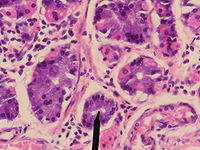
- Gastric chief cell
-
Chief cell 
H&E stain of fundic gland polyp showing shortening of the gastric pits with cystic dilatation 
A fundus gland. A. Transverse section of gland. Latin exocrinocytus principalis Code TH H3.04.02.1.00031 A gastric chief cell (or peptic cell, or gastric zymogenic cell) is a cell in the stomach that releases pepsinogen, gastric lipase and Chymosin. The cell stains basophilic upon H&E prep due to the large proportion of rough endoplasmic reticulum in its cytoplasm.
Chief cells release the zymogen (enzyme precursor) pepsinogen when stimulated by a variety of factors including cholinergic activity from the vagus nerve and acidic condition in the stomach. Gastrin and secretin may also act as secretagogues. [1]
It works in conjunction with the parietal cell, which releases gastric acid, converting the pepsinogen into pepsin.
Contents
Nomenclature
The terms "chief cell" and "zymogenic cell" are often used without the word "gastric" to name this type of cell. However those terms can also be used to describe other cell types (for example, parathyroid chief cells.) Chief cells are also known as peptic cells.
See also
References
- ^ Johnson. Gastrointestinal Physiology 6th Edition. Mosby. 2001
External links
- Anatomy Atlases - Microscopic Anatomy, plate 01.05
- Histology at BU 22201loa - "Ultrastructure of the Cell: chief cells and enteroendocrine cell"
- Histology at BU 11304loa - "Digestive System: Alimentary Canal: fundic stomach, gastric glands, base"
- "chief cell" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
Digestive system, physiology: gastrointestinal physiology GI tract Upper GIExocrineProcessesFluidsLower GIEndocrine/paracrineG cells (gastrin) · D cells (somatostatin) · ECL cells (Histamine)
enterogastrone: I cells (CCK) · K cells (GIP) · S cells (secretin)
Enteroendocrine cells · Enterochromaffin cell · APUD cellFluidsProcessesEither/bothProcessesAccessory FluidsProcessesAbdominopelvic Human cell types / list derived primarily from endoderm Foregut enteroendocrine: G cell · D cell · ECL cell
exocrine: Gastric chief cell · Parietal cell
Foveolar cellCentroacinar cell · Pancreatic stellate cellPharyngeal pouch Hindgut/cloaca Urothelial cellsCategories:- Peptide hormone secreting cells
- Human cells
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.