- Parathion
-
Parathion 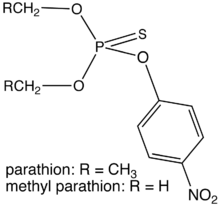 O,O-Diethyl O-(4-nitrophenyl) phosphorothioateOther namesE605
O,O-Diethyl O-(4-nitrophenyl) phosphorothioateOther namesE605Identifiers CAS number 56-38-2 
ChemSpider 13844817 
UNII 61G466064D 
KEGG C06604 
ChEBI CHEBI:27928 
ChEMBL CHEMBL261919 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - S=P(Oc1ccc(cc1)[N+]([O-])=O)(OCC)OCC
Properties Molecular formula C10H14NO5PS Molar mass 291.3 g/mol Appearance White crystals (pure form) Melting point 6 °C
Solubility in water 24mg/L in water, high solubility Hazards MSDS [1] R-phrases R24, R26/28, R48/25, R50/53 S-phrases S28, S36/37, S45, S60, S61 Flash point 120 °C  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Parathion, also called parathion-ethyl or diethyl parathion, is an organophosphate compound. It is a potent insecticide and acaricide. It was originally developed by IG Farben in the 1940s. It is highly toxic to non-target organisms, including humans. Its use is banned or restricted in many countries, and there are proposals to ban it from all use. Closely related is "methyl parathion" (see below).
Contents
Parathion-methyl
"Parathion-methyl" (CAS#298-00-0), also known as methyl parathion or dimethyl parathion, was also developed and is marketed for similar uses. It is a distinct compound with diminished toxicity. Some trade names of parathion-methyl include Bladan M, Metaphos, ME605, and E601.
History
Parathion was developed by Dr. Gerhard Schrader for the German trust IG Farben in the 1940s. After the war and the collapse of IG Farben due to the war crime trials, the Western allies seized the patent, and parathion was marketed worldwide by different companies and under different brand names. The most common German brand was E605 (banned in Germany after 2002); this was not a food-additive "E number" as used in the EU today. "E" stands for Entwicklungsnummer (German for "development number").
Handling properties
When pure, parathion is a white crystalline solid, however it is commonly distributed as a brown liquid that smells of rotting eggs or garlic. The insecticide is more or less stable, although it darkens when exposed to sunlight.
Industrial synthesis
Parathion is synthesized from diethyl dithiophosphoric acid (C2H5O)2PS2H, which is obtained by treatment of P2S5 with ethanol (methanol is used to prepare methyl parathion). Diethyl dithiophosphoric acid is chlorinated to generate diethylthiophosphoryl chloride. The diethyl dithiophosphoric acid is then treated with sodium 4-nitrophenolate (the sodium salt of 4-nitrophenol).[1]
- 2 (C2H5O)2P(S)SH + 3 Cl2 → 2 (C2H5O)2P(S)Cl + S2Cl2 + 2 HCl
- (C2H5O)2P(S)Cl + NaOC6H4NO2 → (C2H5O)2P(S)OC6H4NO2 + NaCl
Applications
As a pesticide, parathion is generally applied by spraying. It is often applied to cotton, rice and fruit trees. The usual concentrations of ready-to-use solutions are 0.05 to 0.1%. The chemical is banned for use on many food crops.
Insecticidal activity
Parathion acts on the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, but indirectly. After being ingested by insects (and unintentionally, by humans), the parathion becomes oxidized by oxidases to give paraoxon, replacing the double bonded sulfur with oxygen.[2]
- (C2H5O)2P(S)OC6H4NO2 + 1/2 O2 → (C2H5O)2P(O)OC6H4NO2 + S
The phosphate ester is more reactive in organisms than the phosphorothiolate ester, as the phosphorus atoms become much more electronegative.[2]
Degradation
Degradation of parathion leads to more water soluble products. Hydrolysis, which deactivates the molecule, occurs at the aryl ester bond resulting in diethyl thiophosphate and 4-nitrophenol.[2]
- (C2H5O)2P(S)OC6H4NO2 + H2O → HOC6H4NO2 + (C2H5O)2P(S)OH
Degradation proceeds differently under anaerobic conditions: the nitro group on parathion is reduced to the amine.
- (C2H5O)2P(S)OC6H4NO2 + 6 H → (C2H5O)2P(S)OC6H4NH2 + 2 H2O
Safety
Parathion is a cholinesterase inhibitor. It generally disrupts the nervous system by inhibiting the acetylcholinesterase. It is absorbed via skin, mucous membranes, and orally. Absorbed parathion is rapidly metabolized to paraoxon, as described above. Paraoxon exposure can result in headaches, convulsions, poor vision, vomiting, abdominal pain, severe diarrhea, unconsciousness, tremor, dyspnea, and finally lung-edema as well as respiratory arrest. Symptoms of poisoning are known to last for extended periods of time, sometimes months. The most common and very specific antidote is atropine in doses of up to 100 mg daily. Because atropine may also be toxic, it is recommended that small frequently repeated doses be used in treatment. If human poisoning is detected early and the treatment is prompt (atropine and artificial respiration), fatalities are infrequent. Insufficient oxygen will lead to cerebral hypoxia and permanent brain damage. Peripheral neuropathy including paralysis is noticed as late sequelae after recovery from acute intoxication. Parathion has been used for committing suicide and deliberately poisoning other persons. It is known as "Schwiegermuttergift" (mother-in-law poison) in Germany. For this reason most formulations contain a blue dye providing warning.
Parathion has been used as a chemical weapon, most notably by the Selous Scouts during the Rhodesian Bush War.[3]
Based on animal studies, parathion is considered by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency to be a possible human carcinogen.[4] Studies show that parathion is toxic to fetuses, but does not cause birth defects.[5]
It is classified as a UNEP Persistent Organic Pollutant and WHO Toxicity Class, "Ia, Extremely Hazardous".
Parathion is very toxic to bees, fish, birds, and other forms of wildlife.[5] Parathion can be replaced by many safer and less toxic alternatives (less toxic organophosphates, carbamates, or synthetic pyrethroids).
Protection against poisoning
To assure human protection the end user must wear protective gloves, clothing, and a respirator of the organic-vapour. Industrial safety during the production process requires special ventilation and continuous measurement of air contamination in order not to exceed PEL levels as well as keeping personal hygiene. Frequent determination of workers' serum acetylcholinesterase activity is also helpful in regards of occupational safety, because the action of parathion is cumulative. If an area of the body is contaminated with parathion, if possible, it should be removed immediately. Also, atropine has been used as a specific antidote.
Proposals to ban
According to the non-governmental organisation Pesticide Action Network or PAN, parathion is one of the most dangerous pesticides. This organization lists parathion also as a 'bad actor chemical'.[6] In the US alone more than 650 agricultural workers have been poisoned since 1966, of which 100 died. In underdeveloped countries many more people have suffered fatal and nonfatal intoxications. The World Health Organization, PAN and numerous environmental organisations propose a general and global ban. Its use is banned or restricted in 23 countries and its import is illegal in a total of 50 countries.[6]
See also
References
- ^ Fee, D. C.; Gard, D. R.; Yang, C. “Phosphorus Compounds” Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. John Wiley & Sons: New York, 2005. doi:10.1002/0471238961.16081519060505.a01.pub2.
- ^ a b c Metcalf, R. L. “Insect Control” Ullman’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: New York, 2002. doi: 10.1002/14356007.a14_263.
- ^ Moorcraft, Paul and McLaughlin, Peter. The Rhodesian War: A Military History. Yorkshire: Pen & Sword, 2008, p. 106
- ^ "Parathion". Integrated Risk Information System. U. S. Environmental Protection Agency. 26 January 2007. http://www.epa.gov/iris/subst/0327.htm.
- ^ a b "Pesticide Information Profiles - Parathion". Extension Toxicology Network. Oregon State University. September 1993. http://extoxnet.orst.edu/pips/parathio.htm.
- ^ a b S. Kegley, B. Hill, S. Orme. "Parathion - Identification, toxicity, use, water pollution potential, ecological toxicity and regulatory information". Pesticide Action Network. http://pesticideinfo.org/Detail_Chemical.jsp?Rec_Id=PC35122.
External links
- ATSDR - Methyl Parathion Expert Panel Report U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (public domain)
- Ethyl parathion: International Chemical Safety Card 0006
- Methyl parathion: International Chemical Safety Card 0626
Cholinergics Receptor ligands Agonists: 77-LH-28-1 • AC-42 • AC-260,584 • Aceclidine • Acetylcholine • AF30 • AF150(S) • AF267B • AFDX-384 • Alvameline • AQRA-741 • Arecoline • Bethanechol • Butyrylcholine • Carbachol • CDD-0034 • CDD-0078 • CDD-0097 • CDD-0098 • CDD-0102 • Cevimeline • cis-Dioxolane • Ethoxysebacylcholine • LY-593,039 • L-689,660 • LY-2,033,298 • McNA343 • Methacholine • Milameline • Muscarine • NGX-267 • Ocvimeline • Oxotremorine • PD-151,832 • Pilocarpine • RS86 • Sabcomeline • SDZ 210-086 • Sebacylcholine • Suberylcholine • Talsaclidine • Tazomeline • Thiopilocarpine • Vedaclidine • VU-0029767 • VU-0090157 • VU-0152099 • VU-0152100 • VU-0238429 • WAY-132,983 • Xanomeline • YM-796
Antagonists: 3-Quinuclidinyl Benzilate • 4-DAMP • Aclidinium Bromide • Anisodamine • Anisodine • Atropine • Atropine Methonitrate • Benactyzine • Benzatropine (Benztropine) • Benzydamine • BIBN 99 • Biperiden • Bornaprine • CAR-226,086 • CAR-301,060 • CAR-302,196 • CAR-302,282 • CAR-302,368 • CAR-302,537 • CAR-302,668 • CS-27349 • Cyclobenzaprine • Cyclopentolate • Darifenacin • DAU-5884 • Dimethindene • Dexetimide • DIBD • Dicyclomine (Dicycloverine) • Ditran • EA-3167 • EA-3443 • EA-3580 • EA-3834 • Elemicin • Etanautine • Etybenzatropine (Ethylbenztropine) • Flavoxate • Himbacine • HL-031,120 • Ipratropium bromide • J-104,129 • Hyoscyamine • Mamba Toxin 3 • Mamba Toxin 7 • Mazaticol • Mebeverine • Methoctramine • Metixene • Myristicin • N-Ethyl-3-Piperidyl Benzilate • N-Methyl-3-Piperidyl Benzilate • Orphenadrine • Otenzepad • Oxybutynin • PBID • PD-102,807 • PD-0298029 • Phenglutarimide • Phenyltoloxamine • Pirenzepine • Piroheptine • Procyclidine • Profenamine • RU-47,213 • SCH-57,790 • SCH-72,788 • SCH-217,443 • Scopolamine (Hyoscine) • Solifenacin • Telenzepine • Tiotropium bromide • Tolterodine • Trihexyphenidyl • Tripitamine • Tropatepine • Tropicamide • WIN-2299 • Xanomeline • Zamifenacin; Others: 1st Generation Antihistamines (Brompheniramine, chlorphenamine, cyproheptadine, dimenhydrinate, diphenhydramine, doxylamine, mepyramine/pyrilamine, phenindamine, pheniramine, tripelennamine, triprolidine, etc) • Tricyclic Antidepressants (Amitriptyline, doxepin, trimipramine, etc) • Tetracyclic Antidepressants (Amoxapine, maprotiline, etc) • Typical Antipsychotics (Chlorpromazine, thioridazine, etc) • Atypical Antipsychotics (Clozapine, olanzapine, quetiapine, etc)Agonists: 5-HIAA • A-84,543 • A-366,833 • A-582,941 • A-867,744 • ABT-202 • ABT-418 • ABT-560 • ABT-894 • Acetylcholine • Altinicline • Anabasine • Anatoxin-a • AR-R17779 • Butyrylcholine • Carbachol • Cotinine • Cytisine • Decamethonium • Desformylflustrabromine • Dianicline • Dimethylphenylpiperazinium • Epibatidine • Epiboxidine • Ethanol • Ethoxysebacylcholine • EVP-4473 • EVP-6124 • Galantamine • GTS-21 • Ispronicline • Lobeline • MEM-63,908 (RG-3487) • Nicotine • NS-1738 • PHA-543,613 • PHA-709,829 • PNU-120,596 • PNU-282,987 • Pozanicline • Rivanicline • Sazetidine A • Sebacylcholine • SIB-1508Y • SIB-1553A • SSR-180,711 • Suberylcholine • TC-1698 • TC-1734 • TC-1827 • TC-2216 • TC-5214 • TC-5619 • TC-6683 • Tebanicline • Tropisetron • UB-165 • Varenicline • WAY-317,538 • XY-4083
Antagonists: 18-Methoxycoronaridine • α-Bungarotoxin • α-Conotoxin • Alcuronium • Amantadine • Anatruxonium • Atracurium • Bupropion (Amfebutamone) • Chandonium • Chlorisondamine • Cisatracurium • Coclaurine • Coronaridine • Dacuronium • Decamethonium • Dextromethorphan • Dextropropoxyphene • Dextrorphan • Diadonium • DHβE • Dimethyltubocurarine (Metocurine) • Dipyrandium • Dizocilpine (MK-801) • Doxacurium • Duador • Esketamine • Fazadinium • Gallamine • Hexafluronium • Hexamethonium (Benzohexonium) • Ibogaine • Isoflurane • Ketamine • Kynurenic acid • Laudexium (Laudolissin) • Levacetylmethadol • Malouetine • Mecamylamine • Memantine • Methadone • Methorphan (Racemethorphan) • Methyllycaconitine • Metocurine • Mivacurium • Morphanol (Racemorphanol) • Neramexane • Nitrous Oxide • Pancuronium • Pempidine • Pentamine • Pentolinium • Phencyclidine • Pipecuronium • Radafaxine • Rapacuronium • Rocuronium • Surugatoxin • Suxamethonium (Succinylcholine) • Thiocolchicoside • Toxiferine • Trimethaphan • Tropeinium • Tubocurarine • Vecuronium • XenonReuptake inhibitors PlasmalemmalCHT InhibitorsHemicholinium-3 (Hemicholine; HC3) • TriethylcholineVAChT InhibitorsEnzyme inhibitors ChAT inhibitors1-(-Benzoylethyl)pyridinium • 2-(α-Naphthoyl)ethyltrimethylammonium • 3-Chloro-4-stillbazole • 4-(1-Naphthylvinyl)pyridine • Acetylseco hemicholinium-3 • Acryloylcholine • AF64A • B115 • BETA • CM-54,903 • CatabolismAChE inhibitorsReversible: Carbamates: Aldicarb • Bendiocarb • Bufencarb • Carbaryl • Carbendazim • Carbetamide • Carbofuran • Chlorbufam • Chloropropham • Ethienocarb • Ethiofencarb • Fenobucarb • Fenoxycarb • Formetanate • Furadan • Ladostigil • Methiocarb • Methomyl • Miotine • Oxamyl • Phenmedipham • Pinmicarb • Pirimicarb • Propamocarb • Propham • Propoxur; Stigmines: Ganstigmine • Neostigmine • Phenserine • Physostigmine • Pyridostigmine • Rivastigmine; Others: Acotiamide • Ambenonium • Donepezil • Edrophonium • Galantamine • Huperzine A • Minaprine • Tacrine • Zanapezil
Irreversible: Organophosphates: Acephate • Azinphos-methyl • Bensulide • Cadusafos • Chlorethoxyfos • Chlorfenvinphos • Chlorpyrifos • Chlorpyrifos-Methyl • Coumaphos • Cyclosarin (GF) • Demeton • Demeton-S-Methyl • Diazinon • Dichlorvos • Dicrotophos • Diisopropyl fluorophosphate (Guthion) • Diisopropylphosphate • Dimethoate • Dioxathion • Disulfoton • EA-3148 • Echothiophate • Ethion • Ethoprop • Fenamiphos • Fenitrothion • Fenthion • Fosthiazate • GV • Isofluorophate • Isoxathion • Malaoxon • Malathion • Methamidophos • Methidathion • Metrifonate • Mevinphos • Monocrotophos • Naled • Novichok agent • Omethoate • Oxydemeton-Methyl • Paraoxon • Parathion • Parathion-Methyl • Phorate • Phosalone • Phosmet • Phostebupirim • Phoxim • Pirimiphos-Methyl • Sarin (GB) • Soman (GD) • Tabun (GA) • Temefos • Terbufos • Tetrachlorvinphos • Tribufos • Trichlorfon • VE • VG • VM • VR • VX; Others: Demecarium • Onchidal (Onchidella binneyi)BChE inhibitorsCymserine * Many of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitors listed above act as butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors.Others Choline (Lecithin) • Citicoline • Cyprodenate • Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE, deanol) • Glycerophosphocholine • Meclofenoxate (Centrophenoxine) • Phosphatidylcholine • Phosphatidylethanolamine • Phosphorylcholine • PirisudanolOthersAcetylcholine releasing agents: α-Latrotoxin • β-Bungarotoxin; Acetylcholine release inhibitors: Botulinum toxin (Botox); Acetylcholinesterase reactivators: Asoxime • Obidoxime • PralidoximeCategories:- Insecticide brands
- Organophosphate insecticides
- Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
- Phosphorothioates
- Nitrobenzenes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
parathion — ● parathion nom masculin Dénomination courante d un insecticide agricole … Encyclopédie Universelle
parathion — ☆ parathion [par΄ə thī′än΄ ] n. [ PARA 1 + THION(IC)] a highly poisonous compound, C10H14O5NPS, commercially a colorless to dark brown liquid, used as an agricultural insecticide … English World dictionary
Parathion — Strukturformel Allgemeines Name Parathion Andere Nam … Deutsch Wikipedia
Parathion — Cette page d’homonymie répertorie les différents sujets et articles partageant un même nom. Le parathion est un composé chimique phytosanitaire (ou pesticide). Plus précisément, le terme parathion peut faire référence à : parathion éthyl… … Wikipédia en Français
Parathion — Pa|ra|thi|on, eigtl. Parathion ethyl [Kurzw. aus O,O Diethyl O (p nitrophenyl)thionophosphat]; Syn.: Ethylparathion: O2N C6H4 O P(S)(OC2H5)2; Common Name für eine gelbe knoblauchartig riechende, giftige Fl., Sdp. 375 °C, die – ebenso wie das… … Universal-Lexikon
parathion — /par euh thuy on/, n. Chem. a deep brown to yellow, poisonous liquid, C10H14NO5PS, used as an insecticide. [1945 50; PARA 1 + THI + ON(E)] * * * ▪ insecticide an organic phosphorus compound well known as an insecticide that is extremely… … Universalium
parathion — tiofosas statusas T sritis chemija apibrėžtis Insekticidas. formulė (C₂H₅O)₂P(=S)OC₆H₄NO₂ atitikmenys: angl. parathion rus. тиофос ryšiai: sinonimas – dietil (4 nitrofenil)tio(orto)fosfatas … Chemijos terminų aiškinamasis žodynas
Parathion methyl — Parathion méthyl Parathion méthyl Général Synonymes Méthyl parathion; Méthylparathion No CAS … Wikipédia en Français
Parathion méthyl — Général Synonymes Méthyl parathion; Méthylparathion No CAS … Wikipédia en Français
Parathion ethyl — Parathion éthyl Parathion éthyl Général Synonymes Parathion Thiophosphate de O,O diéthyle et de O (4 nitrophényle) … Wikipédia en Français

