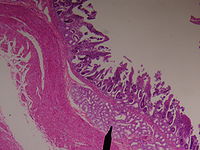
- Brunner's glands
-
Brunner's glands 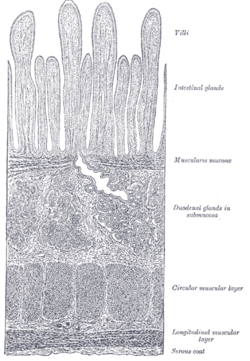
Section of duodenum. (Duodenal glands in submucosa labeled at right, fourth from the top.) Latin glandulae duodenales Gray's subject #248 1176 Brunner's glands (or duodenal glands) are compound tubular submucosal glands found in that portion of the duodenum which is above the hepatopancreatic sphincter (Sphincter of Oddi). The main function of these glands is to produce a mucus-rich alkaline secretion (containing bicarbonate) in order to:
- protect the duodenum from the acidic content of chyme (which is introduced into the duodenum from the stomach);
- provide an alkaline condition for the intestinal enzymes to be active, thus enabling absorption to take place;
- lubricate the intestinal walls.
They are the distinguishing feature of the duodenum, and are named for the Swiss physician who first described them, Johann Conrad Brunner.
External links
- duodenal+glands at eMedicine Dictionary
- Histology at BU 11504loa - "Digestive System: Alimentary Canal: pyloro/duodenal junction, duodenum"
- Histology at BU 11513loa - "Digestive System: Alimentary Canal: pyloro/duodenal junction"
- Histology at BU 11609loa - "Digestive System: Alimentary Canal: duodenum, plicae circularis"
Categories:- Digestive system
- Digestive system stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.