- Pharynx
Infobox Anatomy
Name = PAGENAME
Latin =
GraySubject = 244 | GrayPage = 1141 |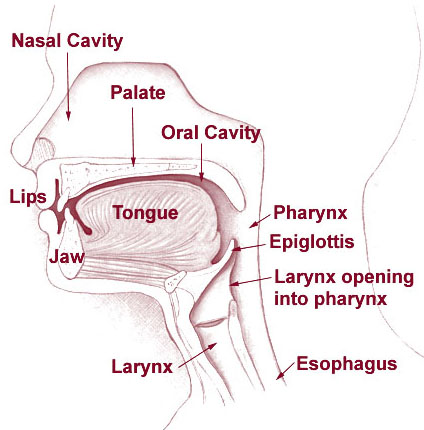 | Caption = Head and neck.
| Caption = Head and neck.

Caption2 = Pharynx
Precursor =
System =
Artery = pharyngeal branches of ascending pharyngeal artery, ascending palatine, descending palatine, pharyngeal branches of inferior thyroid
Vein =pharyngeal veins
Nerve =pharyngeal plexus
Lymph =
MeshName = Pharynx
MeshNumber = A03.556.750
DorlandsPre = p_16
DorlandsSuf = 12633198
The pharynx (plural: "pharynges") is the part of theneck andthroat situated immediatelyposterior to (behind) themouth andnasal cavity , and cranial, or superior, to theoesophagus ,larynx , and trachea.Functions
It was part of the
digestive system andrespiratory system of many organisms.Because both
food and air pass through the pharynx, a flap of connective tissue called theepiglottis closes over the trachea when food is swallowed to preventchoking or aspiration. Inhumans the pharynx is important invocalization .In persons with
hayfever ,oral allergy syndrome and related allergies, the pharynx is often a reaction site to allergens, with common symptoms including burning and itching.Parts
The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections:
Oropharynx
The
oropharynx lies behind the oral cavity. The anterior wall consists of the base of the tongue and the vallecula; the lateral wall is made up of the tonsil, tonsillar fossa, and tonsillar (faucial) pillars; the superior wall consists of the inferior surface of the soft palate and the uvula.Nasopharynx
The
nasopharynx lies behind thenasal cavity .Postero-superiorly this extends from the level of the junction of the hard and soft palates to the base of skull, laterally to include the
fossa of Rosenmuller .The inferior wall consists of the superior surface of the soft palate.
Laryngopharynx
The
laryngopharynx , also known as thehypopharynx , roughly corresponds to the levels between C4 to C6, it includes the pharyngo-esophageal junction (postcricoid area), thepiriform sinus , and the posterior pharyngeal wall.Like the oropharynx above it the hypopharynx serves as a passageway for food and air and is lined with a
stratified squamous epithelium .It lies inferior to the upright epiglottis and extends to the larynx, where the respiratory and digestive pathways diverge.
At that point, the laryngopharynx is continuous with the esophagus posteriorly. The esophagus conducts food and fluids to the
stomach ; air enters the larynx anteriorly. During swallowing, food has the "right of way", and air passage temporarily stops.
=AdditionalReferences
*
* "Human Anatomy and Physiology" Elaine N. Marieb and Katja Hoehn, Seventh Edition.
* "TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours" Sobin LH & Wittekind Ch (eds)Sixth edition UICC 2002 ISBN 0-471-22288-7ee also
*
Adenoid
*Eustachian tube
*Hyoid
*Keratosis pharyngis
*Larynx
*Tonsil
*Uvula External links
*
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
