- Metaraminol
-
Metaraminol 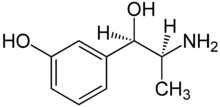
Systematic (IUPAC) name (1R,2S)-3-[-2-amino-1-hydroxy-propyl]phenol Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com International Drug Names Pregnancy cat. C(AU) C(US) Legal status POM (UK) Routes Intravenous Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability n/a Protein binding ~45% Metabolism Hepatic Identifiers CAS number 54-49-9 
ATC code C01CA09 PubChem CID 5906 DrugBank APRD00555 ChemSpider 5695 
UNII 818U2PZ2EH 
KEGG D08192 
ChEBI CHEBI:6794 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1201319 
Chemical data Formula C9H13NO2 Mol. mass 167.205 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Metaraminol (INN, trade name Aramine) is a potent sympathomimetic amine used in the prevention and treatment of hypotension, particularly as a complication of anesthesia. It is an α1-adrenergic receptor agonist with some β effect.
Metaraminol is also used in the treatment of priapism. Although not approved for this use, it appears to be effective.[1][2][3]
Chemistry
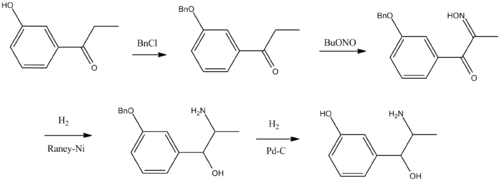
Metaraminol, L-1-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-2-aminopropan-1-ol, is synthesized in two ways. The first way is synthetic, and it is from 3-hydroxypropiophenone. The hydroxyl group is protected by alkylation with benzyl chloride, giving 3-benzyloxypropiophenone. Upon reaction with butyl nitrite, it undergoes nitrosation into the isonitrosoketone, which by reduction using hydrogen over Raney nickel turns into 1-(3-benzyloxyphenyl)-2-aminopropan-1-ol, the protecting benzyl group is removed by reduction using hydrogen over palladium catalyst, to give racemic metaraminol. The desired L-isomer is isolated with the help of (+)-tartaric acid.
- G. Erhart, L. Stein, DE 555404 (1930).
- E. W. Zeh, U.S. Patent 1,951,229 (1934).
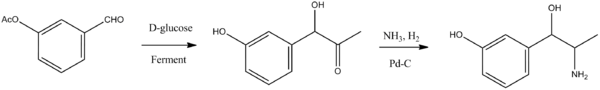
The second way is semisynthetic, consisting of fermentation of D-glucose in the presence of 3-acetoxybenzaldehyde, which forms (-)-1-hydroxy-1-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-acetone, the carbonyl group of which is reduced by hydrogen over a palladium catalyst in the presence of ammonia, giving metaraminol.
- G. Erhart, L. Stein, DE 571229 (1930).
- G. Erhart, L. Stein, U.S. Patent 1,948,162 (1934).
- W. H. Hartung, U.S. Patent 1,995,709 (1935).
- I. G. Farbenindustrie AG, GB 396951 (1932).
See also
References
- ^ McDonald M, Santucci R (2004). "Successful management of stuttering priapism using home self-injections of the alpha-agonist metaraminol.". Int Braz J Urol 30 (2): 121–2. doi:10.1590/S1677-55382004000200007. PMID 15703094.
- ^ Koga S, Shiraishi K, Saito Y (1990). "Post-traumatic priapism treated with metaraminol bitartrate: case report.". J Trauma 30 (12): 1591–3. doi:10.1097/00005373-199012000-00029. PMID 2258979.
- ^ Block T, Sturm W, Ernst G, Staehler G, Schmiedt E (1988). "[Metaraminol in therapy of various forms of priapism]". Urologe A 27 (4): 225–9. PMID 3140463.
Adrenergics Receptor ligands Agonists: 5-FNE • 6-FNE • Amidephrine • Anisodamine • Anisodine • Cirazoline • Dipivefrine • Dopamine • Ephedrine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Etilefrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Indanidine • Levonordefrin • Metaraminol • Methoxamine • Methyldopa • Midodrine • Naphazoline • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Octopamine • Oxymetazoline • Phenylephrine • Phenylpropanolamine • Pseudoephedrine • Synephrine • Tetrahydrozoline
Antagonists: Abanoquil • Adimolol • Ajmalicine • Alfuzosin • Amosulalol • Arotinolol • Atiprosin • Benoxathian • Buflomedil • Bunazosin • Carvedilol • CI-926 • Corynanthine • Dapiprazole • DL-017 • Domesticine • Doxazosin • Eugenodilol • Fenspiride • GYKI-12,743 • GYKI-16,084 • Indoramin • Ketanserin • L-765,314 • Labetalol • Mephendioxan • Metazosin • Monatepil • Moxisylyte (Thymoxamine) • Naftopidil • Nantenine • Neldazosin • Nicergoline • Niguldipine • Pelanserin • Phendioxan • Phenoxybenzamine • Phentolamine • Piperoxan • Prazosin • Quinazosin • Ritanserin • RS-97,078 • SGB-1,534 • Silodosin • SL-89.0591 • Spiperone • Talipexole • Tamsulosin • Terazosin • Tibalosin • Tiodazosin • Tipentosin • Tolazoline • Trimazosin • Upidosin • Urapidil • Zolertine
* Note that many TCAs, TeCAs, antipsychotics, ergolines, and some piperazines like buspirone, trazodone, nefazodone, etoperidone, and mepiprazole all antagonize α1-adrenergic receptors as well, which contributes to their side effects such as orthostatic hypotension.Agonists: (R)-3-Nitrobiphenyline • 4-NEMD • 6-FNE • Amitraz • Apraclonidine • Brimonidine • Cannabivarin • Clonidine • Detomidine • Dexmedetomidine • Dihydroergotamine • Dipivefrine • Dopamine • Ephedrine • Ergotamine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Esproquin • Etilefrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Guanabenz • Guanfacine • Guanoxabenz • Levonordefrin • Lofexidine • Medetomidine • Methyldopa • Mivazerol • Naphazoline • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Phenylpropanolamine • Piperoxan • Pseudoephedrine • Rilmenidine • Romifidine • Talipexole • Tetrahydrozoline • Tizanidine • Tolonidine • Urapidil • Xylazine • Xylometazoline
Antagonists: 1-PP • Adimolol • Aptazapine • Atipamezole • BRL-44408 • Buflomedil • Cirazoline • Efaroxan • Esmirtazapine • Fenmetozole • Fluparoxan • GYKI-12,743 • GYKI-16,084 • Idazoxan • Mianserin • Mirtazapine • MK-912 • NAN-190 • Olanzapine • Phentolamine • Phenoxybenzamine • Piperoxan • Piribedil • Rauwolscine • Rotigotine • SB-269,970 • Setiptiline • Spiroxatrine • Sunepitron • Tolazoline • Yohimbine
* Note that many atypical antipsychotics and azapirones like buspirone and gepirone (via metabolite 1-PP) antagonize α2-adrenergic receptors as well.βAgonists: 2-FNE • 5-FNE • Amibegron • Arbutamine • Arformoterol • Arotinolol • BAAM • Bambuterol • Befunolol • Bitolterol • Broxaterol • Buphenine • Carbuterol • Cimaterol • Clenbuterol • Denopamine • Deterenol • Dipivefrine • Dobutamine • Dopamine • Dopexamine • Ephedrine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Etafedrine • Etilefrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Fenoterol • Formoterol • Hexoprenaline • Higenamine • Indacaterol • Isoetarine • Isoprenaline (Isoproterenol) • Isoxsuprine • Labetalol • Levonordefrin • Levosalbutamol • Mabuterol • Methoxyphenamine • Methyldopa • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Orciprenaline • Oxyfedrine • Phenylpropanolamine • Pirbuterol • Prenalterol • Ractopamine • Procaterol • Pseudoephedrine • Reproterol • Rimiterol • Ritodrine • Salbutamol (Albuterol) • Salmeterol • Solabegron • Terbutaline • Tretoquinol • Tulobuterol • Xamoterol • Zilpaterol • Zinterol
Antagonists: Acebutolol • Adaprolol • Adimolol • Afurolol • Alprenolol • Alprenoxime • Amosulalol • Ancarolol • Arnolol • Arotinolol • Atenolol • Befunolol • Betaxolol • Bevantolol • Bisoprolol • Bopindolol • Bormetolol • Bornaprolol • Brefonalol • Bucindolol • Bucumolol • Bufetolol • Buftiralol • Bufuralol • Bunitrolol • Bunolol • Bupranolol • Burocrolol • Butaxamine • Butidrine • Butofilolol • Capsinolol • Carazolol • Carpindolol • Carteolol • Carvedilol • Celiprolol • Cetamolol • Cicloprolol • Cinamolol • Cloranolol • Cyanopindolol • Dalbraminol • Dexpropranolol • Diacetolol • Dichloroisoprenaline • Dihydroalprenolol • Dilevalol • Diprafenone • Draquinolol • Dropranolol • Ecastolol • Epanolol • Ericolol • Ersentilide • Esatenolol • Esmolol • Esprolol • Eugenodilol • Exaprolol • Falintolol • Flestolol • Flusoxolol • Hydroxycarteolol • Hydroxytertatolol • ICI-118,551 • Idropranolol • Indenolol • Indopanolol • Iodocyanopindolol • Iprocrolol • Isoxaprolol • Isamoltane • Labetalol • Landiolol • Levobetaxolol • Levobunolol • Levocicloprolol • Levomoprolol • Medroxalol • Mepindolol • Metalol • Metipranolol • Metoprolol • Moprolol • Nadolol • Nadoxolol • Nafetolol • Nebivolol • Neraminol • Nifenalol • Nipradilol • Oberadilol • Oxprenolol • Pacrinolol • Pafenolol • Pamatolol • Pargolol • Parodilol • Penbutolol • Penirolol • PhQA-33 • Pindolol • Pirepolol • Practolol • Primidolol • Procinolol • Pronethalol • Propafenone • Propranolol • Ridazolol • Ronactolol • Soquinolol • Sotalol • Spirendolol • SR 59230A • Sulfinalol • TA-2005 • Talinolol • Tazolol • Teoprolol • Tertatolol • Terthianolol • Tienoxolol • Tilisolol • Timolol • Tiprenolol • Tolamolol • Toliprolol • Tribendilol • Trigevolol • Xibenolol • XipranololReuptake inhibitors Selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors: Amedalin • Atomoxetine (Tomoxetine) • Ciclazindol • Daledalin • Esreboxetine • Lortalamine • Mazindol • Nisoxetine • Reboxetine • Talopram • Talsupram • Tandamine • Viloxazine; Norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors: Amineptine • Bupropion (Amfebutamone) • Fencamine • Fencamfamine • Lefetamine • Levophacetoperane • LR-5182 • Manifaxine • Methylphenidate • Nomifensine • O-2172 • Radafaxine; Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors: Bicifadine • Desvenlafaxine • Duloxetine • Eclanamine • Levomilnacipran • Milnacipran • Sibutramine • Venlafaxine; Serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors: Brasofensine • Diclofensine • DOV-102,677 • DOV-21,947 • DOV-216,303 • JNJ-7925476 • JZ-IV-10 • Methylnaphthidate • Naphyrone • NS-2359 • PRC200-SS • SEP-225,289 • SEP-227,162 • Tesofensine; Tricyclic antidepressants: Amitriptyline • Butriptyline • Cianopramine • Clomipramine • Desipramine • Dosulepin • Doxepin • Imipramine • Lofepramine • melitracen • Nortriptyline • Protriptyline • Trimipramine; Tetracyclic antidepressants: Amoxapine • Maprotiline • Mianserin • Oxaprotiline • Setiptiline; Others: Cocaine • CP-39,332 • EXP-561 • Fezolamine • Ginkgo biloba • Indeloxazine • Nefazodone • Nefopam • Pridefrine • Tapentadol • Teniloxazine • Tramadol • ZiprasidoneEnzyme inhibitors 3,4-DihydroxystyreneDBHCGS-19281A • SKF-64139 • SKF-7698Nonselective: Benmoxin • Caroxazone • Echinopsidine • Furazolidone • Hydralazine • Indantadol • Iproclozide • Iproniazid • Isocarboxazid • Isoniazid • Linezolid • Mebanazine • Metfendrazine • Nialamide • Octamoxin • Paraxazone • Phenelzine • Pheniprazine • Phenoxypropazine • Pivalylbenzhydrazine • Procarbazine • Safrazine • Tranylcypromine; MAO-A selective: Amiflamine • Bazinaprine • Befloxatone • Befol • Brofaromine • Cimoxatone • Clorgiline • Esuprone • Harmala alkaloids (Harmine, Harmaline, Tetrahydroharmine, Harman, Norharman, etc) • Methylene Blue • Metralindole • Minaprine • Moclobemide • Pirlindole • Sercloremine • Tetrindole • Toloxatone • Tyrima; MAO-B selective: D-Deprenyl • Selegiline (L-Deprenyl) • Ladostigil • Lazabemide • Milacemide • Mofegiline • Pargyline • Rasagiline • Safinamide
* Note that MAO-B inhibitors also influence norepinephrine/epinephrine levels since they inhibit the breakdown of their precursor dopamine.COMTOthers Ferrous Iron (Fe2+) • S-Adenosyl-L-Methionine • Vitamin B3 (Niacin, Nicotinamide → NADPH) • Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine, Pyridoxamine, Pyridoxal → Pyridoxal Phosphate) • Vitamin B9 (Folic acid → Tetrahydrofolic acid) • Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid) • Zinc (Zn2+)OthersActivity enhancers: BPAP • PPAP; Release blockers: Bethanidine • Bretylium • Guanadrel • Guanazodine • Guanclofine • Guanethidine • Guanoxan; Toxins: Oxidopamine (6-Hydroxydopamine)List of adrenergic drugsPhenethylamines Phenethylamines Psychedelics: 2C-B • 2C-B-FLY • 2C-C • 2C-D • 2C-E • 2C-F • 2C-G • 2C-I • 2C-N • 2C-P • 2C-SE • 2C-T • 2C-T-2 • 2C-T-4 • 2C-T-7 • 2C-T-8 • 2C-T-9 • 2C-T-13 • 2C-T-15 • 2C-T-17 • 2C-T-21 • 2C-TFM • 2C-YN • Allylescaline • DESOXY • Escaline • Isoproscaline • Jimscaline • Macromerine • MEPEA • Mescaline • Metaescaline • Methallylescaline • Proscaline • Psi-2C-T-4 • TCB-2
Stimulants: 2-OH-PEA • β-Me-PEA • Hordenine • N-Me-PEA • Phenethylamine (PEA)
Entactogens: Lophophine • MDPEA • MDMPEA
Others: BOH • DMPEAAmphetamines
PhenylisopropylaminesPsychedelics: 3C-BZ • 3C-E • 3C-P • Aleph • Beatrice • Bromo-DragonFLY • D-Deprenyl • DMA • DMCPA • DMMDA • DOB • DOC • DOEF • DOET • DOI • DOM • DON • DOPR • DOTFM • Ganesha • MMDA • MMDA-2 • Psi-DOM • TMA • TeMA
Stimulants: 4-MA • 4-MMA • 4-MTA • 5-IT • Alfetamine • Amfecloral • Amfepentorex • Amphetamine (Dextroamphetamine, Levoamphetamine) • Amphetaminil • Benfluorex • Benzphetamine • Cathine • Clobenzorex • Dimethylamphetamine • Ephedrine (EPH) • Ethylamphetamine • Fencamfamine • Fencamine • Fenethylline • Fenfluramine (Dexfenfluramine) • Fenproporex • Fludorex • Furfenorex • Isopropylamphetamine • Lefetamine • Mefenorex • Methamphetamine (Dextromethamphetamine, Levomethamphetamine) • Methoxyphenamine • MMA • Norfenfluramine • Oxilofrine • Ortetamine • PBA • PCA • Phenpromethamine • PFA • PFMA • PIA • PMA • PMEA • PMMA • Phenylpropanolamine (PPA) • Prenylamine • Propylamphetamine • Pseudoephedrine (PSE) • Sibutramine • Tiflorex (Flutiorex) • Tranylcypromine • Xylopropamine • Zylofuramine
Entactogens: 5-APDB • 6-APB • 6-APDB • EDA • IAP • MDA • MDEA • MDHMA (FLEA) • MDMA ("Ecstasy") • MDOH • MMDMA • NAP • TAP
Others: Amiflamine • DFMDA • D-Deprenyl • L-Deprenyl (Selegiline)Phentermines Stimulants: Chlorphentermine • Cloforex • Clortermine • Etolorex • Mephentermine • Pentorex (Phenpentermine) • Phentermine
Entactogens: MDPH • MDMPHCathinones Stimulants: Amfepramone • Brephedrone • Buphedrone • Bupropion (Amfebutamone) • Cathinone (Propion) • Dimethylcathinone (Dimethylpropion, Metamfepramone) • Ethcathinone (Ethylpropion) • Flephedrone • Methcathinone (Methylpropion) • Mephedrone • Methedrone
Entactogens: Ethylone • MethylonePhenylisobutylamines Phenylalkylpyrrolidines Stimulants: α-PBP • α-PPP • α-PVP • MDPBP • MDPPP • MDPV • MOPPP • MPBP • MPHP • MPPP • Naphyrone • PEP • Prolintane • PyrovaleroneCatecholamines
(and relatives..)6-FNE • 6-OHDA • α-Me-DA • α-Me-TRA • Adrenochrome • Ciladopa • D-DOPA (Dextrodopa) • Dopamine • Epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Epinine • Fenclonine • Ibopamine • L-DOPA (Levodopa) • L-DOPS (Droxidopa) • L-Phenylalanine • L-Tyrosine • meta-Octopamine • meta-Tyramine • Metanephrine • Metirosine • Methyldopa • Nordefrin (Levonordefrin) • Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) • Normetanephrine • para-Octopamine • para-TyramineMiscellaneous Amidephrine • Arbutamine • Cafedrine • Denopamine • Dobutamine • Dopexamine • Etafedrine • Ethylnorepinephrine • Etilefrine • Famprofazone • Gepefrine • Isoprenaline (Isoproterenol) • Isoetarine • Metaraminol • Metaterol • Methoxamine • Norfenefrine • Orciprenaline • Phenylephrine (Neosynephrine) • Phenoxybenzamine • Prenalterol • Pronethalol • Propranolol • Salbutamol (Albuterol; Levosalbutamol) • Synephrine (Oxedrine) • Theodrenaline • Xamoterol
This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.