- Chloral
-
Chloral 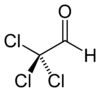
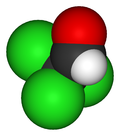 Trichloroethanal
TrichloroethanalIdentifiers CAS number 75-87-6 
ChemSpider 6167 
UNII FLI06WS32H 
KEGG C14866 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - ClC(Cl)(Cl)C=O
Properties Molecular formula C2HCl3O Molar mass 147.388 g/mol Density 1.512 g/cm3 @ 20 °C Melting point −57.5 °C
Boiling point 97.8 °C
Solubility in water forms soluble hydrate Solubility in ethanol miscible Solubility in diethyl ether miscible Solubility in chloroform miscible  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Chloral, also known as trichloroacetaldehyde, is the organic compound with the formula Cl3CCHO. This aldehyde is a colourless oily liquid that is soluble in a wide range of solvents. It reacts with water to form chloral hydrate, a once widely used sedative and hypnotic substance.
Contents
Production
Chloral can be produced by chlorination of ethanol, as reported in 1832 by Justus von Liebig.
Key reactions
Aside from its tendency to hydrate, chloral is most notable as a building block in the synthesis of DDT. For this purpose, chloral is treated with chlorobenzene in the presence of a catalytic amount of sulfuric acid:
- Cl3CCHO + 2 C6H5Cl → Cl3CCH(C6H4Cl)2 + H2O
This reaction was described by Othmar Zeidler in 1874.[1]
Chloral is also used to form chloroform by treating it with sodium hydroxide.
References
- ^ Othmar Zeidler (1874). "Verbindungen von Chloral mit Brom- und Chlorbenzol". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft 7 (2): 1180–1181. doi:10.1002/cber.18740070278.
See also
Categories:- Aldehydes
- Organochlorides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
