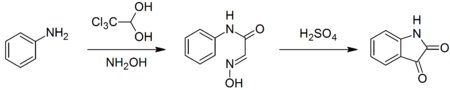- Chloral hydrate
-
Chloral hydrate  2,2,2-trichloroethane-1,1-diolOther namesTrichloroacetaldehyde monohydrate
2,2,2-trichloroethane-1,1-diolOther namesTrichloroacetaldehyde monohydrate
Tradenames: Aquachloral, Novo-Chlorhydrate, Somnos, Noctec, SomnoteIdentifiers CAS number 302-17-0 
PubChem 2707 ChemSpider 2606 
UNII 418M5916WG 
DrugBank DB01563 KEGG D00265 
ChEBI CHEBI:28142 
ChEMBL CHEMBL455917 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - ClC(Cl)(Cl)C(O)O
Properties Molecular formula C2H3Cl3O2 Molar mass 165.40 g/mol Appearance Colorless solid Density 1.91 g/cm3 Melting point 57 °C, 330 K, 135 °F
Boiling point 98 °C, 371 K, 208 °F
Acidity (pKa) 9.66, 11.0[1] Pharmacology Bioavailability well absorbed Routes of
administrationOral codeine/syrup, rectal suppository Metabolism converted to trichloroethanol, hepatic and renal Elimination
half-life8–10 hours in plasma Excretion bile, feces, urine (various metabolites not unchanged) Legal status Pregnancy
categoryC(US) Hazards MSDS External MSDS EU classification Harmful (Xn) R-phrases R22 R36 R37 R38 Related compounds Related compounds Chloral, chlorobutanol  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Chloral hydrate is a sedative and hypnotic drug as well as a chemical reagent and precursor. The name chloral hydrate indicates that it is formed from chloral (trichloroacetaldehyde) by the addition of one molecule of water. Its chemical formula is C2H3Cl3O2.
It was discovered through the chlorination of ethanol in 1832 by Justus von Liebig in Gießen.[2][3] Its sedative properties were first published in 1869 and subsequently, because of its easy synthesis, its use was widespread.[4] It was widely used recreationally and misprescribed in the late 19th century. Chloral hydrate is soluble in both water and alcohol, readily forming concentrated solutions. A solution of chloral hydrate in alcohol called "knockout drops" was used to prepare a Mickey Finn. More reputable uses of chloral hydrate include its use as a clearing agent for chitin and fibers and as a key ingredient in Hoyer's mounting medium, which is used to prepare permanent or semipermanent microscope slides of small organisms, histological sections, and chromosome squashes.
It is, together with chloroform, a minor side-product of the chlorination of water when organic residues are present in the water, though concentrations rarely exceed 5 micrograms per litre (µg/L).[citation needed]
Contents
Production
Chloral hydrate is produced from chlorine and ethanol in acidic solution. In basic conditions the haloform reaction takes place and chloroform is produced.
- 4 Cl2 + C2H5OH + H2O → Cl3CCH(OH)2 + 5 HCl
Uses
Building block
Chloral hydrate is a starting point for the synthesis of more complex chemicals. It is the starting material for the production of chloral, which is produced by the distillation of a mixture of chloral hydrate and sulfuric acid, which serves as the desiccant.
Notably, it is used to synthesize isatin. In this synthesis, chloral hydrate reacts with aniline and hydroxylamine to give a condensation product which cyclicizes in sulfuric acid to give the target compound:[5]
Hypnotic
Chloral hydrate is used for the short-term treatment of insomnia and as a sedative before minor medical or dental treatment. It was largely displaced in the mid-20th century by barbiturates[6] and subsequently by benzodiazepines. It was also formerly used in veterinary medicine as a general anesthetic. Today, it is commonly used as an ingredient in the veterinary anesthetic Equithesin[citation needed]. It is also still used as a sedative prior to EEG procedures, as it is one of the few available sedatives that does not suppress epileptiform discharges.[7]
In therapeutic doses for insomnia chloral hydrate is effective within 60 minutes, it is metabolized within four minutes into trichloroethanol by erythrocytes and plasma esterases and many hours later into trichloroacetic acid. Higher doses can depress respiration and blood pressure.
Adverse effects
Long-term use of chloral hydrate is associated with a rapid development of tolerance to its effects and possible addiction as well as adverse effects including rashes, gastric discomfort and severe renal, cardiac and hepatic failure.[8]
Overdosage
Acute overdosage is often characterized by nausea, vomiting, confusion, convulsions, slow and irregular breathing, cardiac arrhythmia, and coma. The plasma, serum or blood concentrations of chloral hydrate and/or trichloroethanol, its major active metabolite, may be measured to confirm a diagnosis of poisoning in hospitalized patients or to aid in the medicolegal investigation of fatalities. Accidental overdosage of young children undergoing simple dental or surgical procedures has occurred. Hemodialysis has been used successfully to accelerate clearance of the drug in poisoning victims.[9]
Pharmacology
Chloral hydrate exerts its pharmacological properties via enhancing the GABA receptor complex.[10] It is moderately addictive, as chronic use is known to cause dependency and withdrawal symptoms. The chemical can potentiate various anticoagulants and is weakly mutagenic in vitro and in vivo.[citation needed]
Legal status
Chloral hydrate is illegal in the United States without a prescription. Chloral hydrate is a schedule IV controlled substance in the United States. Its properties have sometimes led to its use as a date rape drug.[11][unreliable source?]
Chloral hydrate is also controlled substance in Canada under Schedule F of the Food and Drug Regulations.[12]
Chloral hydrate is not a controlled substance in the United Kingdom.
Hoyer's mounting medium
Chloral hydrate is also an ingredient used for Hoyer's solution, a mounting medium for microscopic observation of diverse organisms such as bryophytes, ferns, seeds, and small arthropods (especially mites). One recipe for making Hoyer's is dissolving gum arabic (30.0 g) in water (50.0 mL), then adding chloral hydrate (200.0 g), and then finally adding glycerol (16.0 mL). An advantage of this medium include an excellent refraction index and clearing (macerating) properties of the small specimens (especially advantageous if specimens require observation with differential interference contrast microscopy). The major disadvantage of Hoyer's is its susceptibility to the effects of dehydration, which causes the mountant to crystallize and threatening the slide to become unusable. It is therefore absolutely necessary, after drying a mounted specimen, to thoroughly ring (2 layers are best) cover slips with a protective coating (e.g., insulating Glyptol), which prevents rehydration and mountant deterioration. Chloral hydrate reportedly does not effectively clear larger specimens, or arthropods that are more heavily sclerotized (e.g., larger insects). These should first be cleared with another product (e.g., 10% KOH or NaOH), and then mounted in Hoyer's. Other disadvantages of Hoyer's (principally due to chloral hydrate) include toxicity (see above), and procurement problems due to chloral hydrate being a controlled substance.
See also
- Initiating the Jonestown Massacre, and metal vat with Flavor Aid, poisoned with Valium, chloral hydrate, cyanide and Phenergan, which was then consumed orally.
- Richard Realf (1832–1878) killed himself with a combination of chloral hydrate and laudanum.[13]
- Jennie Bosschieter (1882–1900) who was murdered with chloral hydrate in Paterson, New Jersey on 12 October 1900.
- John Tyndall (1820–1893) who died of an accidental overdose.
- Anna Nicole Smith (1967–2007) who died of an accidental[14] combination of chloral hydrate with three benzodiazepines, as announced by forensic pathologist Dr. Joshua Perper on 26 March 2007. Chloral hydrate was the major factor, but none of these drugs would have been sufficient by itself to cause her death.[15]
- Marilyn Monroe had chloral hydrate in her system at her death.
- Hank Williams came under the spell of a man calling himself "Doctor" Toby Marshall (actually a paroled forger), who often supplied him with prescriptions and injections of chloral hydrate, which Marshall claimed was a pain reliever, to deal with the pain from Williams' life-long severe back problems.[16]
- William S. Burroughs was expelled from school for experimenting with chloral hydrate along with another pupil. The incident is detailed in the writer's foreword to Junkie.
- Mary Todd Lincoln was given chloral hydrate for sleep problems. See Mary Todd Lincoln by Jean Baker and Mary: Mrs. A. Lincoln, by Janis Cooke Newman.
- André Gide (1869–1951) was given chloral hydrate as a boy for sleep problems by a Doctor named Lizart. Gide states in his autobiography, If It Die... that "all my later weaknesses of will or memory I attribute to him."[17]
- House of Mirth (published in 1905), a novel whose heroine, Lily Bart, dies of an overdose of chloral hydrate.
- Dante Gabriel Rossetti (1830–1882), the English painter, was a regular user of chloral hydrate, originally against insomnia. He is quoted as saying to his friend Hall Caine: "Everyone has skeletons in their cupboards, and this is mine."
- James Bond says, "that's...chloral hydrate" in the movie The Living Daylights before collapsing from its effects.
- In the movie From Russia with Love, Tatiana Romanava is knocked out by chloral hydrate, which SPECTRE agent Red Grant slips in her drink.
- Chloral Betaine, a related drug
- Friedrich Nietzsche regularly used chloral hydrate in the years leading up to his nervous breakdown, according to Lou Salome and other associates. Whether the drug contributed to his insanity is a point of controversy. See "The Madness of Nietzsche" by E.F. Podach.
Notes
- ^ Gawron, O., Draus, F., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1958, 80, 5392.
- ^ Justus Liebig (1832). "Ueber die Zersetzung des Alkohols durch Chlor". Annalen der Pharmacie 1 (1): 31–32. doi:10.1002/jlac.18320010109.
- ^ Justus Liebig (1832). "Ueber die Verbindungen, welche durch die Einwirkung des Chlors auf Alkohol, Aether, ölbildendes Gas und Essiggeist entstehen". Annalen der Pharmacie 1 (2): 182–230. doi:10.1002/jlac.18320010203.
- ^ Liebreich, Oskar (1869). Das Chloralhydrat : ein neues Hypnoticum und Anaestheticum und dessen Anwendung in der Medicin ; eine Arzneimittel-Untersuchung. Berlin: Müller.
- ^ C. S. Marvel and G. S. Hiers (1941), "Isatin", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv1p0327; Coll. Vol. 1: 327
- ^ Tariq, Syed H. and Shailaja Pulisetty; “Pharmacotherapy for Insomnia”, Clinics in Geriatric Medicine (24), 2008 p. 93-105 PMID: 18035234
- ^ http://jcc.kau.edu.sa/Files/140/Researches/11822_Chloral.pdf
- ^ Gelder, M., Mayou, R. and Geddes, J. 2005. Psychiatry. 3rd ed. New York: Oxford. pp238.
- ^ R. Baselt, Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man, 8th edition, Biomedical Publications, Foster City, CA, 2008, pp. 259-261.
- ^ Lu, J; Greco, MA (2006). "Sleep circuitry and the hypnotic mechanism of GABAA drugs.". Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine 2 (2): S19–26. PMID 17557503.
- ^ New York Daily News, 10/25/2008
- ^ http://laws.justice.gc.ca/eng/regulations/C.R.C.,_c._870/page-332.html#h-347 Schedule F of the Food and Drug Regulations, CRC, c 870
- ^ Rathmell, George W. (2002) A Passport to Hell: The Mystery of Richard Realf Lincoln, Nebraska: Authors Choice Press pp. ix, 134 ISBN 0595212514, 9780595212514 http://books.google.com/books?id=mE-_SoTc74wC&printsec=frontcover#v=onepage&q&f=false. Retrieved September 12, 2011
- ^ Anna Nicole Smith Autopsy Report. XI. Manner of death. A. The Exclusion of Homicide The Smoking Gun
- ^ Anna Nicole Smith Autopsy Released. Coroner: Ex-Playmate died from accidental sedative overdose The Smoking Gun
- ^ Hank Williams summary Book Rags
- ^ Gide, André and Dorothy Bussey (trans). If It Die…An Autobiography. New York: Vintage International, 2001. p105
External links
 Media related to Chloral hydrate at Wikimedia CommonsCategories:
Media related to Chloral hydrate at Wikimedia CommonsCategories:- Aldehydes
- Hydrates
- Hypnotics
- Sedatives
- Organochlorides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.