- 4,4'-Methylenebis(2-chloroaniline)
-
4,4'-Methylenebis(2-chloroaniline) 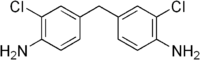 4-[(4-Amino-3-chlorophenyl)methyl]-2-chloroanilineOther names•4,4'-Methylene-bis(2-chloroaniline)
4-[(4-Amino-3-chlorophenyl)methyl]-2-chloroanilineOther names•4,4'-Methylene-bis(2-chloroaniline)
•Cyanaset
•Quodorole
•Dacpm
•Curalin M
•Diamet Kh
•Millionate M
•Bis amine
•MOCA
•Bisamine SIdentifiers CAS number 101-14-4 
PubChem 7543 ChemSpider 7262 KEGG C10999 ChEMBL CHEMBL82846 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - Clc1cc(ccc1N)Cc2ccc(N)c(Cl)c2
- InChI=1S/C13H12Cl2N2/c14-10-6-8(1-3-12(10)16)5-9-2-4-13(17)11(15)7-9/h1-4,6-7H,5,16-17H2
Key: IBOFVQJTBBUKMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
InChI=1/C13H12Cl2N2/c14-10-6-8(1-3-12(10)16)5-9-2-4-13(17)11(15)7-9/h1-4,6-7H,5,16-17H2
Key: IBOFVQJTBBUKMU-UHFFFAOYAI
Properties Molecular formula C13H12Cl2N2 Molar mass 267.15 g/mol Appearance off white powder Density 1.354g/cm3 Melting point 102-107°C (lit.)
Boiling point 412°C @ 760mmHg
Solubility in water insoluble Hazards NFPA 704 Flash point 203°C  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references 4,4'-Methylenebis(2-chloroaniline) (MOCA, MBOCA, bisamine) is a substance used as a curing agent in polyurethane production.[1] It is a suspected human carcinogen, with a current threshold limit value of 0.01 ppm in the industrial atmosphere. Employee exposure is often monitored by measurement of urinary MOCA in free and/or conjugated form.[2]
It is a weak base with a slight odor and is reactive to active metals such as sodium, potassium, magnesium and zinc.[citation needed]
References
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.

