- Cloaca (embryology)
-
For other uses, see Cloaca.
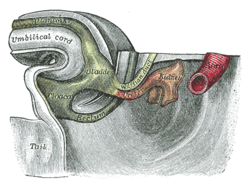
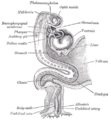
Cloaca (embryology) Tail end of human embryo thirty-two to thirty-three days old. Cloaca is visible at center left. The endodermal cloaca is labeled with green, while the ectodermal cloaca is seen as a colorless crest on the outside. Gray's subject #241 1109 Days 15 Precursor endoderm[1] Gives rise to Urogenital sinus Code TE E5.4.0.0.0.0.14 MeSH Cloaca The cloaca is a structure in the development of the urinary and reproductive organs.
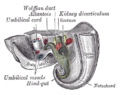
The hind-gut is at first prolonged backward into the body-stalk as the tube of the allantois; but, with the growth and flexure of the tail-end of the embryo, the body-stalk, with its contained allantoic tube, is carried forward to the ventral aspect of the body, and consequently a bend is formed at the junction of the hind-gut and allantois.
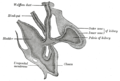
This bend becomes dilated into a pouch, which constitutes the endodermal cloaca; into its dorsal part the hind-gut opens, and from its ventral part the allantois passes forward.
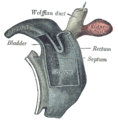
At a later stage the Wolffian duct and Müllerian duct open into its ventral portion.
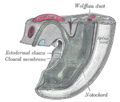
The cloaca is, for a time, shut off from the anterior by a membrane, the cloacal membrane, formed by the apposition of the ectoderm and entoderm, and reaching, at first, as far forward as the future umbilicus.
Behind the umbilicus, however, the mesoderm subsequently extends to form the lower part of the abdominal wall and pubic symphysis.
By the growth of the surrounding tissues the cloacal membrane comes to lie at the bottom of a depression, which is lined by ectoderm and named the ectodermal cloaca.
Contents
Additional images
See also
References
- ^ "Partitioning of Cloaca". http://sprojects.mmi.mcgill.ca/embryology/ug/Reproductives/Normal/cloaca.html. Retrieved 2010-03-20.
External links
- Cloaca at eMedicine Dictionary
- Swiss embryology (from UL, UB, and UF) ugenital/genitinterne04
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Prenatal development/mammalian embryogenesis · Development of the urinary and reproductive organs (GA 11.1204, TE E5.6-7) Common urinary and
reproductive systemUrinary system
developmentNephrotome → Pronephros · Mesonephros (Mesonephric tubules)
WD → Ureteric bud + Metanephrogenic blastema
US → Urinary bladder + Urethra + Primary urethral groove + UrachusReproductive system
developmentPrimarily internalPrimarily externalLPM → Genital tubercle → Labioscrotal swelling → Scrotum or Labia majora
LPM → Genital tubercle → Primordial phallus → Penis or Clitoris
Peritoneum → Processus vaginalis or Canal of NuckHomologues Prenatal development/Mammalian development of digestive system, coelom and septa, and mesenchymal mesenteric masses (GA 11.1101, TE E5.4, 5.8-9) Gut Upper GI tract and accessoryForegut: upper GI (Buccopharyngeal membrane, Rathke's pouch, Tracheoesophageal septum) · accessory (Pancreatic bud, Hepatic diverticulum)Abdominopelvic OtherIntra-embryonic coelom · Extra-embryonic coelomCategories:- Embryology of digestive system
- Developmental biology stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.