- Chrysanthemic acid
-
Chrysanthemic acid 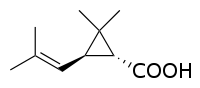 2,2-Dimethyl-3-(2-methylprop-1-enyl)cyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid
2,2-Dimethyl-3-(2-methylprop-1-enyl)cyclopropane-1-carboxylic acidIdentifiers CAS number 4638-92-0 (1R,3R) or (+)-trans PubChem 16747 (1R,3R) or (+)-trans, 33607 (1S,3S) or (-)-trans, 33606 (1R,3S) or (+)-cis, 20755 (1S,3R) or (-)-cis ChemSpider 15876 (+)-trans, 19543 (-)-cis Jmol-3D images Image 1 - CC(=CC1C(C1(C)C)C(=O)O)C
- InChI=1S/C10H16O2/c1-6(2)5-7-8(9(11)12)10(7,3)4/h5,7-8H,1-4H3,(H,11,12)/t7-,8+/m0/s1
Key: XLOPRKKSAJMMEW-JGVFFNPUSA-N
Properties Molecular formula C10H16O2 Molar mass 168.23 g mol−1 Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox references Chrysanthemic acid is an organic compound that is related to a variety of natural and synthetic insecticides. It is related to the pyrethrin I and II, as well as the pyrethroids. One of the four stereoisomers, (1R,3R)- or (+)-trans-chrysanthemic acid (pictured), is the acid-derived group of pyrethrin I, which occurs naturally in the seed cases of Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium. Many synthetic pyrethroids, for example the allethrins, are esters of all four stereoisomers.
Biosynthesis
Chrysanthemic acid is derived from its pyrophosphate ester, which in turn is produced naturally from dimethylallyl diphosphate.[1]
Synthesis
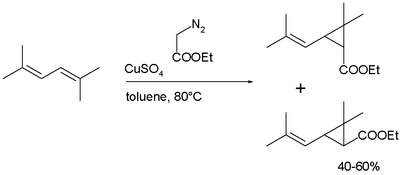
Chrysanthemic acid is produced industrially in a cyclopropanation reaction of a diene as a mixture of cis- and trans isomers, followed by hydrolysis of the ester[2]:
Many pyrethroids are accessible by re-esterification of crysanthemic acid ethylester.
References
- ^ Shattuck-Eidens DM, Wrobel WM, Peiser GD, Poulter CD (2001). "Chrysanthemyl diphosphate synthase: isolation of the gene and characterization of the recombinant non-head-to-tail monoterpene synthase from Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98 (8): 4373–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.071543598. PMC 31842. PMID 11287653. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=31842.
- ^ A synthesis of chrysanthemic ester: An undergraduate experiment. Kelly, Lawrence F. J. Chem. Educ. 1987, 64, 1061.
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.