- Costal surface of lung
-
Costal surface of lung 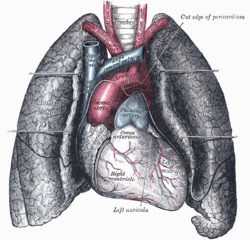
Front view of heart and lungs. Latin facies costalis pulmonis Gray's subject #240 1094 The costal surface of the lung (external or thoracic surface) is smooth, convex, of considerable extent, and corresponds to the form of the cavity of the chest, being deeper behind than in front.
It is in contact with the costal pleura, and presents, in specimens which have been hardened in situ, slight grooves corresponding with the overlying ribs.
External links
- costal+surface+of+lung at eMedicine Dictionary
- -26542023 at GPnotebook
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Anatomy: Lower RT respiratory system (TA A06.3–5, TH H3.05.02, GA 11.1084) TB tree main bronchus (right, left) · lobar/secondary bronchi (eparterial bronchus) · segmental/tertiary bronchiLungs GeneralLeft lung/Right lung · Base/Apex · Root/Hilum
Superior lobe · Lingula of left lung/Middle lobe of right lung · Inferior lobe
borders: Anterior border (Cardiac notch) · Posterior border · Inferior border
surfaces: Costal surface · Mediastinal surface (Cardiac impression) · Diaphragmatic surface
fissures: Oblique fissure · Horizontal fissureBronchiole: Conducting zone (Terminal bronchiole) · Respiratory zone (Respiratory bronchiole · Alveolar duct · Alveolus · Blood-air barrier)CellsCategories:- Respiratory system stubs
- Lung anatomy
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
