- Mesonephros
-
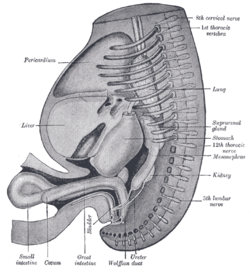
Mesonephros Reconstruction of a human embryo of 17 mm. (Label for Mesonephros is at center right.) Gray's subject #252 1205 Carnegie stage 14 Days 22 Precursor intermediate mesoderm Code TE E5.6.2.0.0.0.1 MeSH Mesonephros The mesonephros (Greek for "middle kidney") is one of three excretory organs that develop in vertebrates. It serves as the main excretory organ of aquatic vertebrates and as a temporary kidney in reptiles, birds, and mammals. The mesonephros is included in the Wolffian body after Caspar Friedrich Wolff who described it in 1759. (The Wolffian body is composed of : mesonephros + paramesonephrotic blastema)
Contents
Structure
The mesonephros is composed of the mesonephric duct (also called the Wolffian duct), mesonephric tubules, and associated capillary tufts. A single tubule and its associated capillary tuft is called a mesonephric excretory unit; these units are similar in structure and function to nephrons of the adult kidney. The mesonephros is derived from intermediate mesoderm in the vertebrate embryo.
Differences between males and females
In human males, the mesonephros gives rise to the efferent ductules of the testis, the epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicle, and vestigial structures such as the appendix testis, appendix epididymis, and paradidymis.
The mesonephros largely regresses in human females, though vestigial structures such as Gartner's cysts, the epoophoron, and paroophoron are common.
Differences among species
The mesonephros persists and forms the anterior portion of the permanent kidneys in fishes and amphibians, but in reptiles, birds, and mammals, it atrophies and for the most part disappears rapidly as the permanent kidney (metanephros) begins to develop[1] during the sixth or seventh week. By the beginning of the fifth month of human development, only the ducts and a few of the tubules of the mesonephros remain.
Additional images
See also
- pronephros
- metanephros
- paramesonephric ducts, ducts beside (para-) the mesonephros
References
Prenatal development/mammalian embryogenesis · Development of the urinary and reproductive organs (GA 11.1204, TE E5.6-7) Common urinary and
reproductive systemUrinary system
developmentNephrotome → Pronephros · Mesonephros (Mesonephric tubules)
WD → Ureteric bud + Metanephrogenic blastema
US → Urinary bladder + Urethra + Primary urethral groove + UrachusReproductive system
developmentPrimarily internalPrimarily externalLPM → Genital tubercle → Labioscrotal swelling → Scrotum or Labia majora
LPM → Genital tubercle → Primordial phallus → Penis or Clitoris
Peritoneum → Processus vaginalis or Canal of NuckHomologues Categories:- Embryology of urogenital system
- Kidney
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.