- Phthalic acid
-
Phthalic acid 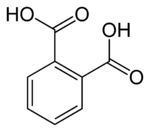
 benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acidOther namesbenzene-1,2-dioic acid, phthalic acid, ortho-phthalic acid
benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acidOther namesbenzene-1,2-dioic acid, phthalic acid, ortho-phthalic acidIdentifiers CAS number 88-99-3 
PubChem 1017 EC number 201-873-2 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C1=CC=C(C(=C1)
C(=O)O)C(=O)O
Properties Molecular formula C8H6O4 Molar mass 166.14 g/mol Appearance white solid Density 1.593 g/cm3, solid Melting point 191 - 230 °C[1]
Solubility in water 0.6 g / 100 mL [2][3] Acidity (pKa) 2.98, 5.28[4] Hazards NFPA 704 Related compounds Related carboxylic acids Isophthalic acid
Terephthalic acidRelated compounds Phthalic anhydride
Phthalimide
Phthalhydrazide
Phthaloyl chloride
Benzene-1,2-
dicarboxaldehyde (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Phthalic acid is an aromatic dicarboxylic acid, with formula C6H4(CO2H)2. It is an isomer of isophthalic acid and terephthalic acid. Although phthalic acid is of modest commercial importance, the closely related derivative phthalic anhydride is a commodity chemical produced on a large scale.[5]
Contents
Production
Phthalic acid is produced by the catalytic oxidation of naphthalene directly to phthalic anhydride and a subsequent hydrolysis of the anhydride.[5]
Phthalic acid was first obtained by French chemist Auguste Laurent in 1836 by oxidizing naphthalene tetrachloride. Believing the resulting substance to be a naphthalene derivative, he named it naphthalenic acid. After the Swiss chemist Jean Charles Galissard de Marignac determined its correct formula, Laurent gave it its present name. Manufacturing methods in the nineteenth century included oxidation of naphthalene tetrachloride with nitric acid, or, better, oxidation of the hydrocarbon with fuming sulfuric acid, using mercury or mercury(II) sulfate as a catalyst.
Reactions and uses
It is a dibasic acid, with pKa's of 2.89 and 5.51. The monopotassium salt, potassium hydrogen phthalate is a standard acid in analytical chemistry. Typically phthalate esters are prepared from the widely available phthalic anhydride. Reduction of phthalic acid with sodium amalgam in the presence of water gives the 1,3-cyclohexadiene derivative.[6]
Isomers
Phthalic acid is one of three isomers of benzenedicarboxylic acid, the others being isophthalic acid and terephthalic acid. Sometimes the term "phthalic acids" is used to refer to this family of isomers, but in the singular, "phthalic acid", refers exclusively to the ortho- isomer.
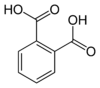
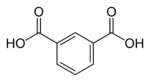
phthalic acid isophthalic acid terephthalic acid (ortho-phthalic acid) (meta-phthalic acid) (para-phthalic acid) Safety
The toxicity of phthalic acid is low with LD50 (mouse) of 550 mg/kg. However, many phthalate esters have been implicated as endocrine disruptors.
See also
- Isophthalic acid
- Terephthalic acid
- Phthalate
- Potassium hydrogen phthalate, a primary standard for acid-base titrations
- Phthalic anhydride
References
- ^ Several melting points are reported, for example: (i) 210-211° C with decomposition (Sigma-Aldrich on-line), (ii) 191 °C in a sealed tube (Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry), (iii) 230 °C with conversion to phthalic anhydride and water (J.T.Baker MSDS).
- ^ http://hazard.com/msds/mf/baker/baker/files/p4270.htm
- ^ http://actrav.itcilo.org/actrav-english/telearn/osh/ic/88993.htm
- ^ Brown, H.C., et al., in Baude, E.A. and Nachod, F.C., Determination of Organic Structures by Physical Methods, Academic Press, New York, 1955.
- ^ a b Peter M. Lorz, Friedrich K. Towae, Walter Enke, Rudolf Jäckh, Naresh Bhargava, Wolfgang Hillesheim “Phthalic Acid and Derivatives” in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2007, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a20_181.pub2
- ^ Richard N. McDonald and Charles E. Reineke (1988), "trans-1,2-Dihydrophthalic Acid", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv6p0461; Coll. Vol. 6: 461
- Merck Index, 9th ed, #7178
External links
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.Categories:
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.Categories:- Dicarboxylic acids
- Benzoic acids
- Phthalates
- C1=CC=C(C(=C1)
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


