barbanoj MJ (2004). "Effects of the South American psychoactive beverage ayahuasca on regional brain electrical activity in humans: a functional neuroimaging study using low-resolution electromagnetic tomography". Neuropsychobiology 50 (1): 89–101. doi:10.1159/000077946. PMID 15179026.
- ^ Riba J, Romero S, Grasa E, Mena E, Carrió I, Barbanoj MJ (May 2006). "Increased frontal and paralimbic activation following ayahuasca, the pan-Amazonian inebriant". Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 186 (1): 93–8. doi:10.1007/s00213-006-0358-7. PMID 16575552.
- ^ Santos, R.G., Moraes, C.C. & Holanda, A. (2006). "Ayahuasca e redução do uso abusivo de psicoativos: eficácia terapêutica?". Psicologia: Teoria e Pesquisa 22 (3): 363–370. doi:10.1590/S0102-37722006000300014. http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0102-37722006000300014&lng=en&nrm=iso&tlng=pt.
- ^ SANTOS, R.G. (2007). "AYAHUASCA: Neuroquímica e Farmacologia.". SMAD - Revista Eletrônica Saúde Mental Álcool e Drogas 3 (1). http://pepsic.bvs-psi.org.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1806-69762007000100007&lng=pt&nrm=iso&tlng=pt.
- ^ Santos RG, Landeira-Fernandez J, Strassman RJ, Motta V, Cruz AP (July 2007). "Effects of ayahuasca on psychometric measures of anxiety, panic-like and hopelessness in Santo Daime members" (PDF). J Ethnopharmacol 112 (3): 507–13. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2007.04.012. PMID 17532158. http://www.maps.org/w3pb/new/2007/2007_Santos_22932_1.pdf.
- ^ Santos, R.G. & Strassman, R.J. (3 December 2008). "Ayahuasca and Psychosis (eLetter)". British Journal of Psychiatry. http://bjp.rcpsych.org/letters/?first-index=561&hits=80#bjrcpsych_el_22556.
- ^ SANTOS, R.G. (2010). "The pharmacology of ayahuasca: a review" (PDF). Brasília Médica 47 (2): 188–195. http://www.ambr.com.br/rb/arquivos/12.pdf.
- ^ SANTOS, R.G. (2010). "Toxicity of chronic ayahuasca administration to the pregnant rat: how relevant it is regarding the human, ritual use of ayahuasca?" (PDF). Birth Defects Research Part B: Developmental and Reproductive Toxicology 89 (6): 533–535. doi:10.1002/bdrb.20272. http://www.deepdyve.com/lp/wiley/toxicity-of-chronic-ayahuasca-administration-to-the-pregnant-rat-how-iNmvzZml0a?key=wiley.
- ^ SANTOS, R.G. (ed.). "The Ethnopharmacology of Ayahuasca". Trivandrum: Transworld Research Network. 2011. http://www.trnres.com/ebookcontents.php?id=93
- ^ Santos RG, Valle M, Bouso JC, Nomdedéu JF, Rodriguez-Espinosa J, McIlhenny EH, Barker SA, Barbanoj MJ, Riba J (December 2011). "Autonomic, neuroendocrine and immunological effects of Ayahuasca. A comparative study with d-amphetamine" (PDF). J Clin Psychopharmacol 31 (6): 217–26. doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e31823607f6. PMID 22005052. http://iceers.org/fileadmin/ICEERS/content/publications/JClinPsychopharmacol.pdf.
References
- Bartholomew, Dean Urarina Society, Cosmology, and History in Peruvian Amazonia, Gainesville: University Press of Florida, 2009. ISBN 978-081303378 [1]
- Burroughs, William S. and Allen Ginsberg. The Yage Letters. San Francisco: City Lights, 1963. ISBN 0-87286-004-3
- Dobkin De Rios, Marlene. Visionary Vine: Hallucinogenic Healing in the Peruvian Amazon, (2nd ed.). Prospect Heights, IL: Waveland, 1984. ISBN 0-88133-093-0
- Dobkin de Rios, Marlene & Roger Rumrrill. A Hallucinogenic Tea, Laced with Controversy: Ayahuasca in the Amazon and the United States. Westport, CT: Praeger, 2008. ISBN 978-0-313-34542-5
- Fraser, Sylvia. The Green Labyrinth: Exploring the Mysteries of the Amazon. Toronto: Thomas Allen, 2003. ISBN 0-88762-123-6.
- Hancock, Graham, Supernatural: Meetings with the Ancient Teachers of Mankind. London: Century, 2005. ISBN 1844136817 [2]
- Heaven, Ross and Howard G. Charing. Plant Spirit Shamanism: Traditional Techniques for Healing the Soul. Rochester, Vt.: Destiny, 2006. ISBN 1-59477-118-9
- Lamb, Bruce F. Rio Tigre and Beyond: The Amazon Jungle Medicine of Manuel Córdova. Berkeley: North Atlantic, 1985. ISBN 0-938190-59-8
- Langdon, E. Jean Matteson & Gerhard Baer, eds. Portals of Power: Shamanism in South America. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press, 1992. ISBN 0-8263-1345-0
- Luna, Luis Eduardo. Vegetalismo: Shamanism among the Mestizo Population of the Peruvian Amazon. Stockholm: Almqvist & Wiksell International, 1986. ISBN 91-22-00819-5
- Luna, Luis Eduardo & Pablo Amaringo. Ayahuasca Visions: The Religious Iconography of A Peruvian Shaman. Berkeley: North Atlantic, 1999. ISBN 1-55643-311-5
- Luna, Luis Eduardo & Stephen F. White, eds. Ayahuasca Reader: Encounters with the Amazon's Sacred Vine. Santa Fe, NM: Synergetic, 2000. ISBN 0-907791-32-8
- McKenna, Terence. Food of the Gods: A Radical History of Plants, Drugs, and Human Evolution.
- Metzner, Ralph, ed. Ayahuasca: Hallucinogens, Consciousness, and the Spirit of Nature. New York: Thunder's Mouth, 1999. ISBN 1-56025-160-3
- Metzner, Ralph (Editor). Sacred Vine of Spirits: Ayahuasca, (2nd ed.) Rochester, Vt.: Park Street, 2006. ISBN 1594770530, ISBN 978-1594770531
- Narby, Jeremy. The Cosmic Serpent: DNA and the Origins of Knowledge. New York: Jeremy P. Tarcher/Putnam, 1998. ISBN 0-87477-911-1
- O'Rourke, P. J., All the Trouble in the World. New York: The Atlantic Monthly, 1994. ISBN 0-87113-611-2
- Ott, Jonathan. Ayahuasca Analogues: Pangæan Entheogens. Kennewick, Wash.: Natural Products, 1994. ISBN 0-9614234-5-5
- Ott, J. Pharmacotheon: Entheogenic Drugs, Their Plant Sources and History , (2nd ed.)(Paperback). Kennewick, Wash.: Natural Products, 1993. ISBN 0961423498. ISBN 978-0961423490
- Ott, J. 1999. Pharmahuasca: Human pharmacology of oral DMT plus harmine, Journal of Psychoactive Drugs 31(2): I7I-177.
- Perkins, John. The World Is As You Dream It: Shamanic Teachings from the Amazon and Andes. Rochester, Vt.: Park Street, 1994. ISBN 0-89281-459-4 [3]
- Pinchbeck, Daniel. Breaking Open the Head: A Psychedelic Journey into the Heart of Contemporary Shamanism. New York: Broadway, 2002. ISBN 0-7679-0743-4 [4]
- Polari de Alverga, Alex. Forest of Visions: Ayahuasca, Amazonian Spirituality, and the Santo Daime Tradition. Rochester, Vt.: Park Street, 1999. ISBN 0-89281-716-X
- Rätsch, Christian. The Encyclopedia of Psychoactive Plants. Rochester, Vt.: Park Street, 2005. ISBN 978-0892819782
- Rätsch, Christian, Claudia Müller-Ebeling & Arno Adelaars. Ayahuasca. Rituale, Zaubertränke und visionäre Kunst aus Amazonien, Aarau, Switzerland: AT, 2006. ISBN 978-3-03800-270-3
- Reichel-Dolmatoff, Gerardo. The Shaman and the Jaguar: A Study of Narcotic Drugs Among the Indians of Colombia. Philadelphia: Temple University Press, 1975. ISBN 0-87722-038-7
- Schultes, Richard Evans & Robert F. Raffauf. Vine of the Soul: Medicine Men, Their Plants and Rituals in the Colombian Amazonia. Oracle, AZ: Synergetic, 1992. ISBN 0-907791-24-7
- Shannon, Benny. The Antipodes of the Mind: Charting the Phenomenology of the Ayahuasca Experience. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2002. ISBN 0-19-925293-9
- Stafford, Peter G. Heavenly Highs: Ayahuasca, Kava-Kava, Dmt, and Other Plants of the Gods. Berkeley: Ronin, 2004. ISBN 1-57951-069-8
- Sting. Broken Music. New York, NY: Bantam Dell, 2003. ISBN 978-0-440-24115-7
- Strassman, Rick. DMT: The Spirit Molecule: A Doctor's Revolutionary Research into the Biology of Near-Death and Mystical Experiences. Rochester, Vt.: Park Street, 2001. ISBN 0-89281-927-8
- Taussig, Michael. Shamanism, Colonialism, and the Wild Man: A Study in Terror and Healing. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1986. ISBN 0-226-79012-6
- Wilcox, Joan Parisi. Ayahuasca: The Visionary and Healing Powers of the Vine of the Soul. Rochester, Vt.: Park Street, 2003. ISBN 0-89281-131-5
Traditional medicine East Asian 
South & Southeast
AsianMediterranean &
Near EasternAfrican Americas Australasia & Oceania General Categories:- Ayahuasca
- Herbal and fungal hallucinogens
- Psychedelic tryptamine carriers
- Indigenous culture of the Amazon
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.