- Phosmet
-
Phosmet[1] 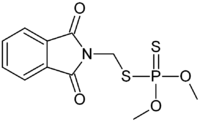 2-(Dimethoxyphosphinothioylthiomethyl)isoindoline-1,3-dioneOther namesFosmet
2-(Dimethoxyphosphinothioylthiomethyl)isoindoline-1,3-dioneOther namesFosmet
Decemthion
Imidathion
PhthalophosIdentifiers CAS number 732-11-6 
PubChem 12901 ChemSpider 12367 
UNII VN04LI540Y 
KEGG C18756 
ChEBI CHEBI:38786 
ATCvet code QP53,QP53BB03 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C2c1ccccc1C(=O)N2CSP(=S)(OC)OC
Properties Molecular formula C11H12NO4PS2 Molar mass 317.32 g mol−1 Appearance White to off-white crystals Density 1.03 g/cm3 Melting point 72 °C, 345 K, 162 °F
Boiling point Decomposes at >100 °C
 (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Phosmet is a phthalimide-derived, non-systemic, organophosphate insecticide used on plants and animals. It is mainly used on apple trees for control of coddling moth, though it is also used on a wide range of fruit crops, ornamentals, and vines for the control of aphids, suckers, mites, and fruit flies.[2]
Safety
Phosmet is on the US Emergency Planning List of Extremely Hazardous Substances. It is highly toxic to bees.[2]
Mark Purdey has made the controversial suggestion that phosmet may have played a key role in the epidemic of bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE).[3]
A 2010 study found that each 10-fold increase in urinary concentration of organophosphate metabolites was associated with a 55% to 72% increase in the odds of ADHD in children.[4]
References
- ^ "Phosmet Safety Card". http://www.itcilo.it/english/actrav/telearn/osh/ic/732116.htm. Retrieved 2006-08-06.
- ^ a b "Toxicology of Phosmet" (Webpage). http://extoxnet.orst.edu/pips/phosmet.htm. Retrieved 2006-08-06.
- ^ Purdey M (1998). "High-dose exposure to systemic phosmet insecticide modifies the phosphatidylinositol anchor on the prion protein: the origins of new variant transmissible spongiform encephalopathies?". Med. Hypotheses 50 (2): 91–111. doi:10.1016/S0306-9877(98)90194-3. PMID 9572563.
- ^ http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/721892
Cholinergics Receptor ligands Agonists: 77-LH-28-1 • AC-42 • AC-260,584 • Aceclidine • Acetylcholine • AF30 • AF150(S) • AF267B • AFDX-384 • Alvameline • AQRA-741 • Arecoline • Bethanechol • Butyrylcholine • Carbachol • CDD-0034 • CDD-0078 • CDD-0097 • CDD-0098 • CDD-0102 • Cevimeline • cis-Dioxolane • Ethoxysebacylcholine • LY-593,039 • L-689,660 • LY-2,033,298 • McNA343 • Methacholine • Milameline • Muscarine • NGX-267 • Ocvimeline • Oxotremorine • PD-151,832 • Pilocarpine • RS86 • Sabcomeline • SDZ 210-086 • Sebacylcholine • Suberylcholine • Talsaclidine • Tazomeline • Thiopilocarpine • Vedaclidine • VU-0029767 • VU-0090157 • VU-0152099 • VU-0152100 • VU-0238429 • WAY-132,983 • Xanomeline • YM-796
Antagonists: 3-Quinuclidinyl Benzilate • 4-DAMP • Aclidinium Bromide • Anisodamine • Anisodine • Atropine • Atropine Methonitrate • Benactyzine • Benzatropine (Benztropine) • Benzydamine • BIBN 99 • Biperiden • Bornaprine • CAR-226,086 • CAR-301,060 • CAR-302,196 • CAR-302,282 • CAR-302,368 • CAR-302,537 • CAR-302,668 • CS-27349 • Cyclobenzaprine • Cyclopentolate • Darifenacin • DAU-5884 • Dimethindene • Dexetimide • DIBD • Dicyclomine (Dicycloverine) • Ditran • EA-3167 • EA-3443 • EA-3580 • EA-3834 • Elemicin • Etanautine • Etybenzatropine (Ethylbenztropine) • Flavoxate • Himbacine • HL-031,120 • Ipratropium bromide • J-104,129 • Hyoscyamine • Mamba Toxin 3 • Mamba Toxin 7 • Mazaticol • Mebeverine • Methoctramine • Metixene • Myristicin • N-Ethyl-3-Piperidyl Benzilate • N-Methyl-3-Piperidyl Benzilate • Orphenadrine • Otenzepad • Oxybutynin • PBID • PD-102,807 • PD-0298029 • Phenglutarimide • Phenyltoloxamine • Pirenzepine • Piroheptine • Procyclidine • Profenamine • RU-47,213 • SCH-57,790 • SCH-72,788 • SCH-217,443 • Scopolamine (Hyoscine) • Solifenacin • Telenzepine • Tiotropium bromide • Tolterodine • Trihexyphenidyl • Tripitamine • Tropatepine • Tropicamide • WIN-2299 • Xanomeline • Zamifenacin; Others: 1st Generation Antihistamines (Brompheniramine, chlorphenamine, cyproheptadine, dimenhydrinate, diphenhydramine, doxylamine, mepyramine/pyrilamine, phenindamine, pheniramine, tripelennamine, triprolidine, etc) • Tricyclic Antidepressants (Amitriptyline, doxepin, trimipramine, etc) • Tetracyclic Antidepressants (Amoxapine, maprotiline, etc) • Typical Antipsychotics (Chlorpromazine, thioridazine, etc) • Atypical Antipsychotics (Clozapine, olanzapine, quetiapine, etc)Agonists: 5-HIAA • A-84,543 • A-366,833 • A-582,941 • A-867,744 • ABT-202 • ABT-418 • ABT-560 • ABT-894 • Acetylcholine • Altinicline • Anabasine • Anatoxin-a • AR-R17779 • Butyrylcholine • Carbachol • Cotinine • Cytisine • Decamethonium • Desformylflustrabromine • Dianicline • Dimethylphenylpiperazinium • Epibatidine • Epiboxidine • Ethanol • Ethoxysebacylcholine • EVP-4473 • EVP-6124 • Galantamine • GTS-21 • Ispronicline • Lobeline • MEM-63,908 (RG-3487) • Nicotine • NS-1738 • PHA-543,613 • PHA-709,829 • PNU-120,596 • PNU-282,987 • Pozanicline • Rivanicline • Sazetidine A • Sebacylcholine • SIB-1508Y • SIB-1553A • SSR-180,711 • Suberylcholine • TC-1698 • TC-1734 • TC-1827 • TC-2216 • TC-5214 • TC-5619 • TC-6683 • Tebanicline • Tropisetron • UB-165 • Varenicline • WAY-317,538 • XY-4083
Antagonists: 18-Methoxycoronaridine • α-Bungarotoxin • α-Conotoxin • Alcuronium • Amantadine • Anatruxonium • Atracurium • Bupropion (Amfebutamone) • Chandonium • Chlorisondamine • Cisatracurium • Coclaurine • Coronaridine • Dacuronium • Decamethonium • Dextromethorphan • Dextropropoxyphene • Dextrorphan • Diadonium • DHβE • Dimethyltubocurarine (Metocurine) • Dipyrandium • Dizocilpine (MK-801) • Doxacurium • Duador • Esketamine • Fazadinium • Gallamine • Hexafluronium • Hexamethonium (Benzohexonium) • Ibogaine • Isoflurane • Ketamine • Kynurenic acid • Laudexium (Laudolissin) • Levacetylmethadol • Malouetine • Mecamylamine • Memantine • Methadone • Methorphan (Racemethorphan) • Methyllycaconitine • Metocurine • Mivacurium • Morphanol (Racemorphanol) • Neramexane • Nitrous Oxide • Pancuronium • Pempidine • Pentamine • Pentolinium • Phencyclidine • Pipecuronium • Radafaxine • Rapacuronium • Rocuronium • Surugatoxin • Suxamethonium (Succinylcholine) • Thiocolchicoside • Toxiferine • Trimethaphan • Tropeinium • Tubocurarine • Vecuronium • XenonReuptake inhibitors PlasmalemmalCHT InhibitorsVAChT InhibitorsEnzyme inhibitors ChAT inhibitors1-(-Benzoylethyl)pyridinium • 2-(α-Naphthoyl)ethyltrimethylammonium • 3-Chloro-4-stillbazole • 4-(1-Naphthylvinyl)pyridine • Acetylseco hemicholinium-3 • Acryloylcholine • AF64A • B115 • BETA • CM-54,903 • CatabolismAChE inhibitorsReversible: Carbamates: Aldicarb • Bendiocarb • Bufencarb • Carbaryl • Carbendazim • Carbetamide • Carbofuran • Chlorbufam • Chloropropham • Ethienocarb • Ethiofencarb • Fenobucarb • Fenoxycarb • Formetanate • Furadan • Ladostigil • Methiocarb • Methomyl • Miotine • Oxamyl • Phenmedipham • Pinmicarb • Pirimicarb • Propamocarb • Propham • Propoxur; Stigmines: Ganstigmine • Neostigmine • Phenserine • Physostigmine • Pyridostigmine • Rivastigmine; Others: Acotiamide • Ambenonium • Donepezil • Edrophonium • Galantamine • Huperzine A • Minaprine • Tacrine • Zanapezil
Irreversible: Organophosphates: Acephate • Azinphos-methyl • Bensulide • Cadusafos • Chlorethoxyfos • Chlorfenvinphos • Chlorpyrifos • Chlorpyrifos-Methyl • Coumaphos • Cyclosarin (GF) • Demeton • Demeton-S-Methyl • Diazinon • Dichlorvos • Dicrotophos • Diisopropyl fluorophosphate (Guthion) • Diisopropylphosphate • Dimethoate • Dioxathion • Disulfoton • EA-3148 • Echothiophate • Ethion • Ethoprop • Fenamiphos • Fenitrothion • Fenthion • Fosthiazate • GV • Isofluorophate • Isoxathion • Malaoxon • Malathion • Methamidophos • Methidathion • Metrifonate • Mevinphos • Monocrotophos • Naled • Novichok agent • Omethoate • Oxydemeton-Methyl • Paraoxon • Parathion • Parathion-Methyl • Phorate • Phosalone • Phosmet • Phostebupirim • Phoxim • Pirimiphos-Methyl • Sarin (GB) • Soman (GD) • Tabun (GA) • Temefos • Terbufos • Tetrachlorvinphos • Tribufos • Trichlorfon • VE • VG • VM • VR • VX; Others: Demecarium • Onchidal (Onchidella binneyi)BChE inhibitorsCymserine * Many of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitors listed above act as butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors.Others Choline (Lecithin) • Citicoline • Cyprodenate • Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE, deanol) • Glycerophosphocholine • Meclofenoxate (Centrophenoxine) • Phosphatidylcholine • Phosphatidylethanolamine • Phosphorylcholine • PirisudanolOthersAcetylcholine releasing agents: α-Latrotoxin • β-Bungarotoxin; Acetylcholine release inhibitors: Botulinum toxin (Botox); Acetylcholinesterase reactivators: Asoxime • Obidoxime • PralidoximeCategories:- Organophosphate insecticides
- Phthalimides
- Phosphorodithioates
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Phosmet — Général Nom IUPAC 2 (diméthoxyphosphinothioylthiométhyl)isoindoline 1,3 dione No CAS … Wikipédia en Français
phosmet — noun A phthalimide derived nonsystemic organophosphate insecticide used on plants and animals … Wiktionary
Organophosphate — General chemical structure of an organophosphate An organophosphate (sometimes abbreviated OP) is the general name for esters of phosphoric acid. Phosphates are probably the most pervasive organophosphorus compounds. Many of the most important… … Wikipedia
Mark Purdey — John Mark Purdey (December 25, 1953 – November 12, 2006) was a British organic farmer who came to public attention in the 1980s, when he began to circulate his own theories regarding the causes of bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE or mad cow… … Wikipedia
Bovine spongiforme Enzephalopathie — (BSE), zu Deutsch etwa „die schwammartige Gehirnkrankheit der Rinder“ oder umgangssprachlich auch Rinderwahn genannt, ist eine Tierseuche. Die tödliche Erkrankung des Gehirns vor allem bei Hausrindern wird vermutlich durch Prionen (atypische… … Deutsch Wikipedia
Insecticide — For other uses, see Insecticide (disambiguation). An insecticide is a pesticide used against insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against the eggs and larvae of insects respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine,… … Wikipedia
Omethoate — IUPAC name 2 [(Dimethoxyphosphoryl)sulfanyl] N methyl acetamide … Wikipedia
Parathion — IUPAC name O,O Diethyl O (4 nitrophenyl) phosphorothioate … Wikipedia
Malathion — Malathion … Wikipedia
Chlorfenvinphos — IUPAC name [(EZ) 2 Chloro 1 (2,4 dichlorophenyl)ethenyl] diethyl phosphate … Wikipedia
