- Cloacal membrane
-
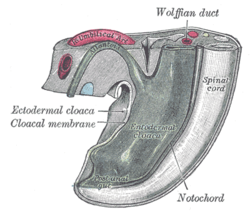
Cloacal membrane Tail end of human embryo from fifteen to eighteen days old. Latin membrana cloacalis Gray's subject #6 47 Carnegie stage 7 Days 15 Precursor caudal end of the primitive streak Code TE E5.4.0.0.0.0.15 The cloacal membrane is the membrane that covers the embryonic cloaca when still in the development of the urinary and reproductive organs.
It is formed by ectoderm and endoderm coming into contact with each other.[1] After separation of the cloaca into the urogenital and anal parts, the cloacal membrane, in turn, is separated into a urogenital membrane and an anal membrane.
It has been suggested that developmental errors may be associated with enlarged clitorises.[2]
References
- ^ "Endoderm -- Developmental Biology -- NCBI Bookshelf". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=dbio&part=A3745.
- ^ van der Putte SC (November 2009). "Penislike clitorises with megalourethras in nonvirilized female fetuses and a newborn. A histopathologic study and its bearing on their pathogenesis". J. Pediatr. Surg. 44 (11): 2223–9. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2009.07.024. PMID 19944238. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0022-3468(09)00582-X.
External links
- Swiss embryology (from UL, UB, and UF) hdisqueembry/triderm04
- genital-021 — Embryology at UNC
- Diagram at unsw.edu.au
- Overview at ana.ed.ac.uk
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Prenatal development/mammalian embryogenesis · Development of the urinary and reproductive organs (GA 11.1204, TE E5.6-7) Common urinary and
reproductive systemMesoderm → Intermediate mesoderm
Mesoderm → Lateral plate mesoderm ("LPM")
Endoderm → Cloaca → Urogenital sinus ("US")
Endoderm+Ectoderm → Cloacal membraneUrinary system
developmentNephrotome → Pronephros · Mesonephros (Mesonephric tubules)
WD → Ureteric bud + Metanephrogenic blastema
US → Urinary bladder + Urethra + Primary urethral groove + UrachusReproductive system
developmentPrimarily internalPrimarily externalLPM → Genital tubercle → Labioscrotal swelling → Scrotum or Labia majora
LPM → Genital tubercle → Primordial phallus → Penis or Clitoris
Peritoneum → Processus vaginalis or Canal of NuckHomologues Prenatal development/Mammalian development of digestive system, coelom and septa, and mesenchymal mesenteric masses (GA 11.1101, TE E5.4, 5.8-9) Gut Upper GI tract and accessoryForegut: upper GI (Buccopharyngeal membrane, Rathke's pouch, Tracheoesophageal septum) · accessory (Pancreatic bud, Hepatic diverticulum)Abdominopelvic OtherIntra-embryonic coelom · Extra-embryonic coelomCategories:- Developmental biology stubs
- Embryology of urogenital system
- Embryology of digestive system
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.