- Goblet cell
-
Goblet cell 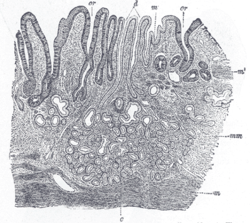
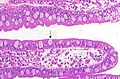
Section of mucus membrane of human stomach, near the cardiac orifice. X 45.
c. Cardiac glands.
d. Their ducts.
cr. Gland similar to the intestinal glands, with goblet cells.
mm. Mucous membrane.
m. Muscularis mucosae.
m’. Muscular tissue within the mucous membrane.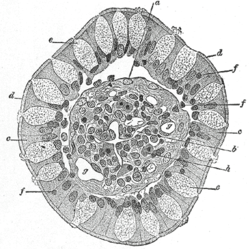
Transverse section of a villus, from the human intestine. X 350.
a. Basement membrane, here somewhat shrunken away from the epithelium.
b. Lacteal.
c. Columnar epithelium.
d. Its striated border.
e. Goblet cells.
f. Leucocytes in epithelium.
f’. Leucocytes below epithelium.
g. Blood vessels.
h. Muscle cells cut across.Latin exocrinocytus caliciformis Code TH H3.04.03.0.00009;
H3.04.03.0.00016
H3.05.00.0.00006Goblet cells are glandular simple columnar epithelial cells whose sole function is to secrete mucin, which dissolves in water to form mucus. They use both apocrine and merocrine methods for secretion.
The majority of the cell's cytoplasm is occupied by mucinogen granules, except at the bottom. Rough endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, the nucleus, and other organelles are concentrated in the basal portion. The apical plasma membrane projects microvilli to increase surface area for secretion. Recent study suggests that glycoprotein is located inside goblet cells. It is an organ-specific antigen in the gut.
Contents
Locations
They are found scattered among the epithelial lining of organs, such as the intestinal and respiratory tracts.[1] They are found inside the trachea, bronchus, and larger bronchioles in respiratory tract, small intestines, the colon, and conjunctiva in the upper eyelid.
They may be an indication of metaplasia, such as in Barrett's esophagus.
Histology
In mucicarmine stains, deep red mucin found within goblet cell bodies.
The nuclei of goblet cells tend to be displaced toward the basal end of the cell body, leading to intense basophilic staining.
Etymology
The term goblet refers to these cells' goblet-like shape. The apical portion is shaped like a cup, as it is distended by abundant mucinogen granules; its basal portion is shaped like a stem, as it is narrow for lack of these granules.
There are other cells that secrete mucus (as in the foveolar cells of the stomach[2]), but they are not usually called "goblet cells" because they do not have this distinctive shape.
Basal secretion
This is the normal base level secretion of mucus, which is accomplished by cytoskeletal movement of secretory granules.
Stimulated secretion
Secretion may be stimulated by dust, smoke, etc.
Other stimuli include viruses, bacteria, etc.
See also
- Goblet cell carcinoid - a tumor that has a component that is similar to goblet cells
Additional images
-
Goblet cell in ileum
References
- ^ "goblet cell" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ Histology at BU 11303loa - Digestive System: Alimentary Canal: fundic stomach, gastric glands, lumen"
External links
- Histology at KUMC epithel-epith08 "Slide 8: Trachea"
- Goblet+cell at eMedicine Dictionary
- Goblet Cells at cvmbs.colostate.edu
- Diagram at uwlax.edu
- Bioweb at UWLAX Zoolab
Digestive system, physiology: gastrointestinal physiology GI tract Upper GIExocrineProcessesFluidsLower GIEndocrine/paracrineG cells (gastrin) · D cells (somatostatin) · ECL cells (Histamine)
enterogastrone: I cells (CCK) · K cells (GIP) · S cells (secretin)
Enteroendocrine cells · Enterochromaffin cell · APUD cellFluidsProcessesEither/bothProcessesAccessory FluidsProcessesAbdominopelvic Anatomy: Lower RT respiratory system (TA A06.3–5, TH H3.05.02, GA 11.1084) TB tree main bronchus (right, left) · lobar/secondary bronchi (eparterial bronchus) · segmental/tertiary bronchiLungs GeneralLeft lung/Right lung · Base/Apex · Root/Hilum
Superior lobe · Lingula of left lung/Middle lobe of right lung · Inferior lobe
borders: Anterior border (Cardiac notch) · Posterior border · Inferior border
surfaces: Costal surface · Mediastinal surface (Cardiac impression) · Diaphragmatic surface
fissures: Oblique fissure · Horizontal fissureBronchiole: Conducting zone (Terminal bronchiole) · Respiratory zone (Respiratory bronchiole · Alveolar duct · Alveolus · Blood-air barrier)CellsHuman cell types / list derived primarily from endoderm Foregut enteroendocrine: G cell · D cell · ECL cell
exocrine: Gastric chief cell · Parietal cell
Foveolar cellenteroendocrine: K cell · S cell · D cell · I cell
Goblet cell · Paneth cell
Enterocyte (Microfold cell)Centroacinar cell · Pancreatic stellate cellPharyngeal pouch Hindgut/cloaca Urothelial cellsCategories:- Mucus secreting cells
- Human cells
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.