- 4-Nitroaniline
-
p-Nitroaniline  Other names4-nitroaniline
Other names4-nitroaniline
1-amino-4-nitrobenzene
p-nitrophenylamineIdentifiers CAS number 100-01-6 
ChemSpider 7195 
UNII 1MRQ0QZG7G 
ChEMBL CHEMBL14282 
Properties Molecular formula C6H6N2O2 Molar mass 138.12 g/mol Appearance yellow or brown powder Density 1.437 g/ml, solid Melting point 146-149 °C(lit.)
Boiling point 332 °C
Solubility in water 0.8 mg/ml at 18.5°C (IPCS) Hazards MSDS JT Baker EU classification  T
T  N
NR-phrases R23/24/25 R33 R52/53 S-phrases S28 S36/37 S45 S61 Main hazards Toxic NFPA 704 Flash point 199 °C Related compounds Related compounds 2-Nitroaniline, 3-Nitroaniline  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references 4-Nitroaniline, p-nitroaniline or 1-amino-4-nitrobenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H6N2O2. It is an organic chemical compound, consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group which is para to a nitro group. The chemical structure of p-nitroaniline is shown at the right. This chemical is commonly used as an intermediate in the synthesis of dyes, antioxidants, pharmaceuticals and gasoline, in gum inhibitors, poultry medicines, and as a corrosion inhibitor.
Contents
Synthesis
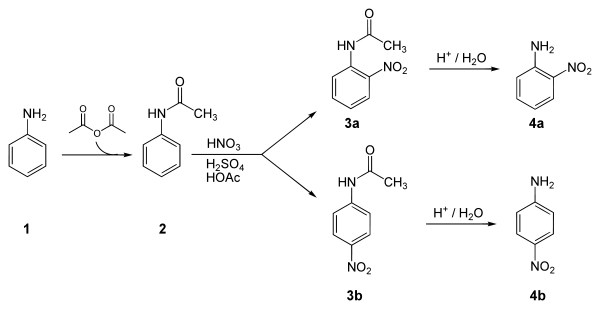
Below is an example synthesis of p-nitroaniline from aniline. The key step in this reaction sequence is an electrophilic aromatic substitution to install the nitro group para to the amino group. After this reaction, a separation must be performed to remove 2-nitroaniline, which is also formed in a small amount during the reaction.[1]
Applications
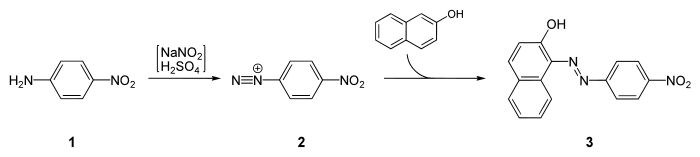
4-Nitroaniline is a starting material for the synthesis of Para Red, the first Azo dye:[2]
Toxicity
The compound is toxic by way of inhalation, ingestion, and absorption, and should be handled with care. Its LD50 in rats is 750 mg/kg when administered orally. p-Nitroaniline is particularly harmful to all aquatic organisms, and can cause long-term damage to the environment if released as a pollutant.
References
- ^ Mohrig, J.R.; Morrill, T.C.; Hammond, C.N.; Neckers, D.C. "Synthesis 5: Synthesis of the Dye Para Red from Aniline." Experimental Organic Chemistry. Freeman: New York, NY, 1997; pp 456-467.
- ^ Williamson, Kenneth L. (2002). Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments, Fourth Edition. Houghton-Mifflin. ISBN 0-618-19702-8.
External links
See also
Categories:- Anilines
- Dyes
- Hazardous air pollutants
- IARC Group 3 carcinogens
- Nitrobenzenes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.