- Dopamine receptor D5
-
D(1B) dopamine receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD5 gene.[1][2][1]
This gene encodes the D5 subtype of the dopamine receptor. The D5 subtype is a G-protein coupled receptor which stimulates adenylyl cyclase.[3] This receptor is expressed in neurons in the limbic regions of the brain. It has a 10-fold higher affinity for dopamine than the D1 subtype. Pseudogenes related to this gene reside on chromosome 1 and chromosome 2.[2]
Contents
Ligands
The D1 and D5 receptors have a high degree of structural homology and few ligands are available that can distinguish between them as yet, however there are a number of ligands that are selective for D1/5 over the other dopamine receptors. The recent development of a selective D5 antagonist has allowed the action of D1-mediated responses to be studied in the absence of a D5 component, but no selective D5 agonists are yet available.
Agonists
Antagonists
- 4-Chloro-7-methyl-5,6,7,8,9,14-hexahydrodibenz[d,g]azecin-3-ol: antagonist, moderate binding selectivity over D1[4]
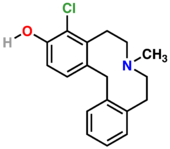 Chemical structure of a D5-preferring ligand 4-chloro-7-methyl-5,6,7,8,9,14-hexahydrodibenz[d,g]azecin-3-ol.[4]
Chemical structure of a D5-preferring ligand 4-chloro-7-methyl-5,6,7,8,9,14-hexahydrodibenz[d,g]azecin-3-ol.[4]
Interactions
Dopamine receptor D5 has been shown to interact with GABRG2.[5]
See also
References
- ^ a b Polymeropoulos MH, Xiao H, Merril CR (Mar 1992). "The human D5 dopamine receptor (DRD5) maps on chromosome 4". Genomics 11 (3): 777–778. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(91)90091-R. PMID 1774076.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: DRD5 dopamine receptor D5". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=1816.
- ^ Sidhu A (1998). "Coupling of D1 and D5 dopamine receptors to multiple G proteins: Implications for understanding the diversity in receptor-G protein coupling". Mol. Neurobiol. 16 (2): 125–134. doi:10.1007/BF02740640. PMID 9588624.
- ^ a b Mohr P, Decker M, Enzensperger C, Lehmann J (2006). "Dopamine/serotonin receptor ligands. 12(1): SAR studies on hexahydro-dibenz[d,g]azecines lead to 4-chloro-7-methyl-5,6,7,8,9,14-hexahydrodibenz[d,g]azecin-3-ol, the first picomolar D5-selective dopamine-receptor antagonist". J. Med. Chem. 49 (6): 2110–2116. doi:10.1021/jm051237e. PMID 16539400.
- ^ Liu, F; Wan Q, Pristupa Z B, Yu X M, Wang Y T, Niznik H B (Jan. 2000). "Direct protein-protein coupling enables cross-talk between dopamine D5 and gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptors". Nature (ENGLAND) 403 (6767): 274–280. doi:10.1038/35002014. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 10659839.
Further reading
- Missale C, Nash SR, Robinson SW et al. (1998). "Dopamine receptors: from structure to function". Physiol. Rev. 78 (1): 189–225. PMID 9457173.
- Grandy DK, Allen LJ, Zhang Y et al. (1992). "Chromosomal localization of three human D5 dopamine receptor genes". Genomics 13 (4): 968–973. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(92)90009-H. PMID 1387108.
- Eubanks JH, Altherr M, Wagner-McPherson C et al. (1992). "Localization of the D5 dopamine receptor gene to human chromosome 4p15.1-p15.3, centromeric to the Huntington's disease locus". Genomics 12 (3): 510–516. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(92)90442-U. PMID 1532789.
- Sunahara RK, Guan HC, O'Dowd BF et al. (1991). "Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D5 receptor with higher affinity for dopamine than D1". Nature 350 (6319): 614–619. doi:10.1038/350614a0. PMID 1826762.
- Tiberi M, Jarvie KR, Silvia C et al. (1991). "Cloning, molecular characterization, and chromosomal assignment of a gene encoding a second D1 dopamine receptor subtype: differential expression pattern in rat brain compared with the D1A receptor". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88 (17): 7491–7495. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.17.7491. PMC 52326. PMID 1831904. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=52326.
- Grandy DK, Zhang YA, Bouvier C et al. (1991). "Multiple human D5 dopamine receptor genes: a functional receptor and two pseudogenes". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88 (20): 9175–9179. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.20.9175. PMC 52675. PMID 1833775. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=52675.
- Weinshank RL, Adham N, Macchi M et al. (1991). "Molecular cloning and characterization of a high affinity dopamine receptor (D1 beta) and its pseudogene". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (33): 22427–35. PMID 1834671.
- Sobell JL, Lind TJ, Sigurdson DC et al. (1995). "The D5 dopamine receptor gene in schizophrenia: identification of a nonsense change and multiple missense changes but lack of association with disease". Hum. Mol. Genet. 4 (4): 507–514. doi:10.1093/hmg/4.4.507. PMID 7633397.
- Beischlag TV, Marchese A, Meador-Woodruff JH et al. (1995). "The human dopamine D5 receptor gene: cloning and characterization of the 5'-flanking and promoter region". Biochemistry 34 (17): 5960–5970. doi:10.1021/bi00017a025. PMID 7727453.
- Sherrington R, Mankoo B, Attwood J et al. (1994). "Cloning of the human dopamine D5 receptor gene and identification of a highly polymorphic microsatellite for the DRD5 locus that shows tight linkage to the chromosome 4p reference marker RAF1P1". Genomics 18 (2): 423–425. doi:10.1006/geno.1993.1489. PMID 8288248.
- Sidhu A, Kimura K, Uh M et al. (1998). "Multiple coupling of human D5 dopamine receptors to guanine nucleotide binding proteins Gs and Gz". J. Neurochem. 70 (6): 2459–2467. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.70062459.x. PMID 9603210.
- Cargill M, Altshuler D, Ireland J et al. (1999). "Characterization of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in coding regions of human genes". Nat. Genet. 22 (3): 231–238. doi:10.1038/10290. PMID 10391209.
- Liu F, Wan Q, Pristupa ZB et al. (2000). "Direct protein-protein coupling enables cross-talk between dopamine D5 and gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptors". Nature 403 (6767): 274–280. doi:10.1038/35002014. PMID 10659839.
- Misbahuddin A, Placzek MR, Chaudhuri KR et al. (2004). "A polymorphism in the dopamine receptor DRD5 is associated with blepharospasm". Neurology 58 (1): 124–6. PMID 11781417.
- Kabbani N, Negyessy L, Lin R et al. (2002). "Interaction with neuronal calcium sensor NCS-1 mediates desensitization of the D2 dopamine receptor". J. Neurosci. 22 (19): 8476–86. PMID 12351722.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–16903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Hemby SE, Trojanowski JQ, Ginsberg SD (2003). "Neuron-specific age-related decreases in dopamine receptor subtype mRNAs". J. Comp. Neurol. 456 (2): 176–183. doi:10.1002/cne.10525. PMID 12509874.
- Zheng S, Yu P, Zeng C et al. (2003). "Galpha12- and Galpha13-protein subunit linkage of D5 dopamine receptors in the nephron". Hypertension 41 (3): 604–610. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000057422.75590.D7. PMID 12623966.
External links
- "Dopamine Receptors: D1". IUPHAR Database of Receptors and Ion Channels. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. http://www.iuphar-db.org/GPCR/ReceptorDisplayForward?receptorID=2260.
- MeSH DRD5+protein,+human
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
Cell surface receptor: G protein-coupled receptors Class A:
Rhodopsin likeOtherMetabolites and
signaling moleculesOtherBile acid · Cannabinoid (CB1, CB2, GPR (18, 55, 119)) · EBI2 · Estrogen · Free fatty acid (1, 2, 3, 4) · Lactate · Lysophosphatidic acid (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) · Lysophospholipid (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8) · Niacin (1, 2) · Oxoglutarate · PAF · Sphingosine-1-phosphate (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) · SuccinatePeptideOtherAnaphylatoxin (C3a, C5a) · Angiotensin (1, 2) · Apelin · Bombesin (BRS3, GRPR, NMBR) · Bradykinin (B1, B2) · Chemokine · Cholecystokinin (A, B) · Endothelin (A, B) · Formyl peptide (1, 2, 3) · FSH · Galanin (1, 2, 3) · GHB receptor · Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (1, 2) · Ghrelin · Kisspeptin · Luteinizing hormone/choriogonadotropin · MAS (1, 1L, D, E, F, G, X1, X2, X3, X4) · Melanocortin (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) · MCHR (1, 2) · Motilin · Opioid (Delta, Kappa, Mu, Nociceptin & Zeta, but not Sigma) · Orexin (1, 2) · Oxytocin · Prokineticin (1, 2) · Prolactin-releasing peptide · Relaxin (1, 2, 3, 4) · Somatostatin (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) · Tachykinin (1, 2, 3) · Thyrotropin · Thyrotropin-releasing hormone · Urotensin-II · Vasopressin (1A, 1B, 2)MiscellaneousGPR (1, 3, 4, 6, 12, 15, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 25, 26, 27, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 37, 39, 42, 44, 45, 50, 52, 55, 61, 62, 63, 65, 68, 75, 77, 78, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 87, 88, 92, 101, 103, 109A, 109B, 119, 120, 132, 135, 137B, 139, 141, 142, 146, 148, 149, 150, 151, 152, 153, 160, 161, 162, 171, 173, 174, 176, 177, 182, 183)OtherClass B: Secretin like OtherBrain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor (1, 2, 3) · Cadherin (1, 2, 3) · Calcitonin · CALCRL · CD97 · Corticotropin-releasing hormone (1, 2) · EMR (1, 2, 3) · Glucagon (GR, GIPR, GLP1R, GLP2R) · Growth hormone releasing hormone · PACAPR1 · GPR · Latrophilin (1, 2, 3, ELTD1) · Methuselah-like proteins · Parathyroid hormone (1, 2) · Secretin · Vasoactive intestinal peptide (1, 2)Class C: Metabotropic
glutamate / pheromoneOtherClass F:
Frizzled / SmoothenedFrizzledSmoothened
This transmembrane receptor-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.