- Ariadne (psychedelic)
-
Ariadne (psychedelic) 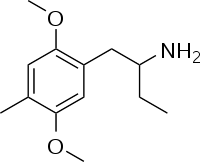 1-(2,5-Dimethoxy-4-methyl-benzyl)-propylamineOther names4-Methyl-2,5-dimethoxy-alpha-ethylphenethylamine
1-(2,5-Dimethoxy-4-methyl-benzyl)-propylamineOther names4-Methyl-2,5-dimethoxy-alpha-ethylphenethylamine
2-(4-Methyl-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethan-alpha-ethylamineIdentifiers CAS number 52842-59-8 PubChem 169886 ChemSpider 148565 
Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- O(c1cc(c(OC)cc1C[C@H](N)CC)C)C
O(c1cc(c(OC)cc1CC(N)CC)C)C
- InChI=1S/C13H21NO2/c1-5-11(14)7-10-8-12(15-3)9(2)6-13(10)16-4/h6,8,11H,5,7,14H2,1-4H3

Key: MLYCFWZIAJAIGW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
InChI=1/C13H21NO2/c1-5-11(14)7-10-8-12(15-3)9(2)6-13(10)16-4/h6,8,11H,5,7,14H2,1-4H3/t11-/m1/s1
Key: MLYCFWZIAJAIGW-LLVKDONJBY
InChI=1/C13H21NO2/c1-5-11(14)7-10-8-12(15-3)9(2)6-13(10)16-4/h6,8,11H,5,7,14H2,1-4H3
Key: MLYCFWZIAJAIGW-UHFFFAOYAX
Properties Molecular formula C13H21NO2 Molar mass 223.31 g/mol Exact mass 223.157229  (psychedelic) (verify) (what is:
(psychedelic) (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Ariadne (Dimoxamine, α-Et-DOM), or 4-methyl-2,5-dimethoxy-alpha-ethylphenethylamine, is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is a homologue of 2C-D and DOM. Ariadne was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines i Have Known And Loved), Shulgin reported testing Ariadne up to a dose of 32 mg, and reported that it produces psychedelia and a bare threshold.[1] Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of Ariadne in humans apart from Shulgin's limited testing.
However, in more recent animal studies, α-Et-DOM was shown to produce stimulus generalisation in rats trained to respond to the drug MDMA.[2] This suggests that while α-Et-DOM may lack hallucinogenic effects, it might potentially produce empathogenic effects similar to those of MDMA if used at higher dose ranges, beyond those trialled by Shulgin (the potency of α-Et-DOM in this study was similar to that of MDMA, 1.5 mg/kg, which would equate to a dose of ~100 mg in a human).
References
- ^ Shulgin, Alexander; Ann Shulgin (September 1991). PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story. Berkeley, California: Transform Press. ISBN 0-9630096-0-5. OCLC 25627628. http://www.erowid.org/library/books_online/pihkal/pihkal.shtml.
- ^ Glennon RA. MDMA-Like Stimulus Effects of α-Ethyltryptamine and the α-Ethyl Homolog of DOM. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behaviour. 1993; 46: 459-462.
See also
External links
Entactogens Aminoindanes 5-IAI • ETAI • TAIAminotetralins 6-CATPhenethylamines
(and amphetamines,
cathinones, etc)4-CAB • 4-FA • 4-FMA • 4-MTA • 4-FPP • 5-APDB • 6-APDB • Ariadne • BDB • Brephedrone • Eutylone • Flephedrone • IAP • IMP • Metaescaline • Mephedrone • Methedrone • MMA • NAP • Norfenfluramine • Pentylone • PMA • PMEA • PMMA • TAPMDxx 2-Methyl-MDA • 5-Methyl-MDA • 6-Methyl-MDA • bk-MBDB (butylone) • bk-MDEA (ethylone) • bk-MDMA (methylone) • DMMDA • DMMDA-2 • EBDB • EBDP • EDMA • MDAI • MDMAI • MMAI • MDAT • MDMAT • MDA • MDDM • MDEA • MDIP • MDMA • MDMOH • MDMP • MDMPEA • MDOH • MDPEA • MDPH • MDPR • MMDPEA (Lophophine) • MBDB • MBDP • MMDA • MMDA-2 • MMDMATryptamines 4-Methyl-αET • αET
This psychoactive drug-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. - O(c1cc(c(OC)cc1C[C@H](N)CC)C)C
