- Definitive urogenital sinus
-
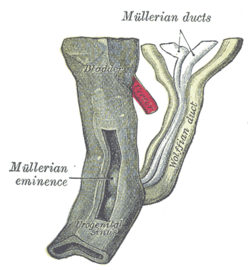
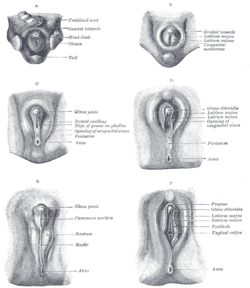
Definitive urogenital sinus Urogenital sinus of female human embryo of eight and a half to nine weeks old. (Urogenital sinus labeled at bottom.) Stages in the development of the external sexual organs in the male and female. ("Opening of urogenital sinus" labeled in diagram D.) Latin sinus urogenitalis definitivus Gray's subject #252 1213 Carnegie stage 15 Precursor Cloaca Gives rise to urethra, bladder, vagina Code TE E5.7.3.1.0.0.1
The definitive urogenital sinus (also known as the persistent cloaca) is a part of the human body only present in the development of the urinary and reproductive organs. It is the ventral part of the cloaca, formed after the cloaca separates from the anal canal during the fourth to seventh weeks of development.[1]In males, the UG sinus is divided into three regions: upper, pelvic, and phallic. The upper part gives rise to the urinary bladder and the pelvic part gives rise to the prostatic and membranous parts of the urethra.[1]
In females, the pelvic part of the UG sinus gives rise to the sinovaginal bulbs, structures that will eventually form the inferior portion vagina. This process begins when the lower tip of the paramesonephric ducts, the structures that will eventually form the uterus and vaginal fornices, come in contact with the UG sinus. Shortly afterwards, the sinovaginal bulbs form as two solid evaginations of the UG sinus. Cells in these bulbs divide to form a solid vaginal plate, which extends and then canalizes (hollows) to form the inferior portion of the vagina.[2]
Contents
Pathology
A urogenital sinus anomaly is also a rare birth defect in women where the urethra and vagina both open into a common channel.
Additional images
See also
References
External links
Prenatal development/mammalian embryogenesis · Development of the urinary and reproductive organs (GA 11.1204, TE E5.6-7) Common urinary and
reproductive systemMesoderm → Intermediate mesoderm
Mesoderm → Lateral plate mesoderm ("LPM")
Endoderm → Cloaca → Urogenital sinus ("US")
Endoderm+Ectoderm → Cloacal membraneUrinary system
developmentNephrotome → Pronephros · Mesonephros (Mesonephric tubules)
WD → Ureteric bud + Metanephrogenic blastema
US → Urinary bladder + Urethra + Primary urethral groove + UrachusReproductive system
developmentPrimarily internalPrimarily externalLPM → Genital tubercle → Labioscrotal swelling → Scrotum or Labia majora
LPM → Genital tubercle → Primordial phallus → Penis or Clitoris
Peritoneum → Processus vaginalis or Canal of NuckHomologues Categories:- Embryology of urogenital system
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.