- Arene substitution patterns
-
Arene substitution patterns are part of organic chemistry IUPAC nomenclature and pinpoint the position of substituents other than hydrogen in relation to each other on an aromatic hydrocarbon.
Contents
Ortho, meta, and para substitution
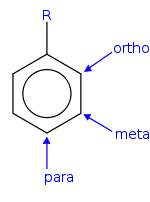
See also: Electrophilic aromatic substitution- In ortho-substitution, two substituents occupy positions next to each other, which may be numbered 1 and 2. In the diagram, these positions are marked R and ortho.
- In meta-substitution the substituents occupy positions 1 and 3 (corresponding to R and meta in the diagram).
- In para-substitution, the substituents occupy the opposite ends (positions 1 and 4, corresponding to R and para in the diagram). The toluidines serve as an example for these three types of substitution.
Ipso, meso, and peri substitution
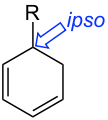
- Ipso-substitution describes two substituents sharing the same ring position in an intermediate compound in an electrophilic aromatic substitution.
- Meso-substitution refers to the substituents occupying a benzylic position. It is observed in compounds such as calixarenes and acridines.
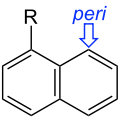
- Peri-substitution occurs in naphthalenes for substituents at the 1 and 8 positions.
Cine and tele substitution
- In cine-substitution, the entering group takes up a position adjacent to that occupied by the leaving group. For example, cine-substitution is observed in aryne chemistry.[1]
- Tele-substitution occurs when the new position is more than one atom away on the ring.[2]
Origins
The prefixes ortho, meta, and para are all derived from Greek, meaning straight or correct, following or after, and akin to or similar, respectively. The relationship to the current meaning is perhaps not obvious. The ortho description was historically used to designate the original compound, and an isomer was often called the meta compound. For instance, the trivial names orthophosphoric acid and trimetaphosphoric acid have nothing to do with aromatics at all. Likewise, the description para was reserved for just closely related compounds. Thus Berzelius originally called the racemic form of aspartic acid paraaspartic acid (another obsolete term: racemic acid) in 1830. The use of the descriptions ortho, meta and para for multiple substituted aromatic rings starts with Wilhelm Körner in the period 1866–1874 although he chose to reserve the ortho prefix for the 1,4 isomer and the meta prefix for the 1,2-isomer. The current nomenclature (different again from that of Körner) was introduced by the Chemical Society in 1879 [3].
Examples
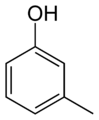
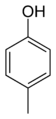
Examples of the use of this nomenclature are given for isomers of cresol:
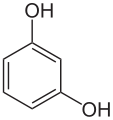
Catechol has two isomers, the meta isomer resorcinol and the para isomer hydroquinone:
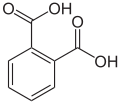
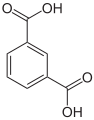
Phthalic acid has two isomers, the meta isomer isophthalic acid and the para isomer terephthalic acid:
References
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "cine-substitution".
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "tele-substitution".
- ^ The Origins of the Ortho-, Meta-, and Para- Prefixes in Chemical Nomenclature, William B. Jensen, Journal of Chemical Education • Vol. 83 No. 3 March p. 356 2006
Categories:- Aromatic compounds
- Chemical nomenclature
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.