- 4-Chloroaniline
-
4-Chloroaniline 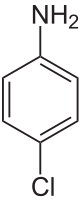 4-chloroanilineOther namesp-chloroaniline
4-chloroanilineOther namesp-chloroanilineIdentifiers CAS number 106-47-8 
PubChem 7812 ChemSpider 7524 
KEGG C14450 
ChEMBL CHEMBL15888 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C1=CC(=CC=C1N)Cl
Properties Molecular formula C6H6ClN Molar mass 127.57154 g/mol Appearance pale yellow solid Density 1.43 g·cm−3 Melting point 72.5 °C
Boiling point 232 °C
Solubility in water Negligible Hazards MSDS External MSDS Main hazards Very toxic, possible carcinogen. Absorbed through skin.[1] Flash point 113 °C  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references 4-Chloroaniline is a organochlorine compound with the formula ClC6H4NH2. This pale yellow solid is one of several known chloroanilines.
Preparation
4-Chloroaniline is not prepared from aniline, which tends to overchlorinate. Instead, it is prepared by hydrogenation of 4-Nitrochlorobenzene, which in turn is prepared by nitration of chlorobenzene.[2]
Uses
4-Chloroaniline is an important building block used in the chemical industry for the production of pesticides, drugs, and dyestuffs. It is a precursor to the widely used antimicrobial and bacteriocide Chlorhexidine and is used in the manufacture of pesticides, including pyraclostrobin, anilofos, monolinuron and chlorphthalim.[3] Some benzodiazepine drugs use 4-chloroaniline in their manufacture.
References
- ^ "Safety data for 4-chloroaniline". Oxford University. http://physchem.ox.ac.uk/MSDS/CH/4-chloroaniline.html.
- ^ Gerald Booth (2007). "Nitro Compounds, Aromatic". In: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry# John Wiley & Sons: New York# doi:10#1002/14356007#a17_411
- ^ Ashford’s Dictionary of Industrial Chemicals, 3rd edition, 2011, page 1998

This article about an amine is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
