- Chlorobenzene
-
Chlorobenzene 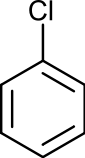
 chlorobenzeneOther namesbenzene chloride
chlorobenzeneOther namesbenzene chloride
monochlorobenzene
Phenyl chlorideIdentifiers CAS number 108-90-7 
PubChem 7964 ChemSpider 7676 
UNII K18102WN1G 
KEGG C06990 
ChEBI CHEBI:28097 
ChEMBL CHEMBL16200 
RTECS number CZ0175000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - c1ccc(cc1)Cl
Properties Molecular formula C6H5Cl Molar mass 112.56 g/mol Appearance colorless liquid Density 1.11 g/cm³, liquid Melting point -45 °C, 228 K, -49 °F
Boiling point 131 °C, 404 K, 268 °F
Solubility in water low Solubility in other solvents soluble in most organic solvents Hazards MSDS External MSDS R-phrases R10 R20 R51/53 S-phrases S24/25 S61 NFPA 704 Flash point 29 °C Related compounds Related Halobenzenes Fluorobenzene
Bromobenzene
IodobenzeneRelated compounds benzene
1,4-dichlorobenzeneSupplementary data page Structure and
propertiesn, εr, etc. Thermodynamic
dataPhase behaviour
Solid, liquid, gasSpectral data UV, IR, NMR, MS  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Chlorobenzene is an aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5Cl. This colorless, flammable liquid is a common solvent and a widely used intermediate in the manufacture of other chemicals.
Contents
Uses
Chlorobenzene once was used in the manufacture of certain pesticides, most notably DDT by reaction with chloral (trichloroacetaldehyde), but this application has declined with the diminished use of DDT. At one time, chlorobenzene was the main precursor for the manufacture of phenol:[1]
- C6H5Cl + NaOH → C6H5OH + NaCl
The major use of chlorobenzene is as an intermediate in the production of commodities such as herbicides, dyestuffs, and rubber. Chlorobenzene is also used as a high-boiling solvent in many industrial applications as well as in the laboratory.[2] Chlorobenzene is nitrated on a large scale to give a mixture of 2- and 4-nitrochlorobenzenes, which can be separated by fractional crystallization followed by distillation. 2-Nitrochlorobenzene (CAS#88-73-3) is converted to related 2-nitrophenol, 2-nitroanisole, bis(2-nitrophenyl)disulfide, and 2-nitropaniline by nucleophilic displacement of the chloride with sodium hydroxide, sodium methoxide, sodium disulfide and ammonia. The conversion of the 4-nitrochlorobenzene (CAS#100-00-5) are similar.[3]
Synthesis
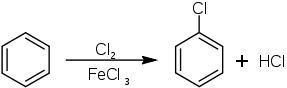
Chlorobenzene was first described in 1851. Presently it is manufactured by chlorination of benzene in the presence of a catalytic amount of Lewis acid such as ferric chloride and anhydrous aluminium chloride:
The catalyst enhances the electrophilicity of the chlorine. Because chlorine is electronegative, C6H5Cl exhibits decreased susceptibility to attack by other electrophiles. For this reason, the chlorination process produces only small amounts of dichloro- and trichlorobenzenes.
Safety
Chlorobenzene exhibits "low to moderate" toxicity as indicated by its LD50 of 2.9 g/kg.[2]
Toxicology
Chlorobenzene is not a naturally occurring compound, but because of its manufacture, can persist in soil for several months, in air for about 3.5 days, and in water for less than one day. Humans may be exposed to this agent via breathing contaminated air (primarily via occupational exposure), eating contaminated food or water, or by coming into contact with contaminated soil (typically near hazardous waste sites). However, because it has only been found at 97 out of 1,177 NPL hazardous waste sites, it is not considered a widespread environmental contaminant.
Upon entering the body, typically via contaminated air, chlorobenzene is excreted both via the lungs and the urinary system.
References
- ^ Manfred Weber, Markus Weber, Michael Kleine-Boymann, “Phenol” in Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19 299.pub2
- ^ a b Manfred Rossberg et al. “Chlorinated Hydrocarbons” in Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2006. doi:10.1002/14356007.a06 233.pub2
- ^ Gerald Booth (2007). "Nitro Compounds, Aromatic". In: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons: New York. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_411
Categories:- Aromatic compounds
- Halogenated solvents
- Organochlorides
- Hazardous air pollutants
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.