- Adrenal medulla
-
Adrenal medulla 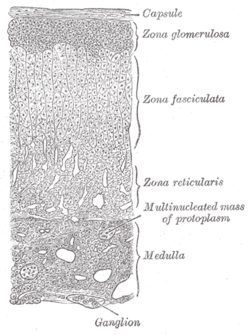
Medulla labeled at bottom right. Gray's subject #277 1280 Artery superior suprarenal artery, middle suprarenal artery, Inferior suprarenal artery Vein suprarenal veins Nerve celiac plexus, renal plexus Lymph lumbar glands Precursor Neural crest The adrenal medulla is part of the adrenal gland. It is located at the center of the gland, being surrounded by the adrenal cortex. It is the innermost part of the adrenal gland, consisting of cells that secrete epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and a small amount of dopamine in response to stimulation by sympathetic preganglionic neurons.
Contents
Basic
The adrenal medulla consists of irregularly shaped cells grouped around blood vessels. These cells are intimately connected with the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system (ANS). In fact, these adrenal medullary cells are modified postganglionic neurons, and preganglionic autonomic nerve fibers lead to them directly from the central nervous system.
Function
Rather than releasing a neurotransmitter, the cells of the adrenal medulla secrete hormones.
Composed mainly of hormone-producing chromaffin cells, the adrenal medulla is the principal site of the conversion of the amino acid tyrosine into the catecholamines epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine.
Because the ANS exerts direct control over the chromaffin cells the hormone release can occur rather quickly. In response to stressors such as exercise or imminent danger, medullary cells release catecholamines into the blood in a 17:3 ratio of adrenaline to noradrenaline.[1]
Notable effects of adrenaline and noradrenaline include increased heart rate and blood pressure, blood vessel constriction in the skin and gastrointestinal tract, bronchiole dilation, and increased metabolism, all of which are characteristic of the fight-or-flight response. Release of catecholamines is stimulated by nerve impulses, and receptors for catecholamines are widely distributed throughout the body.
Origin
Medullary cells are derived from the embryonic neural crest and, as such, are simply modified neurons.
In particular, they are modified postganglionic cells of the Autonomic nervous system that have lost their axons and dendrites, receiving innervation from corresponding preganglionic fibers. The cells form clusters around large blood vessels.
Moreover, as the synapses between pre- and postganglionic fibers are called ganglia, the adrenal medulla is actually a ganglion of the sympathetic nervous system.
Pathology
Neoplasms including:
- Pheochromocytoma (most common), a catecholamine-secreting tumor of the adrenal medulla
- Neuroblastoma, a neuroendocrine tumor of any neural crest tissue of the sympathetic nervous system
- Ganglioneuroma, a tumor in the nerve cells of the peripheral nervous system
See also
References
External links
- SUNY Labs 40:04-0202 - "Posterior Abdominal Wall: Blood Supply to the Suprarenal Glands"
- Anatomy Atlases - Microscopic Anatomy, plate 15.292 - "Adrenal Gland"
- Location of Adrenal medulla
Human anatomy, endocrine system: endocrine glands (TA A11, TH H3.08, GA 11.1269) Islets of pancreas Hypothalamic/
pituitary axes
+parathyroidPituitaryPars intermedia · Pars tuberalis · Pars distalis
Acidophil cell (Somatotropic cell, Prolactin cell) · Basophil cell (Corticotropic cell, Gonadotropic cell, Thyrotropic cell) · Chromophobe cellThyroid isthmus · Lobes of thyroid gland · Pyramidal lobe of thyroid gland
Follicular cell · Parafollicular cellMedullaPineal gland Other Categories:- Glands
- Abdomen
- Endocrine system
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.