- DMCM
-
DMCM 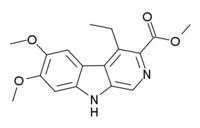
 methyl 4-ethyl-6,7-dimethoxy-9H-pyrido[5,4-b]indole-3-carboxylateOther namesDMCM
methyl 4-ethyl-6,7-dimethoxy-9H-pyrido[5,4-b]indole-3-carboxylateOther namesDMCMIdentifiers CAS number 82499-00-1 PubChem 104999 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - CCC1=C2C3=CC(=C(C=C3NC2=CN=C1C(=O)OC)OC)OC
Properties Molecular formula C17H18N2O4 Molar mass 314.336 g/mol Boiling point 87 °C
 (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references DMCM (methyl-6,7-dimethoxy-4-ethyl-beta-carboline-3-carboxylate) is a drug from the beta-carboline family. It acts as an inverse agonist of benzodiazepine receptors, meaning that it causes the opposite effects to the benzodiazepine class of drugs. As such, DMCM has anxiogenic and convulsant properties,[1] and is used in scientific research to induce anxiety so that new anxiolytic medications can be tested,[2] and to produce convulsions so that anticonvulsant medications can be tested.[3][4][5] It has also been shown to produce analgesic effects in animals, thought to be because it produces panic which reduces the perception of pain.[6]
References
- ^ Contó, MB; De Carvalho, JG; Benedito, MA (2005). "Behavioral differences between subgroups of rats with high and low threshold to clonic convulsions induced by DMCM, a benzodiazepine inverse agonist". Pharmacology, biochemistry, and behavior 82 (3): 417–26. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2005.09.012. PMID 16297441.
- ^ Cole, BJ; Hillmann, M; Seidelmann, D; Klewer, M; Jones, GH (1995). "Effects of benzodiazepine receptor partial inverse agonists in the elevated plus maze test of anxiety in the rat". Psychopharmacology 121 (1): 118–26. doi:10.1007/BF02245598. PMID 8539336.
- ^ Brodie, MJ (1995). "Tiagabine pharmacology in profile". Epilepsia 36 Suppl 6: S7–S9. PMID 8595791.
- ^ De Sarro, G; Chimirri, A; McKernan, R; Quirk, K; Giusti, P; De Sarro, A (1997). "Anticonvulsant activity of azirino1,2-d1,4benzodiazepines and related 1,4-benzodiazepines in mice". Pharmacology, biochemistry, and behavior 58 (1): 281–9. doi:10.1016/S0091-3057(96)00565-5. PMID 9264104.
- ^ Leppä, E; Vekovischeva, OY; Lindén, AM; Wulff, P; Oberto, A; Wisden, W; Korpi, ER (2005). "Agonistic effects of the beta-carboline DMCM revealed in GABA(A) receptor gamma 2 subunit F77I point-mutated mice". Neuropharmacology 48 (4): 469–78. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2004.11.007. PMID 15755475.
- ^ Sieve, AN; King, TE; Ferguson, AR; Grau, JW; Meagher, MW (2001). "Pain and negative affect: evidence the inverse benzodiazepine agonist DMCM inhibits pain and learning in rats". Psychopharmacology 153 (2): 180–90. doi:10.1007/s002130000535. PMID 11205417.
GABAergics Receptor
ligandsReuptake
inhibitorsPlasmalemmalGAT inhibitorsCI-966 • Deramciclane • EF-1502 • Gabaculine • Guvacine • Nipecotic acid • NNC 05-2090 • SKF-89976A • SNAP-5114 • TiagabineEnzyme
inhibitorsGAD inhibitorsAllylglycineGABA-T inhibitors3-Hydrazinopropionic acid • Aminooxyacetic acid • Gabaculine • Isoniazid • Phenelzine • Phenylethylidenehydrazine • Sodium valproate • Valnoctamide • Valproate pivoxil • Valproate semisodium (Divalproex sodium) • Valproic acid • Valpromide • VigabatrinOthers Glutamate • GlutamineOthers
This drug article relating to the nervous system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
