- Metabotropic glutamate receptor 2
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRM2 gene.[1][2]
L-glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system and activates both ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptors. Glutamatergic neurotransmission is involved in most aspects of normal brain function and can be perturbed in many neuropathologic conditions. The metabotropic glutamate receptors are a family of G protein-coupled receptors, that have been divided into 3 groups on the basis of sequence homology, putative signal transduction mechanisms, and pharmacologic properties. Group I includes GRM1 and GRM5 and these receptors have been shown to activate phospholipase C. Group II includes GRM2 and GRM3 while Group III includes GRM4, GRM6, GRM7 and GRM8. Group II and III receptors are linked to the inhibition of the cyclic AMP cascade but differ in their agonist selectivities.[2]
Contents
Ligands
PAMs
The development of subtype-2-selective positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) experienced steady advance in recent years.[3] mGluR2 potentiation is a new approach for the treatment of schizophrenia.[4]
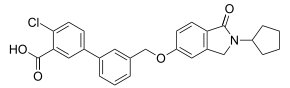 Highly selective mGluR2 PAM (2010)[5], analog of BINA
Highly selective mGluR2 PAM (2010)[5], analog of BINA
- GSK1331258[6]
- Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines[7]
- 3-Aryl-5-phenoxymethyl-1,3-oxazolidin-2-ones[8]
- 3-(Imidazolyl methyl)-3-aza-bicyclo[3.1.0]hexan-6-yl)methyl ethers: potent, orally stable[9]
- BINA:[10][11] potent; modest ago-allosteric modulator; robust in-vivo activity.
- LY487379:[12][13][14] devoid of orthosteric activity; along with related 3-pyridylmethylsulfonamides[15][16] the first subtype-2-selective potentiator published (2003).
See also
References
- ^ Flor PJ, Lindauer K, Puttner I, Ruegg D, Lukic S, Knopfel T, Kuhn R (Aug 1995). "Molecular cloning, functional expression and pharmacological characterization of the human metabotropic glutamate receptor type 2". Eur J Neurosci 7 (4): 622–9. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.1995.tb00666.x. PMID 7620613.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: GRM2 glutamate receptor, metabotropic 2". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=2912.
- ^ PMID 19552508
- ^ Conn PJ, Jones CK (January 2009). "Promise of mGluR2/3 activators in psychiatry". Neuropsychopharmacology 34 (1): 248–9. doi:10.1038/npp.2008.156. PMC 2907744. PMID 19079073. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2907744.
- ^ PMID 21155570
- ^ D'Alessandro PL, Corti C, Roth A, Ugolini A, Sava A, Montanari D, Bianchi F, Garland SL, Powney B, Koppe EL, Rocheville M, Osborne G, Perez P, de la Fuente J, De Los Frailes M, Smith PW, Branch C, Nash D, Watson SP (January 2010). "The identification of structurally novel, selective, orally bioavailable positive modulators of mGluR2". Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20 (2): 759–62. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.11.032. PMID 20005096.
- ^ Tresadern G, Cid JM, Macdonald GJ, Vega JA, de Lucas AI, García A, Matesanz E, Linares ML, Oehlrich D, Lavreysen H, Biesmans I, Trabanco AA (January 2010). "Scaffold hopping from pyridones to imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines. New positive allosteric modulators of metabotropic glutamate 2 receptor". Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20 (1): 175–9. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.11.008. PMID 19932615.
- ^ EJ Brnardic 2010
- ^ Zhang L, Rogers BN, Duplantier AJ et al. (2008). "3-(Imidazolyl methyl)-3-aza-bicyclo[3.1.0]hexan-6-yl)methyl ethers: a novel series of mGluR2 positive allosteric modulators". Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters 18 (20): 5493–6. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2008.09.026. PMID 18812259.
- ^ Galici R, Jones CK, Hemstapat K et al. (2006). "Biphenyl-indanone A, a positive allosteric modulator of the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 2, has antipsychotic- and anxiolytic-like effects in mice". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 318 (1): 173–85. doi:10.1124/jpet.106.102046. PMID 16608916.
- ^ Bonnefous C, Vernier JM, Hutchinson JH et al. (2005). "Biphenyl-indanones: allosteric potentiators of the metabotropic glutamate subtype 2 receptor". Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 15 (19): 4354–8. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.06.062. PMID 16046122.
- ^ Johnson MP, Baez M, Jagdmann GE et al. (2003). "Discovery of allosteric potentiators for the metabotropic glutamate 2 receptor: synthesis and subtype selectivity of N-(4-(2-methoxyphenoxy)phenyl)-N-(2,2,2- trifluoroethylsulfonyl)pyrid-3-ylmethylamine". J. Med. Chem. 46 (15): 3189–92. doi:10.1021/jm034015u. PMID 12852748.
- ^ Johnson MP, Barda D, Britton TC et al. (2005). "Metabotropic glutamate 2 receptor potentiators: receptor modulation, frequency-dependent synaptic activity, and efficacy in preclinical anxiety and psychosis model(s)". Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 179 (1): 271–83. doi:10.1007/s00213-004-2099-9. PMID 15717213.
- ^ Schaffhauser H, Rowe BA, Morales S et al. (2003). "Pharmacological characterization and identification of amino acids involved in the positive modulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 2". Mol. Pharmacol. 64 (4): 798–810. doi:10.1124/mol.64.4.798. PMID 14500736.
- ^ Barda DA, Wang ZQ, Britton TC et al. (2004). "SAR study of a subtype selective allosteric potentiator of metabotropic glutamate 2 receptor, N-(4-phenoxyphenyl)-N-(3-pyridinylmethyl)ethanesulfonamide". Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 14 (12): 3099–102. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2004.04.017. PMID 15149652.
- ^ Pinkerton AB, Vernier JM, Schaffhauser H et al. (2004). "Phenyl-tetrazolyl acetophenones: discovery of positive allosteric potentiatiors for the metabotropic glutamate 2 receptor". J. Med. Chem. 47 (18): 4595–9. doi:10.1021/jm040088h. PMID 15317469.
External links
- "Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors: mGlu2". IUPHAR Database of Receptors and Ion Channels. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. http://www.iuphar-db.org/GPCR/ReceptorDisplayForward?receptorID=2270.
Further reading
- Scherer SW, Duvoisin RM, Kuhn R et al. (1997). "Localization of two metabotropic glutamate receptor genes, GRM3 and GRM8, to human chromosome 7q". Genomics 31 (2): 230–3. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0036. PMID 8824806.
- Gomeza J, Mary S, Brabet I et al. (1996). "Coupling of metabotropic glutamate receptors 2 and 4 to G alpha 15, G alpha 16, and chimeric G alpha q/i proteins: characterization of new antagonists". Mol. Pharmacol. 50 (4): 923–30. PMID 8863838.
- Snow BE, Hall RA, Krumins AM et al. (1998). "GTPase activating specificity of RGS12 and binding specificity of an alternatively spliced PDZ (PSD-95/Dlg/ZO-1) domain". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (28): 17749–55. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.28.17749. PMID 9651375.
- Malherbe P, Knoflach F, Broger C et al. (2001). "Identification of essential residues involved in the glutamate binding pocket of the group II metabotropic glutamate receptor". Mol. Pharmacol. 60 (5): 944–54. PMID 11641422.
- Martí SB, Cichon S, Propping P, Nöthen M (2002). "Human metabotropic glutamate receptor 2 gene (GRM2): chromosomal sublocalization (3p21.1-p21.2) and genomic organization". Am. J. Med. Genet. 114 (1): 12–4. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1622. PMID 11840499.
- Krampfl K, Schlesinger F, Zörner A et al. (2002). "Control of kinetic properties of GluR2 flop AMPA-type channels: impact of R/G nuclear editing". Eur. J. Neurosci. 15 (1): 51–62. doi:10.1046/j.0953-816x.2001.01841.x. PMID 11860506.
- Dietrich D, Kral T, Clusmann H et al. (2002). "Presynaptic group II metabotropic glutamate receptors reduce stimulated and spontaneous transmitter release in human dentate gyrus". Neuropharmacology 42 (3): 297–305. doi:10.1016/S0028-3908(01)00193-9. PMID 11897108.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Kuwabara T, Hsieh J, Nakashima K et al. (2004). "A small modulatory dsRNA specifies the fate of adult neural stem cells". Cell 116 (6): 779–93. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00248-X. PMID 15035981.
- Tang FR, Chia SC, Chen PM et al. (2004). "Metabotropic glutamate receptor 2/3 in the hippocampus of patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy, and of rats and mice after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus". Epilepsy Res. 59 (2–3): 167–80. doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2004.04.002. PMID 15246118.
- Anneser JM, Chahli C, Ince PG et al. (2004). "Glial proliferation and metabotropic glutamate receptor expression in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis". J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 63 (8): 831–40. PMID 15330338.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=528928.
- Cube RV, Vernier JM, Hutchinson JH, et al. (2005). "3-(2-Ethoxy-4-{4-[3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4-(3-methylbutanoyl)phenoxy]butoxy}phenyl)propanoic acid: a brain penetrant allosteric potentiator at the metabotropic glutamate receptor 2 (mGluR2).". Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 15 (9): 2389–93. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.02.078. PMID 15837331.
- Rodd ZA, McKinzie DL, Bell RL et al. (2006). "The metabotropic glutamate 2/3 receptor agonist LY404039 reduces alcohol-seeking but not alcohol self-administration in alcohol-preferring (P) rats". Behav. Brain Res. 171 (2): 207–15. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2006.03.032. PMID 16678921.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
Cell surface receptor: G protein-coupled receptors Class A:
Rhodopsin likeOtherMetabolites and
signaling moleculesOtherBile acid · Cannabinoid (CB1, CB2, GPR (18, 55, 119)) · EBI2 · Estrogen · Free fatty acid (1, 2, 3, 4) · Lactate · Lysophosphatidic acid (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) · Lysophospholipid (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8) · Niacin (1, 2) · Oxoglutarate · PAF · Sphingosine-1-phosphate (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) · SuccinatePeptideOtherAnaphylatoxin (C3a, C5a) · Angiotensin (1, 2) · Apelin · Bombesin (BRS3, GRPR, NMBR) · Bradykinin (B1, B2) · Chemokine · Cholecystokinin (A, B) · Endothelin (A, B) · Formyl peptide (1, 2, 3) · FSH · Galanin (1, 2, 3) · GHB receptor · Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (1, 2) · Ghrelin · Kisspeptin · Luteinizing hormone/choriogonadotropin · MAS (1, 1L, D, E, F, G, X1, X2, X3, X4) · Melanocortin (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) · MCHR (1, 2) · Motilin · Opioid (Delta, Kappa, Mu, Nociceptin & Zeta, but not Sigma) · Orexin (1, 2) · Oxytocin · Prokineticin (1, 2) · Prolactin-releasing peptide · Relaxin (1, 2, 3, 4) · Somatostatin (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) · Tachykinin (1, 2, 3) · Thyrotropin · Thyrotropin-releasing hormone · Urotensin-II · Vasopressin (1A, 1B, 2)MiscellaneousGPR (1, 3, 4, 6, 12, 15, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 25, 26, 27, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 37, 39, 42, 44, 45, 50, 52, 55, 61, 62, 63, 65, 68, 75, 77, 78, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 87, 88, 92, 101, 103, 109A, 109B, 119, 120, 132, 135, 137B, 139, 141, 142, 146, 148, 149, 150, 151, 152, 153, 160, 161, 162, 171, 173, 174, 176, 177, 182, 183)OtherClass B: Secretin like OtherBrain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor (1, 2, 3) · Cadherin (1, 2, 3) · Calcitonin · CALCRL · CD97 · Corticotropin-releasing hormone (1, 2) · EMR (1, 2, 3) · Glucagon (GR, GIPR, GLP1R, GLP2R) · Growth hormone releasing hormone · PACAPR1 · GPR · Latrophilin (1, 2, 3, ELTD1) · Methuselah-like proteins · Parathyroid hormone (1, 2) · Secretin · Vasoactive intestinal peptide (1, 2)Class C: Metabotropic
glutamate / pheromoneOtherClass F:
Frizzled / SmoothenedFrizzledSmoothenedB trdu: iter (nrpl/grfl/cytl/horl), csrc (lgic, enzr, gprc, igsr, intg, nrpr/grfr/cytr), itra (adap, gbpr, mapk), calc, lipd; path (hedp, wntp, tgfp+mapp, notp, jakp, fsap, hipp, tlrp) Categories:- Human proteins
- G protein coupled receptors
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.