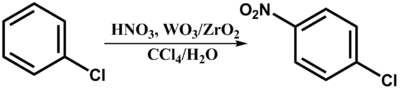- 4-Nitrochlorobenzene
-
4-nitrochlorobenzene 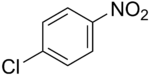 1-Chloro-4-nitrobenzeneOther names4-Chloro-1-nitrobenzene; 4-Chloronitrobenzene; p-Nitrochlorobenzene; PNCBO
1-Chloro-4-nitrobenzeneOther names4-Chloro-1-nitrobenzene; 4-Chloronitrobenzene; p-Nitrochlorobenzene; PNCBOIdentifiers CAS number 100-00-5 
ChemSpider 7194 
KEGG C14456 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - ClC1=CC=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C1
Properties Molecular formula C6H4ClNO2 Molar mass 157.55 g mol−1 Appearance Light yellow solid Density 1.52 g/cm³ (20 °C) Melting point 83.6 °C, 357 K, 182 °F
Boiling point 242.0 °C, 515 K, 468 °F
Solubility in water Insoluble Solubility in other solvents Soluble in toluene, ether, acetone, hot ethanol Hazards MSDS External MSDS  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references 4-Nitrochlorobenzene is the organic compound with the formula ClC6H4NO2. This compound is a light yellow crystalline solid that is stable to air. 4-Nitrochlorobenzene is a common intermediate in the industrial production of a number of compounds, including common antioxidants found in rubber.
Preparation
4-Nitrochlorobenzene was originally prepared by the nitration of 4 bromochlorobenzene by Holleman and coworkers[1]:
Currently, 4-nitrochlorobenzene is prepared on an industrial scale from chlorobenzene via phase-transfer catalysis using tungsten or zirconium catalysts:[2]
Applications
4-Nitrochlorobenzene is an intermediate in the preparation of a variety of derivatives, including 4-chloroaniline, 4-nitrophenol, 4-nitroanisole, 4-nitroaniline, 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene, and 3,4-dichloronitrobenzene.[3] These reactions mainly involve the nucleophilic displacement of chloride . The electron-withdrawing nature of the appended nitro-group makes the benzene ring especially susceptible to nucleophilic aromatic substitution, unlike related chlorobenzene.
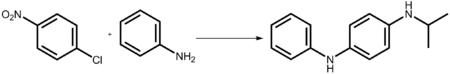
Another major use of 4-nitrochlorobenzene is its condensation with aniline to produce 4 nitrodiphenylamine. Reductive alkylation of the nitro group affords secondary aryl amines, which are useful antioxidants for rubber.[3]
References
- ^ The nitration of mixed dihalogen benzenes. Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas et de la Belgique. Amsterdam, 1915; pp. 204-235.
- ^ Zhang, Cun; Liu, Tao; Ma, Chunyan. U.S. Patent 10,235,242, 2008.
- ^ a b Nitro Compounds, Aromatic. Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 7th Ed.; Wiley & Sons: New York, 1997; pp. 18-19
Categories:- Organochlorides
- Nitrobenzenes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.