- Delta cell
-
Delta cell 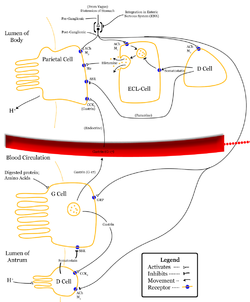
Control of stomach acid Latin endocrinocytus D MeSH D+Cells Code TH H3.04.02.0.00027 Delta cells (δ-cells or D cells) are somatostatin-producing cells.
They can be found in the stomach, intestine and the Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas.
In rodents delta-cells are located in the periphery of the islets; in humans the islet architecture is generally less organized and delta-cells are frequently observed inside the islets as well.
In the electron microscope, delta-cells can be identified as cells with smaller and slightly more compact granules than beta cells.
D cells contain CCKBR (which respond to gastrin) and M3 receptors (which respond to Ach). Respectively, these receptors will increase somatostatin output and decrease somatostatin output from the D cells.
VIP, vasoactive intestinal peptide, acts positively on D cells resulting in more somatostatin being released.
Clinical significance
A tumor of the delta cells is called a "somatostatinoma".
Digestive system, physiology: gastrointestinal physiology GI tract Upper GIExocrineProcessesFluidsLower GIEndocrine/paracrineG cells (gastrin) · D cells (somatostatin) · ECL cells (Histamine)
enterogastrone: I cells (CCK) · K cells (GIP) · S cells (secretin)
Enteroendocrine cells · Enterochromaffin cell · APUD cellFluidsProcessesEither/bothProcessesAccessory FluidsProcessesAbdominopelvic Human cell types / list derived primarily from endoderm Foregut enteroendocrine: G cell · D cell · ECL cell
exocrine: Gastric chief cell · Parietal cell
Foveolar cellPharyngeal pouch Hindgut/cloaca Urothelial cellsCategories:- Peptide hormone secreting cells
- Digestive system stubs
- Cell biology stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
