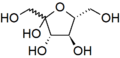- Structural formula
-
The structural formula of a chemical compound is a graphical representation of the molecular structure, showing how the atoms are arranged. The chemical bonding within the molecule is also shown, either explicitly or implicitly. There are several common representations used in publications. These are described below. Also several other formats are used, as in chemical databases, such as SMILES, InChI and CML.
Unlike chemical formulas or chemical names, structural formulas provide a representation of the molecular structure. Chemists nearly always describe a chemical reaction or synthesis using structural formulas rather than chemical names, because the structural formulas allow the chemist to visualize the molecules and the changes that occur.
Many chemical compounds exist in different isomeric forms, which have different structures but the same overall chemical formula. A structural formula indicates the arrangements of atoms in a way that a chemical formula cannot.
Contents
Lewis structures
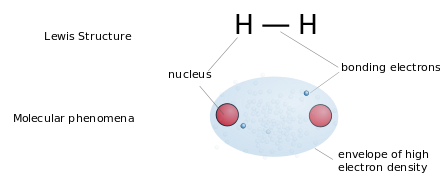
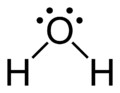
Lewis structures (or "Lewis dot structures") are flat graphical formulas that show atom connectivity and lone pair or unpaired electrons, but not three-dimensional structure. This notation is mostly used for small molecules. Each line represents the two electrons of a single bond. Two or three parallel lines between pairs of atoms represent double or triple bonds, respectively. Alternatively, pairs of dots may used to represent bonding pairs. In addition, all non-bonded electrons (paired or unpaired) and any formal charges on atoms are indicated.
-
The Lewis structure of water.
Condensed formulas
In early organic-chemistry publications, where use of graphics was severely limited, a typographic system arose to describe organic structures in a line of text. Although this system tends to be problematic in application to cyclic compounds, it remains a convenient way to represent simple structures:
CH3CH2OH (ethanol)
Parentheses are used to indicate multiple identical groups, indicating attachment to the nearest non-hydrogen atom on the left when appearing within a formula, or to the atom on the right when appearing at the start of a formula:
(CH3)2CHOH or CH(CH3)2OH (2-propanol)
In all cases, all atoms are shown, including hydrogen atoms.
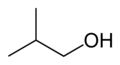
Skeletal formulas
Skeletal formulas are the standard notation for more complex organic molecules. First used by the organic chemist Friedrich August Kekulé von Stradonitz the carbon atoms in this type of diagram are implied to be located at the vertices (corners) and termini of line segments rather than being indicated with the atomic symbol C. Hydrogen atoms attached to carbon atoms are not indicated: each carbon atom is understood to be associated with enough hydrogen atoms to give the carbon atom four bonds. The presence of a positive or negative charge at a carbon atom takes the place of one of the implied hydrogen atoms. Hydrogen atoms attached to atoms other than carbon must be written explicitly.
-
Skeletal formula of isobutanol
Indication of stereochemistry
Several methods exist to picture the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule (stereochemistry).
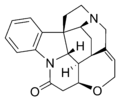
Stereochemistry in skeletal formulas
Chirality in skeletal formulas is indicated by the Natta projection method. Solid or dashed wedged bonds represent bonds pointing above-the-plane or below-the-plane of the paper, respectively.
-
Skeletal formula of strychnine
Unspecified stereochemistry
Wavy single bonds represent unknown or unspecified stereochemistry or a mixture of isomers. For example the diagram below shows the fructose molecule with a wavy bond to the HOCH2- group at the left. In this case the two possible ring structures are in chemical equilibrium with each other and also with the open-chain structure. The ring continually opens and closes, sometimes closing with one stereochemistry and sometimes with the other.
-
Unknown projection of fructose
Perspective drawings
Newman projection and sawhorse projection
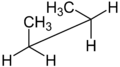
The Newman projection and the sawhorse projection are used to depict specific conformers or to distinguish vicinal stereochemistry. In both cases, two specific carbon atoms and their connecting bond are the center of attention. The only difference is a slightly different perspective: the Newman projection looking straight down the bond of interest, the sawhorse projection looking at the same bond but from a somewhat oblique vantage point. In the Newman projection, a circle is used to represent a plane perpendicular to the bond, distinguishing the substituents on the front carbon from the substituents on the back carbon. In the sawhorse projection, the front carbon is usually on the left and is always slightly lower:
-

Newman projection of butane
Cyclohexane conformations
Certain conformations of cyclohexane and other small-ring compounds can be shown using a standard convention. For example, the standard chair conformation of cyclohexane involves a perspective view from slightly above the average plane of the carbon atoms and indicates clearly which groups are axial and which are equatorial. Bonds in front may or may not be highlighted with stronger lines or wedges.
Haworth projection
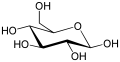
The Haworth projection is used for cyclic sugars. Axial and equatorial positions are not distinguished; instead, substituents are positioned directly above or below the ring atom to which they are connected. Hydrogen substituents are typically omitted.
Fischer projection
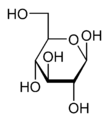
The Fischer projection is mostly used for linear monosaccharides. At any given carbon center, vertical bond lines are equivalent to stereochemical hashed markings, directed away from the observer, while horizontal lines are equivalent to wedges, pointing toward the observer. The projection is totally unrealistic, as a saccharide would never adopt this multiply eclipsed conformation. Nonetheless, the Fischer projection is a simple way of depicting multiple sequential stereocenters that does not require or imply any knowledge of actual conformation:
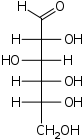
Fischer projection of D-GlucoseSee also
External links
References
Categories:- Chemical formulas
-
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.