- Methohexital
-
Methohexital 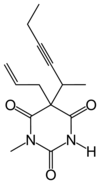
Systematic (IUPAC) name 5-hex-3-yn-2-yl-1- methyl-5-prop-2-enyl-1, 3-diazinane-2,4,6-trione Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com Consumer Drug Information Pregnancy cat. B (USA) Legal status Schedule IV Routes Intravenous, rectal Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability I.V. ~100%
Rectal ~17%Metabolism Hepatic Half-life 5.6 ± 2.7 minutes Excretion ? Identifiers CAS number 151-83-7 
ATC code N01AF01 N05CA15 PubChem CID 9034 DrugBank APRD00058 ChemSpider 8683 
UNII E5B8ND5IPE 
KEGG D04985 
ChEBI CHEBI:102216 
ChEMBL CHEMBL7413 
Chemical data Formula C14H18N2O3 Mol. mass 262.304 SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Methohexital, also called methohexitone, (marketed under the brand name Brevital) is a drug which is a barbiturate derivative. It is classified as short-acting, and has a rapid onset of action. It is similar in its effects to sodium thiopental, a drug with which it competed in the market for anaesthetics.
Contents
Pharmacology
Methohexital binds to a distinct site which is associated with Cl− ionophores at GABAA receptors.[1] This increases the length of time which the Cl− ionopores are open, thus causing an inhibitory effect.
Metabolism of methohexital is primarily hepatic (i.e., taking place in the liver) via demethylation and oxidation.[citation needed] Side-chain oxidation is the primary means of metabolism involvedtermination of the drug's biological activity.
Protein binding is approximately 73% for methohexital.[citation needed]
Indications
Methohexital is primarily used to induce anesthesia, and is generally provided as a sodium salt (i.e. methohexital sodium). It is only used in hospital or similar settings, under strict supervision.[citation needed] It has been commonly used to induce deep sedation, "twilight sleep" or general anesthesia for oral surgery and dentistry. It is also used to induce anesthesia prior to ECT (electroconvulsive therapy).
Chemistry
Methohexital, 5-allyl-1-methyl-5-(1-methyl-2-pentinyl barbituric acid, is synthesized in the classic manner of making barbituric acid derivatives, in particular by the reaction of malonic ester derivatives with derivatives of urea. The resulting allyl-(1-methyl-2-pentynyl) malonic ester is synthesized by subsequent alkylation of the malonic ester itself, beginning with 2-bromo-3-hexyne, which gives (1-methyl-2-pentynyl)malonic ester, and then by allylbromide. In the final step, reaction of the disubstituted malonic ester with N-methylurea gives desired methohexital.
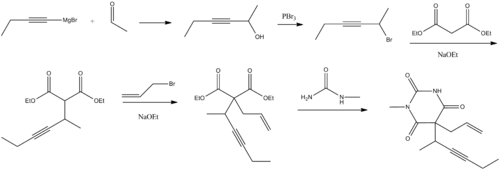
W.J. Doran, U.S. Patent 2,872,448 (1959).
References
- ^ Katzung, Bertram G., Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, 10th ed., p. 406-407
External links
- RxList.com - Methohexital
- Drugs.com - Methohexital Sodium
- DrugLib.com - Brevital (Methohexital Sodium)
Anesthesia Types Techniques Measurements Instruments Anaesthetic machine · Boyle's machine · Gas cylinder · IoC-View monitor · Laryngeal mask airway · Medical monitor · Odom's indicator · Relative analgesia machine · VaporiserDrugs General anaesthetic · Benzodiazepine · Etomidate · FlyNap · Infiltration analgesia · Ketamine · Local anesthetic · Methohexital · Midazolam · Neuraxial blockade · Propofol · Thiopental · ThiopentoneComplications Allergic reactions · Anesthesia awareness · Local anesthetic toxicity · Perioperative mortality · Malignant hyperthermiaFields of study Professions Anaesthetic technician · Anesthesiologist · Certified Anesthesia Technician · Certified Anesthesia Technologist · Nurse anaesthetistHistory A.C.E. mixture · Helsinki Declaration for Patient Safety in Anaesthesiology · History of tracheal intubationOrganizations American Society of Anesthesia Technologists & Technicians · American Society of Anesthesiologists · Anaesthesia Trauma and Critical Care · Association of Anaesthetists of Great Britain and Ireland · Association of Veterinary Anaesthetists · Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists · Australian Society of Anaesthetists · International Anesthesia Research SocietyAnesthetic: General anesthetics (N01A) Inhalation OthersInjection OthersHypnotics/Sedatives (N05C) GABAA Agonists/PAMs Barbiturates: Allobarbital • Amobarbital • Aprobarbital • Barbital • Butabarbital • Butobarbital • Cyclobarbital • Ethallobarbital • Heptabarbital • Hexobarbital • Mephobarbital • Methohexital • Pentobarbital • Phenobarbital • Proxibarbal • Reposal • Secobarbital • Talbutal • Thiamylal • Thiopental • Vinbarbital • Vinylbital; Benzodiazepines: Brotizolam • Clonazepam • Cinolazepam • Climazolam • Doxefazepam • Estazolam • Flunitrazepam • Flurazepam • Flutoprazepam • Haloxazolam • Loprazolam • Lormetazepam • Midazolam • Nimetazepam • Nitrazepam • Quazepam • Temazepam • Triazolam; Carbamates: Carisoprodol • Ethinamate • Hexapropymate • Meprobamate • Methocarbamol • Procymate • Tybamate; Neuroactive Steroids: Acebrochol • Allopregnanolone • Alphadolone • Alphaxolone • Eltanolone • Ganaxolone • Hydroxydione • Minaxolone • Org 20599 • Org 21465 • Tetrahydrodeoxycorticosterone; Nonbenzodiazepines: CL-218,872 • Eszopiclone • Indiplon • JM-1232 • Lirequinil • Necopidem • Pazinaclone • ROD-188 • Saripidem • Suproclone • Suriclone • SX-3228 • U-89843A • U-90042 • Zaleplon • Zolpidem • Zopiclone; Phenols: Fospropofol • Propofol; Piperidinediones: Glutethimide • Methyprylon • Pyrithyldione • Piperidione; Quinazolinones: Afloqualone • Cloroqualone • Diproqualone • Etaqualone • Mebroqualone • Mecloqualone • Methaqualone • Methylmethaqualone • Nitromethaqualone; Others: 2-Methyl-2-butanol • Acetophenone • Acetylglycinamide chloral hydrate • Bromide (Lithium bromide, Potassium bromide, Sodium bromide) • Centalun • Chloral hydrate • Chloralose • Chloralodol • Clomethiazole • Dichloralphenazone • Ethanol (Alcohol) • Ethchlorvynol • Etomidate • Gaboxadol • Loreclezole • Methylpentynol • Metomidate • Paraldehyde • Petrichloral • Sulfonmethane • Trichloroethanol • Triclofos • Valerenic acid (Valerian)GABAB Agonists H1 Inverse agonists Antihistamines: Captodiame • Cyproheptadine • Dimenhydrinate • Diphenhydramine • Doxylamine • Hydroxyzine • Methapyrilene • Pheniramine • Promethazine • Propiomazine; Others: Tricyclic antidepressants (Amitriptyline, Doxepin, Trimipramine, etc.) • Tetracyclic antidepressants (Mianserin, Mirtazapine, etc.) • Typical antipsychotics (Chlorpromazine, Thioridazine, etc.) • Atypical antipsychotics (Olanzapine, Quetiapine, Risperidone, etc.)α1-Adrenergic Antagonists Mianserin • Niaprazine • Trazodone; Others: Tricyclic antidepressants (Amitriptyline, Doxepin, Trimipramine, etc.) • Typical antipsychotics (Chlorpromazine, Thioridazine, etc.) • Atypical antipsychotics (Olanzapine, Quetiapine, Risperidone, etc.)α2-Adrenergic Agonists 4-NEMD • Clonidine • Detomidine • Dexmedetomidine • Lofexidine • Medetomidine • Romifidine • Tizanidine • Xylazine5-HT2A Antagonists Eplivanserin • Niaprazine • Pruvanserin • Trazodone • Volinanserin; Others: Tricyclic antidepressants (Amitriptyline, Doxepin, Trimipramine, etc.) • Tetracyclic antidepressants (Mianserin, Mirtazapine, etc.) • Typical antipsychotics (Chlorpromazine, Thioridazine, etc.) • Atypical antipsychotics (Olanzapine, Quetiapine, Risperidone, etc.)Melatonin Agonists Orexin Antagonists Almorexant • SB-334,867 • SB-408,124 • SB-649,868 • Suvorexant • TCS-OX2-29Others Acecarbromal • Apronal • Bromisoval • Cannabidiol (Cannabis) • Carbromal • Embutramide • Evoxine • Fenadiazole • Gabapentin • Kavalactones (Kava) • Mephenoxalone • Opiates/Opioids (Hydrocodone, Morphine (Opium), etc.) • Passion flower • Scopolamine (Mandrake) • ValnoctamideCategories:- Barbiturates
- General anesthetics
- Alkenes
- Alkynes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
