- 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene
-
2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene 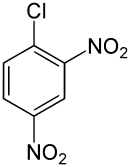 1-Chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzeneOther namesDinitrochlorobenzene; Chlorodinitrobenzene; 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene; 2,4-Dinitrophenyl chloride; 4-Chloro-1,3-dinitrobenzene
1-Chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzeneOther namesDinitrochlorobenzene; Chlorodinitrobenzene; 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene; 2,4-Dinitrophenyl chloride; 4-Chloro-1,3-dinitrobenzeneIdentifiers Abbreviations CDNB; DNCB CAS number 97-00-7 
PubChem 6 ChemSpider 5 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - c1cc(c(cc1[N+](=O)[O-])[N+](=O)[O-])Cl
Properties Molecular formula C6H3ClN2O4 Molar mass 202.55 g mol−1  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB) is a benzene derivative. It is an electrophilic, cytotoxic compound that is used in biochemical research involving glutathione-S-transferases (GSTs).
Uses
DNCB induces a type IV hypersensitivity reaction in almost all people exposed to it, so it is used medically to assess the T cell activity in patients. This is a useful diagnostic test for immunocompromised patients. It can also be used to treat warts.[1]
DNCB is used as a substrate in GST enzyme activity assays.[2] The molecule is conjugated to a single molecule of reduced glutathione which then fluoresces at 340 nm. Affinity of CDNB for each class of GST varies and so it is not a good measure of activity for some forms (e.g. GSTT and GSTZ).[citation needed]
Safety
DNCB can cause contact dermatitis.[3]
References
- ^ "Treating warts". Harvard Medical School. http://www.health.harvard.edu/fhg/updates/update0303d.shtml. Retrieved April 2, 2010.
- ^ Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974). "Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation". J Biol Chem 249 (22): 7130–7139. PMID 4436300.
- ^ White SI, Friedmann PS, Moss C, Simpson JM (1986). "The effect of altering area of application and dose per unit area on sensitization by DNCB". Br. J. Dermatol. 115 (6): 663–8. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1986.tb06646.x. PMID 3801307.
Categories:- Nitrobenzenes
- Organochlorides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
