- Noopept
-
Noopept 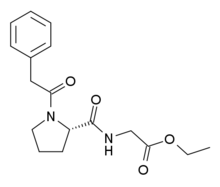
Systematic (IUPAC) name N-phenylacetyl-L-prolylglycine ethyl ester Clinical data Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status legal Identifiers CAS number 157115-85-0 ATC code ? PubChem CID 180496 Chemical data Formula C17H22N2O4 Mol. mass 318.367 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Noopept (Russian: Ноопепт; GVS-111, N-phenylacetyl-L-prolylglycine ethyl ester) is a medication promoted and prescribed in Russia and neighbouring countries as a nootropic remedy. It is derived from the racetam family of drugs and shares similar mechanisms of action,[1][2] but is up to 1000 times more potent than the prototypical racetam drug, piracetam.[3] Animal studies have shown noopept to be neuroprotective and enhance memory in various tests.[4][5][6][7][8] Unusually for a peptide-derived compound, noopept displays both high oral bioavailability[9] and good blood-brain barrier penetration[10] in rats (although a previous study concluded that "GVS-111 itself was not found in rat brain 1 h after 5 mg/kg i.p. administration up to limit of detection" and that administration of Noopept only increases the concentration of endogenous nootropic Cyclo-L-propylglycine[2]), and human studies have shown promising results, with potential application in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.[11] It is also an "immunocorrector" in mice.[12]
References
- ^ Solntseva EI, Bukanova JV, Ostrovskaya RU, Gudasheva TA, Voronina TA, Skrebitsky VG. The effects of piracetam and its novel peptide analogue GVS-111 on neuronal voltage-gated calcium and potassium channels. General Pharmacology. 1997 Jul;29(1):85-9. PMID 9195198
- ^ a b Gudasheva TA, Boyko SS, Ostrovskaya RU, Voronina TA, Akparov VK, Trofimov SS, Rozantsev GG, Skoldinov AP, Zherdev VP, Seredenin SB. The major metabolite of dipeptide piracetam analogue GVS-111 in rat brain and its similarity to endogenous neuropeptide cyclo-L-prolylglycine. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics. 1997 Jul-Sep;22(3):245-52. PMID 9358206
- ^ Ostrovskaia RU, Gudasheva TA, Voronina TA, Seredenin SB (2002). "[The original novel nootropic and neuroprotective agent noopept]" (in Russian). Eksp Klin Farmakol 65 (5): 66–72. PMID 12596521.
- ^ Ostrovskaya RU, Romanova GA, Barskov IV, Shanina EV, Gudasheva TA, Victorov IV, Voronina TA, Seredenin SB. Memory restoring and neuroprotective effects of the proline-containing dipeptide, GVS-111, in a photochemical stroke model. Behavioural Pharmacology. 1999 Sep;10(5):549-53. PMID 10780261
- ^ Pelsman A, Hoyo-Vadillo C, Gudasheva TA, Seredenin SB, Ostrovskaya RU, Busciglio J. GVS-111 prevents oxidative damage and apoptosis in normal and Down's syndrome human cortical neurons. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience. 2003 May;21(3):117-24. PMID 12711349
- ^ Ostrovskaya RU, Gruden MA, Bobkova NA, Sewell RD, Gudasheva TA, Samokhin AN, Seredinin SB, Noppe W, Sherstnev VV, Morozova-Roche LA. The nootropic and neuroprotective proline-containing dipeptide noopept restores spatial memory and increases immunoreactivity to amyloid in an Alzheimer's disease model. Journal of Psychopharmacology. 2007 Aug;21(6):611-9. PMID 17092975
- ^ Ostrovskaya RU, Gudasheva TA, Zaplina AP, Vahitova JV, Salimgareeva MH, Jamidanov RS, Seredenin SB. Noopept stimulates the expression of NGF and BDNF in rat hippocampus. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2008 Sep;146(3):334-7.PMID: 19240853
- ^ Romanova GA, Shakova FM, Gudasheva TA, Ostrovskaya RU. Impairment of learning and memory after photothrombosis of the prefrontal cortex in rat brain: effects of Noopept. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine 2002 Dec;134(6):528-30. PMID 12660828
- ^ Ostrovskaya RU, Mirsoev TK, Romanova GA, Gudasheva TA, Kravchenko EV, Trofimov CC, Voronina TA, Seredenin SB. Proline-containing dipeptide GVS-111 retains nootropic activity after oral administration. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2001 Oct;132(4):959-62. PMID 11782792
- ^ Boiko SS, Ostrovskaya RU, Zherdev VP, Korotkov SA, Gudasheva TA, Voronina TA, Seredenin SB. Pharmacokinetics of new nootropic acylprolyldipeptide and its penetration across the blood-brain barrier after oral administration. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2000 Apr;129(4):359-61. PMID 10977920
- ^ Neznamov GG, Teleshova ES. Comparative studies of Noopept and piracetam in the treatment of patients with mild cognitive disorders in organic brain diseases of vascular and traumatic origin. Neuroscience and Behavioural Physiology. 2009 Mar;39(3):311-21. PMID 19234797
- ^ Kovalenko LP, Shipaeva EV, Alekseeva SV, Pronin AV, Durnev AD, Gudasheva TA, Ostrovskaja RU, Seredenin SB. Immunopharmacological properties of noopept. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine 2007 Jul;144(1):49-52. PMID 18256750
Psychostimulants, agents used for ADHD, and nootropics (N06B) Centrally acting sympathomimetics Xanthine derivatives Glutamate receptor CX-516 • CX-546 • CX-614 • CX-691 • CX-717 • IDRA-21 • LY-404,187 • LY-503,430 • PEPA • S-18986 • Sunifiram • UnifiramEugeroics / Benzhydryl compounds Histamine H3 receptor antagonists GABAA α5 inverse agonists Dopamine D1 receptor agonists α7 nicotinic agonists / PAMs AR-R17779 • PNU-282,987 • SSR-180,711Prolyl endopeptidase inhibitors S-17092Alpha-adrenergic agonists Other psychostimulants and nootropics Acetylcarnitine • Adafenoxate • Bifemelane • Carbenoxolone • Citicoline • Cyprodenate • Ensaculin • Idebenone • Ispronicline • Deanol • Dimebon • Fipexide • Leteprinim • Linopirdine • Meclofenoxate • Nizofenone • P7C3 • Pirisudanol • Pyritinol • Rubidium • Sulbutiamine • Taltirelin • Tricyanoaminopropene • VinpocetineRacetams Aloracetam • Aniracetam • Brivaracetam • Cebaracetam • Coluracetam • Dimiracetam • Doliracetam • Dupracetam • Etiracetam/Levetiracetam • Fasoracetam • Imuracetam • Molracetam • Nebracetam • Nefiracetam • Noopept • Oxiracetam • Phenylpiracetam • Piperacetam • Piracetam • Pramiracetam • Rolipram • Rolziracetam • SeletracetamCategories:- Racetams
- Nootropics
- Pyrrolidines
- Amides
- Ethyl esters
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
