- Oxiracetam
-
Oxiracetam 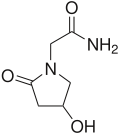
Systematic (IUPAC) name (RS)-2-(4-hydroxy-2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)acetamide Clinical data Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status Unscheduled (US) Routes Oral Identifiers CAS number 62613-82-5 
ATC code N06BX07 PubChem CID 4626 ChemSpider 4465 
UNII P7U817352G 
KEGG D07346 
ChEMBL CHEMBL36633 
Chemical data Formula C6H10N2O3 Mol. mass 158.155 SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Oxiracetam is a nootropic drug of the racetam family.[1]
Several animal studies suggest that the substance is safe even when high doses are consumed for a long period of time. However, the mechanism of action of the racetam drug family is still a matter of research.
Contents
Clinical findings
There has been put effort into investigation the possible use of oxiracetam as a medication to attenuate the symptoms of dementia. [2] However, no convincing results were obtained from studies where patients suffering from Alzheimer's dementia or organic solvent abuse were given 800 mg of the drug orally twice daily.[2]
The proven effects of the drug are limited to beneficial effects that lead to higher scores in tests for logical performance, attention, concentration, memory and spatial orientation. These tests were performed on patients with mild to moderate dementia, and the doses were 800-2400 mg orally twice a day for one to six months. Improvement has also been seen in patients with exogenic post-concussion syndrome, organic brain syndromes and other dementias. According to V. Gallai et al, oxiracetam is more effective than piracetam for this purpose.[2]
Pharmacokinetics
Oxiracetam is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract with a bioavailability of 68-82% according to one source (E. Perucca et al) and 56% according to another[2]. Peak serum levels are reached within one to three hours after a single 800 mg or 2000 mg oral dose, with the maximal serum concentration reaching between 19-31 µg/ml at these doses. Oxiracetam is mainly cleared renally and thus 84% is excreted unchanged in the urine. The half-life of oxiracetam in healthy individuals is about 8 hours, whereas it is 10-68 hours in patients with renal impairment. There is some penetration of the blood-brain barrier with brain concentrations reaching 5.3% of that in the blood (measured one hour after a single 2000 mg intravenous dose)[2]. Clearance rates range from 9 to 95 ml/min and steady-state concentrations when 800 mg is given twice daily range from 60 µM to 530 µM. The highest concentrations of oxiracetam is found in the septum pellucidum, followed by the hippocampus, the cerebral cortex and with the lowest concentrations in the striatum after a 200 mg/kg oral dose given to rats.[2]
See also
- Racetams
References
- ^ Malykh, AG; Sadaie, MR (2010). "Piracetam and piracetam-like drugs: from basic science to novel clinical applications to CNS disorders". Drugs 70 (3): 287–312. doi:10.2165/11319230-000000000-00000. PMID 20166767.
- ^ a b c d e f Piracetam and other structurally related nootropics, Alex Haahr Gouliaeva, Alexander Senning, Brain Research Reviews Volume 19, Issue 2, May 1994, Pages 180-222, doi:10.1016/0165-0173(94)90011-6
External links
Racetams Aloracetam • Aniracetam • Brivaracetam • Cebaracetam • Coluracetam • Dimiracetam • Doliracetam • Dupracetam • Etiracetam/Levetiracetam • Fasoracetam • Imuracetam • Molracetam • Nebracetam • Nefiracetam • Noopept • Oxiracetam • Phenylpiracetam • Piperacetam • Piracetam • Pramiracetam • Rolipram • Rolziracetam • SeletracetamPsychostimulants, agents used for ADHD, and nootropics (N06B) Centrally acting sympathomimetics Xanthine derivatives Glutamate receptor CX-516 • CX-546 • CX-614 • CX-691 • CX-717 • IDRA-21 • LY-404,187 • LY-503,430 • PEPA • S-18986 • Sunifiram • UnifiramEugeroics / Benzhydryl compounds Histamine H3 receptor antagonists GABAA α5 inverse agonists Dopamine D1 receptor agonists α7 nicotinic agonists / PAMs AR-R17779 • PNU-282,987 • SSR-180,711Prolyl endopeptidase inhibitors S-17092Alpha-adrenergic agonists Other psychostimulants and nootropics Acetylcarnitine • Adafenoxate • Bifemelane • Carbenoxolone • Citicoline • Cyprodenate • Ensaculin • Idebenone • Ispronicline • Deanol • Dimebon • Fipexide • Leteprinim • Linopirdine • Meclofenoxate • Nizofenone • P7C3 • Pirisudanol • Pyritinol • Rubidium • Sulbutiamine • Taltirelin • Tricyanoaminopropene • Vinpocetine
This drug article relating to the nervous system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
